Category: life extension – Page 112

Dasatinib + Quercetin: Longevity Biohacker Kenneth Scott’s Experience
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
How Does Space Affect the Brain? Groundbreaking ISS Experiment Reveals Surprising Insights
Microgravity is known to affect muscles, bones, the immune system, and cognition, but its specific effects on the brain remain largely unexplored. To investigate this, scientists from Scripps Research partnered with the New York Stem Cell Foundation to send tiny clusters of brain cells, known as “organoids,” to the International Space Station (ISS). These organoids were derived from stem cells and designed to mimic certain aspects of brain development.
Remarkably, the organoids returned from their month-long stay in orbit still healthy. However, they exhibited accelerated maturation compared to identical organoids grown on Earth. The space-exposed cells progressed closer to becoming fully developed neurons and showed early signs of specialization. These findings, recently published in Stem Cells Translational Medicine, offer new insights into how space travel might influence neurological development and brain function.
“The fact that these cells survived in space was a big surprise,” says co-senior author Jeanne Loring, PhD, professor emeritus in the Department of Molecular Medicine and founding director of the Center for Regenerative Medicine at Scripps Research. “This lays the groundwork for future experiments in space, in which we can include other parts of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative disease.”
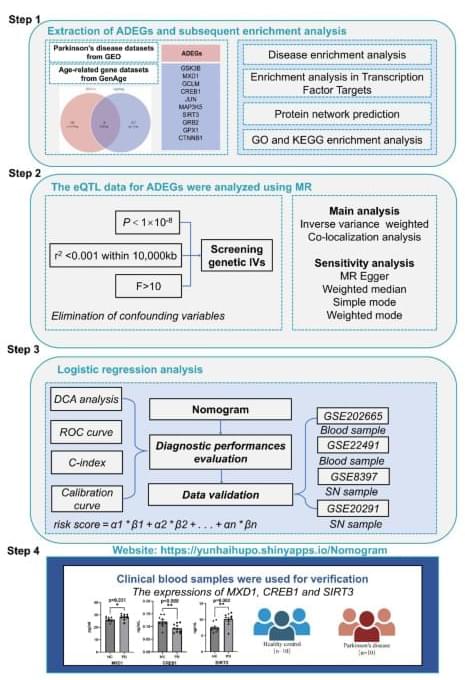
Multi-omics analysis reveals the genetic aging landscape of Parkinson’s disease
Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, P. et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals the genetic aging landscape of Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 14, 31,167 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-82470-z.
Seven Scientific Discoveries From 2024 That Could Lead to New Inventions
From indestructible tardigrades to body-merging comb jellies, animals can teach humans so much about medicine, robotics, aging and survival.

Critical review of aging clocks and factors that may influence the pace of aging
Background and objectives: Aging clocks are computational models designed to measure biological age and aging rate based on age-related markers including epigenetic, proteomic, and immunomic changes, gut and skin microbiota, among others. In this narrative review, we aim to discuss the currently available aging clocks, ranging from epigenetic aging clocks to visual skin aging clocks.
Methods: We performed a literature search on PubMed/MEDLINE databases with keywords including: “aging clock,” “aging,” “biological age,” “chronological age,” “epigenetic,” “proteomic,” “microbiome,” “telomere,” “metabolic,” “inflammation,” “glycomic,” “lifestyle,” “nutrition,” “diet,” “exercise,” “psychosocial,” and “technology.”
Results: Notably, several CpG regions, plasma proteins, inflammatory and immune biomarkers, microbiome shifts, neuroimaging changes, and visual skin aging parameters demonstrated roles in aging and aging clock predictions. Further analysis on the most predictive CpGs and biomarkers is warranted. Limitations of aging clocks include technical noise which may be corrected with additional statistical techniques, and the diversity and applicability of samples utilized.

