Quantum computers work by applying quantum operations, such as quantum gates, to delicate quantum states. Ideally, quantum computers can solve complex equations at staggeringly fast speeds that vastly outpace regular computers. In real hardware, the operations of quantum computers often deviate from the ideal behavior because of device imperfections and unwanted noise from the environment. To build reliable quantum machines, researchers need a way to accurately determine what a quantum device is actually doing.
Quantum process tomography (QPT) is a standard method for this. However, traditional QPT becomes very costly as the system grows, because the number of required measurements and calculations increases rapidly with the number of qubits.
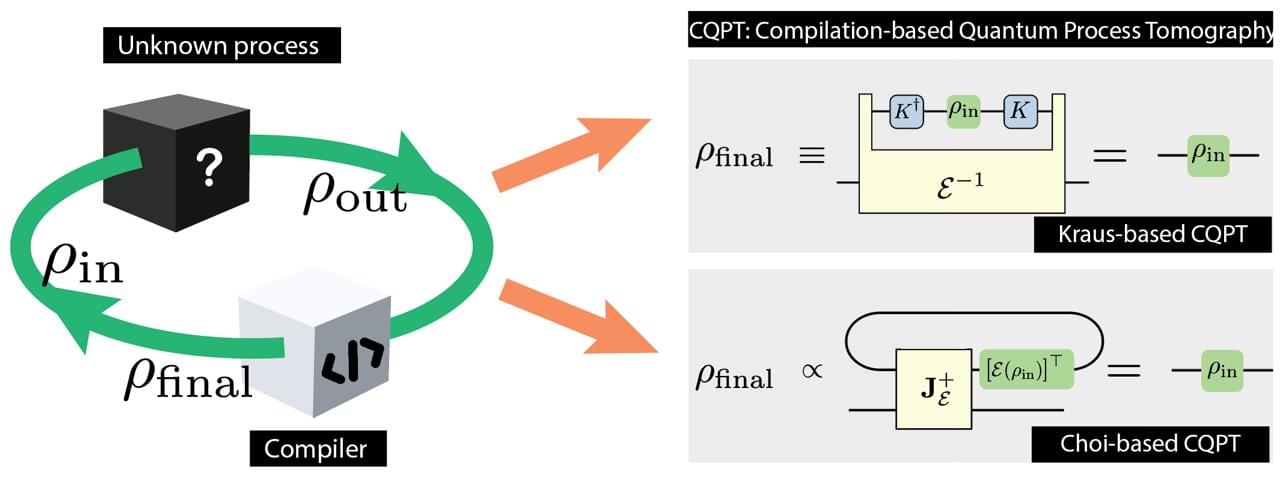
To address this challenge, a research team from Tohoku University, the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), and the University of Information Technology (Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City) has introduced a new framework called compilation-based quantum process tomography (CQPT). The work is published in Advanced Quantum Technologies.