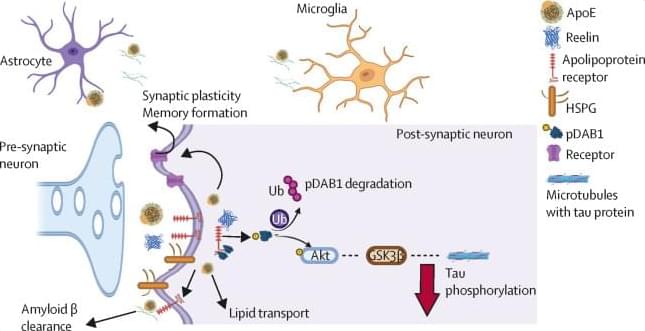
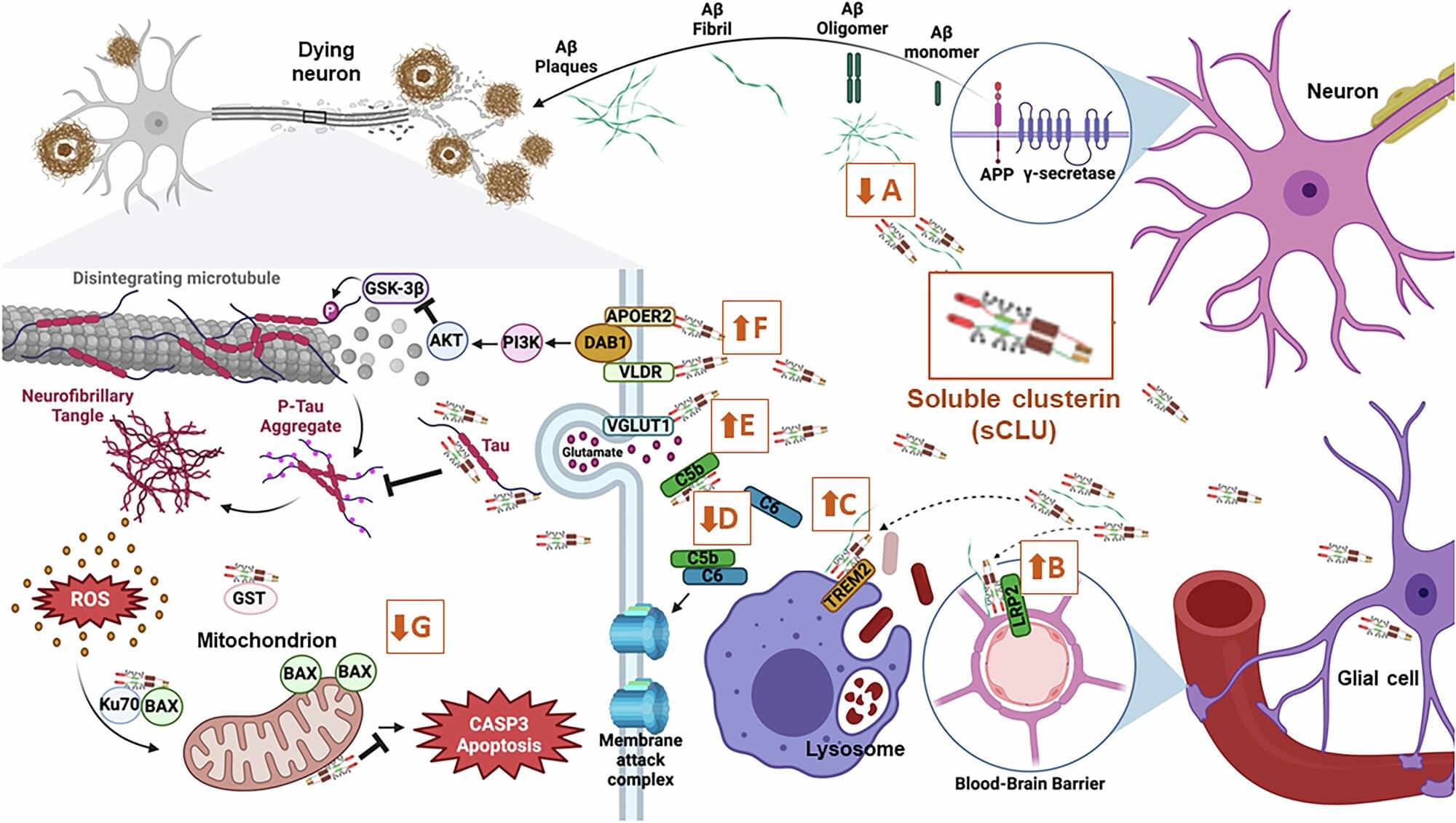
A new study published in Nature reveals how olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) achieve extraordinary precision in selecting which genes to express.
The mechanism is surprising in that it involves solid-like molecular condensates that last for days, helping to solve a long-standing puzzle in genome organization.
The research, led by Prof. Stavros Lomvardas from Columbia University, addresses one of biology’s most intriguing questions: How do olfactory sensory neurons in the nose manage to express only one olfactory receptor (OR) gene out of approximately 1,000 available options?