Scientists Discover “Mortality Timer” Inside Our Cells
The secret to cellular youth may lie in maintaining a small nucleolus—a dense structure within the cell nucleus—according to investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine. These findings were uncovered in yeast, a model organism renowned for its role in making bread and beer, yet surprisingly similar to humans at the cellular level.
The study, published Nov. 25 in Nature Aging, may lead to new longevity treatments that could extend human lifespan. It also establishes a mortality timer that reveals how long a cell has left before it dies.
As people get older, they are more likely to develop health conditions, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative diseases.
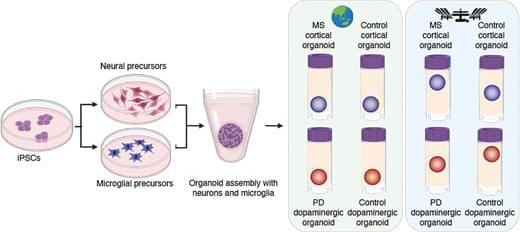
Effects of microgravity on human iPSC-derived neural organoids on the International Space Station
Surprisingly, the organoids were still healthy when they returned from orbit a month later, but the cells had matured faster compared to identical organoids grown on Earth—they were closer to becoming adult neurons and were beginning to show signs of specialization. The results, which could shed light on potential neurological effects of space travel, were published on October 23, 2024, in Stem Cells Translational Medicine.
“The fact that these cells survived in space was a big surprise,” says co-senior author Jeanne Loring, PhD, professor emeritus in the Department of Molecular Medicine and founding director of the Center for Regenerative Medicine at Scripps Research. “This lays the groundwork for future experiments in space, in which we can include other parts of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative disease.”
On Earth, the team used stem cells to create organoids consisting of either cortical or dopaminergic neurons, which are the neuronal populations impacted in multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease—diseases that Loring has studied for decades. Some organoids also included microglia, a type of immune cell that is resident within the brain, to examine the impact of microgravity on inflammation.
Abstract. Research conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) in low-Earth orbit (LEO) has shown the effects of microgravity on multiple organs. To investigate the effects of microgravity on the central nervous system, we developed a unique organoid strategy for modeling specific regions of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative diseases. We generated 3-dimensional human neural organoids from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from individuals affected by primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) or Parkinson’s disease (PD) and non-symptomatic controls, by differentiating them toward cortical and dopaminergic fates, respectively, and combined them with isogenic microglia. The organoids were cultured for a month using a novel sealed cryovial culture method on the International Space Station (ISS) and a parallel set that remained on Earth. Live samples were returned to Earth for analysis by RNA expression and histology and were attached to culture dishes to enable neurite outgrowth. Our results show that both cortical and dopaminergic organoids cultured in LEO had lower levels of genes associated with cell proliferation and higher levels of maturation-associated genes, suggesting that the cells matured more quickly in LEO. This study is continuing with several more missions in order to understand the mechanisms underlying accelerated maturation and to investigate other neurological diseases. Our goal is to make use of the opportunity to study neural cells in LEO to better understand and treat neurodegenerative disease on Earth and to help ameliorate potentially adverse neurological effects of space travel.
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Awarded $21 Million NIH Grant to Advance Understanding of Aging-Related Hormone
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have been awarded a $21 million grant from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to further advance understanding of an aging-related hormone known as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), including its potential role in obesity, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. The work could lead to the development of new treatments for these and other conditions involving aging.
This is a collaborative effort with the NIA, led by Mone Zaidi, MD, PhD, Director of the Center for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology at Icahn Mount Sinai, and Clifford J. Rosen, MD, at the MaineHealth Institute for Research in Scarborough, Maine. Dr. Zaidi and Dr. Rosen are Program Directors, and principal investigators of individual projects are Anne Schafer, MD, at the University of California in San Francisco, as well as scientists at Icahn Mount Sinai, including Tony Yuen, PhD, Associate Professor and Research Director of the Center for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology, and Daria Lizneva, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Pharmacological Sciences. Together, the investigators will work toward translating their findings into viable treatments for patients.
“We are delighted that the NIH has recognized the potential of our work by awarding this generous grant,” says Dr. Zaidi, the Mount Sinai Professor of Clinical Medicine at Icahn Mount Sinai. “Our focus for more than 25 years has been on identifying actionable targets for major public health diseases. This research offers the potential for a new drug for menopause and could also possibly help advance treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, obesity, and osteoporosis, affecting millions of people worldwide.”
17.2y Younger Biological Age (Blood Test #8 In 2024, Test #56 Since 2015)
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/