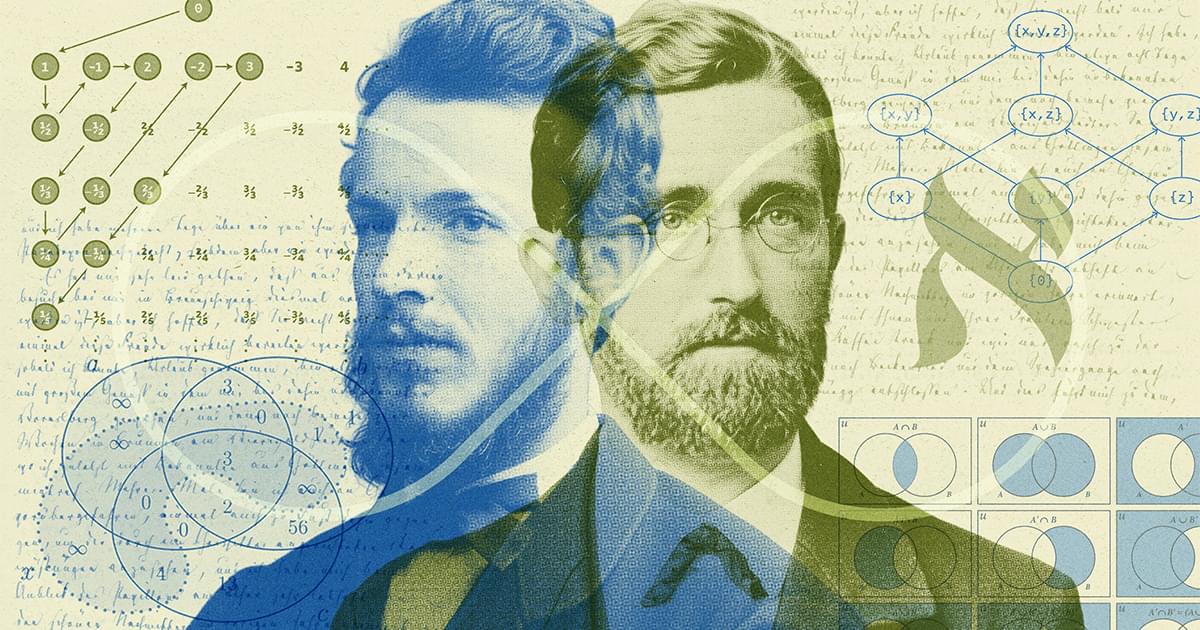
In 1874, German mathematician Georg Cantor published a groundbreaking paper showing that there are different sizes of infinity — a result that fundamentally changed mathematics by treating infinity as a concrete mathematical concept rather than a mere philosophical idea.
That paper became the foundation of set theory, a central pillar of modern mathematics.
Newly discovered letters from Cantor’s correspondence with fellow mathematician Richard Dedekind, believed lost until recently, suggest that a crucial part of the proof Cantor published came directly from Dedekind’s work.
Historian and journalist Demian Goos uncovered these letters while researching Cantor’s life. He found a key letter from November 30, 1873 that shows Dedekind’s proof of the countability of algebraic numbers — the same result Cantor would publish later under his own name.
Earlier histories had portrayed Cantor as a lone genius, but the new evidence reveals he relied heavily on Dedekind’s ideas and published them without proper credit, effectively erasing Dedekind’s role in the discovery.
Cantor’s strategy was partly tactical: because influential mathematician Leopold Kronecker vehemently opposed actual infinity, Cantor framed the paper under a less controversial title (about algebraic numbers), using Dedekind’s simplified methods to “sneak” in the revolutionary idea of comparing infinities.
The result was not just a new theorem but a new way of thinking about infinity, setting the stage for set theory and reshaping mathematics — even though the true story of its origins was more collaborative and ethically complicated than commonly told.