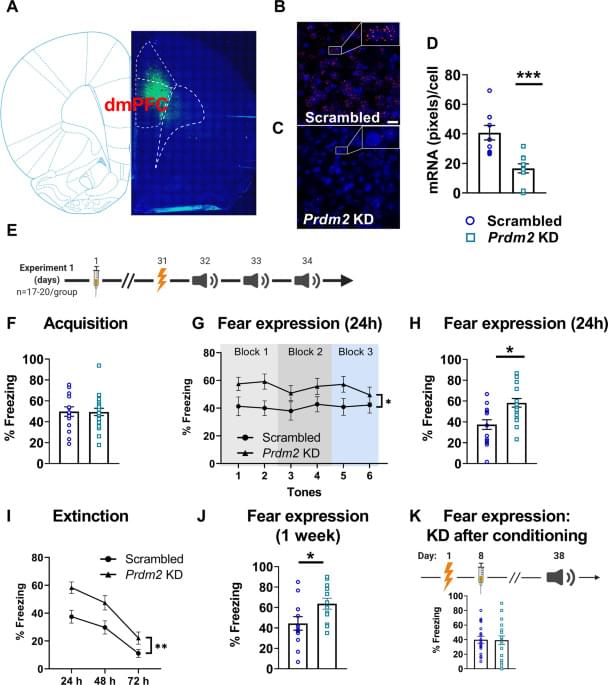
Jan 27, 2023
A drug that increases dopamine can reverse the effects of inflammation on the brain in depression, Emory study shows
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, neuroscience
𝐀 𝐝𝐫𝐮𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐧𝐜𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐝𝐨𝐩𝐚𝐦𝐢𝐧𝐞 𝐜𝐚𝐧 𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐢𝐧𝐟𝐥𝐚𝐦𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐢𝐧 𝐝𝐞𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐄𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐬𝐭𝐮𝐝𝐲 𝐬𝐡𝐨𝐰𝐬
𝘼𝙣 𝙀𝙢𝙤𝙧𝙮 𝙐𝙣𝙞𝙫𝙚𝙧𝙨𝙞𝙩𝙮 𝙨𝙩𝙪𝙙𝙮 𝙥𝙪𝙗𝙡𝙞𝙨𝙝𝙚𝙙 𝙞𝙣 𝙉𝙖𝙩𝙪𝙧𝙚’𝙨 𝙈𝙤𝙡𝙚𝙘𝙪𝙡𝙖𝙧 𝙋𝙨𝙮𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙖𝙩𝙧𝙮 𝙨𝙝𝙤𝙬𝙨 𝙡𝙚𝙫𝙤𝙙𝙤𝙥𝙖, 𝙖 𝙙𝙧𝙪𝙜 𝙩𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙞𝙣𝙘𝙧𝙚𝙖𝙨𝙚𝙨 𝙙𝙤𝙥𝙖𝙢𝙞𝙣𝙚 𝙞𝙣 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣, 𝙝𝙖𝙨 𝙥𝙤𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙖𝙡 𝙩𝙤 𝙧𝙚𝙫𝙚𝙧𝙨𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙚𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙘𝙩𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙞𝙣𝙛𝙡𝙖𝙢𝙢𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙤𝙣 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣 𝙧𝙚𝙬𝙖𝙧𝙙 𝙘𝙞𝙧𝙘𝙪𝙞𝙩𝙧𝙮, 𝙪𝙡𝙩𝙞𝙢𝙖𝙩𝙚𝙡𝙮 𝙞𝙢𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙫𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙨𝙮𝙢𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙣𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙙𝙚𝙥𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙨𝙞𝙤𝙣.
Numerous labs across the world have shown that inflammation causes reduced motivation and anhedonia, a core symptom of depression, by affecting the brain’s reward pathways.