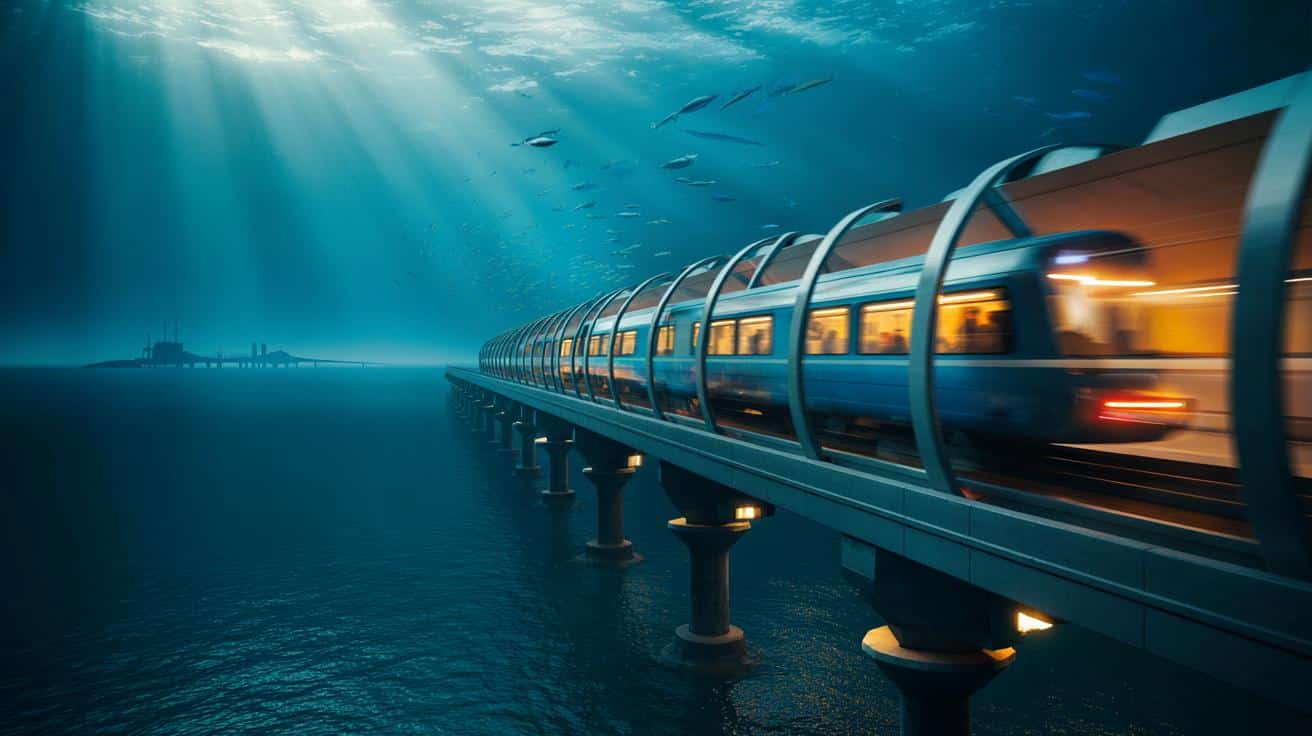
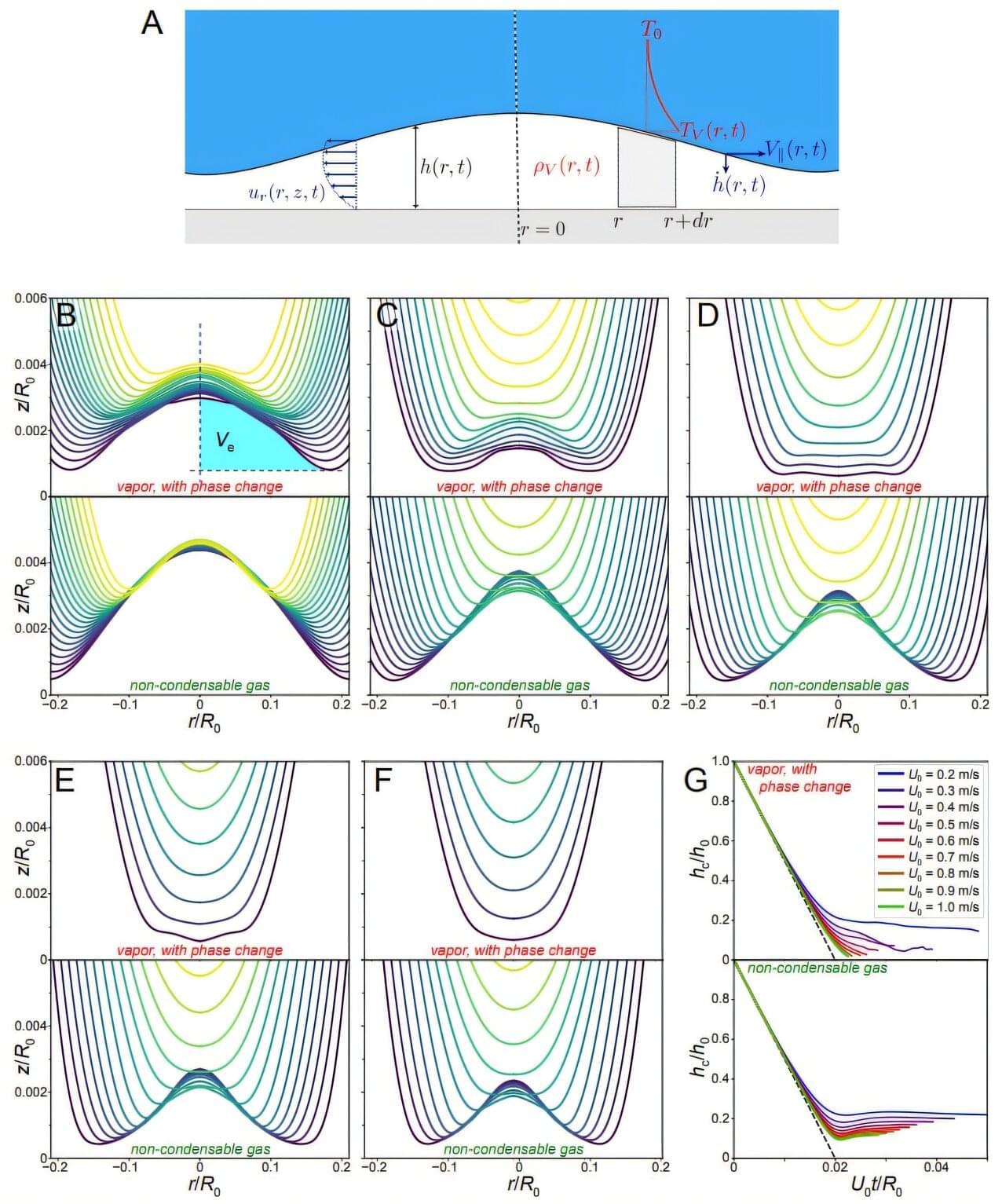
