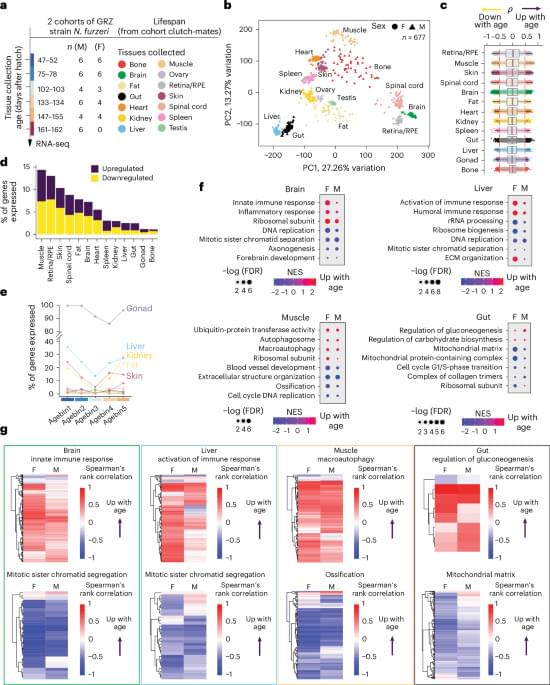
Defined as reduced caloric intake or selective limitation of specific nutrients without malnutrition, is one of the most robust interventions known to extend lifespan and healthspan across species. Studies from yeast to mammals demonstrate that DR elicits conserved genetic, transcriptional, and epigenetic programs that promote cellular maintenance and stress resistance. At the molecular level, DR engages evolutionarily conserved nutrient-sensing pathways, including insulin/IGF-1 signaling (IIS), the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and NAD+-dependent sirtuins, which converge on key transcription factors (TFs) and transcriptional coactivators (TCs) to coordinate metabolic and longevity-associated gene expression. Downstream, these pathways enhance autophagy and proteostasis, remodel mitochondrial function and redox balance, reshape immune and inflammatory networks, and induce epigenetic and transcriptional reprogramming. Recent work further highlights amino acid–specific sensing mechanisms, endocrine mediators such as fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), the gut microbiome, circadian regulators, and nuclear pore–associated transcriptional plasticity as integral components of DR responses. Importantly, the physiological outcomes of DR are context dependent and influenced by genetic background, sex, age at intervention, and the type and duration of restriction. In this review, we summarize current knowledge on the genetic and molecular architecture underlying DR-induced longevity and health benefits across species, discuss implications for aging-related diseases, and outline future directions toward precision nutrition and safe translational strategies.
Aging is characterized by a progressive decline in physiological integrity, reduced stress resilience, and increased susceptibility to chronic diseases (Lopez-Otin et al., 2023). Among numerous genetic, pharmacological, and lifestyle interventions examined over the past decades, dietary restriction (DR) remains the most robust and evolutionarily conserved strategy for extending lifespan and improving healthspan. Originally described in rodents nearly a century ago, the beneficial effects of reduced nutrient intake have since been validated in a wide range of organisms, including yeast, nematodes, flies, and mammals (Wu et al., 2022). While often used interchangeably, it is critical to distinguish between different nutritional interventions to avoid conceptual overlap. Caloric restriction (CR) typically refers to a chronic reduction in total calorie intake (usually 20%–40%) without malnutrition.