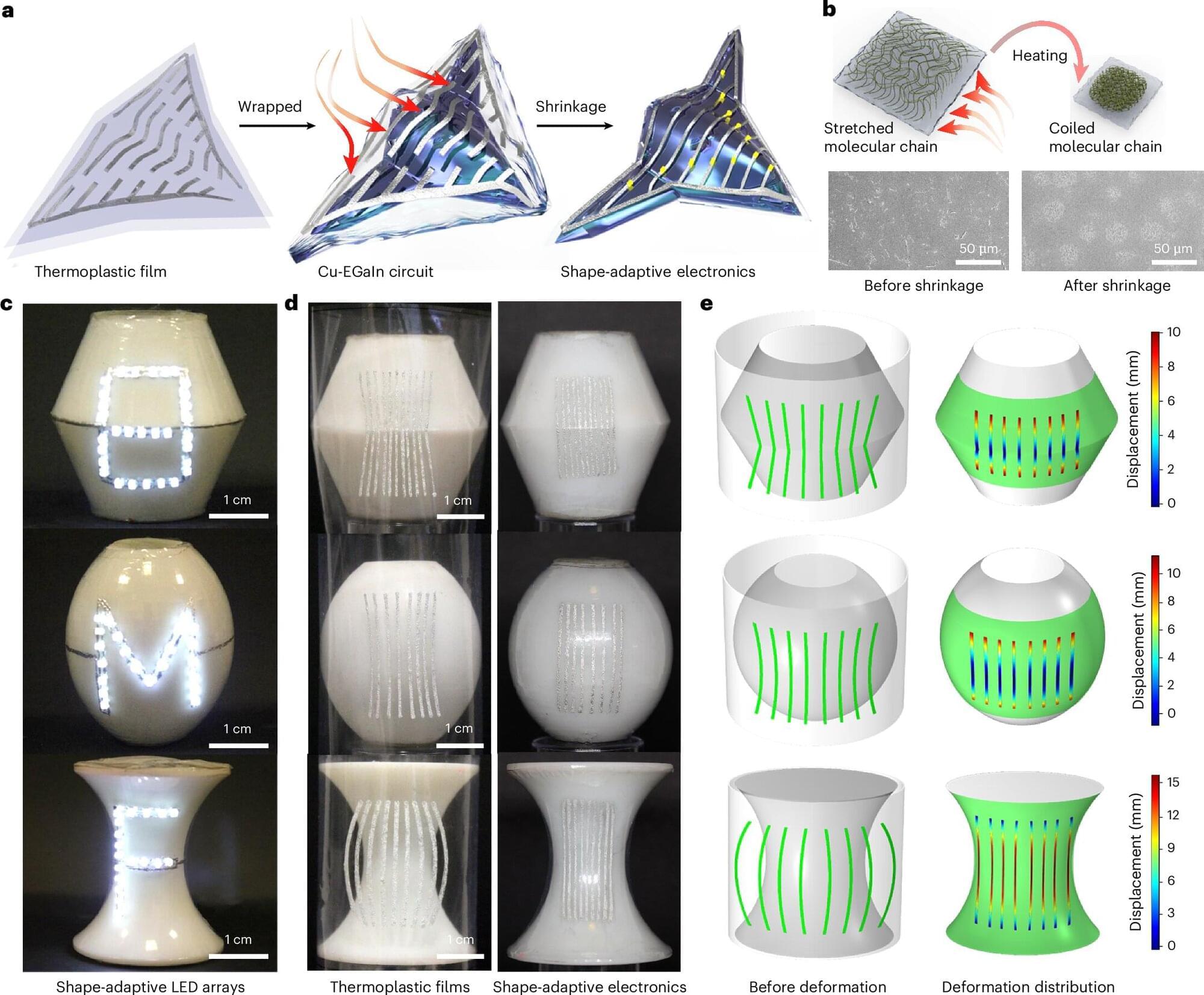
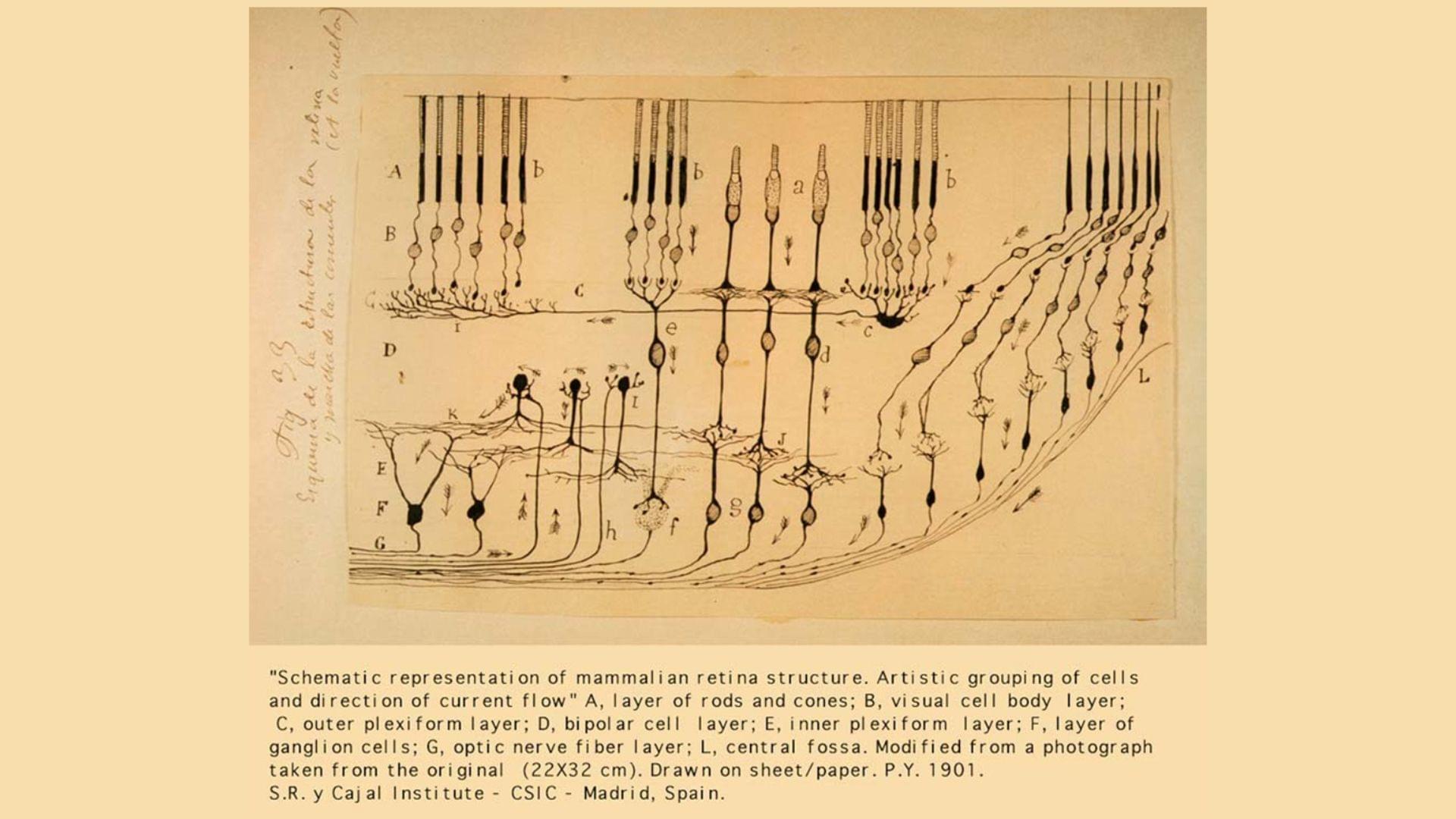
On a foggy morning off the coast of Finland, the sea looks perfectly ordinary. A few fishing boats, a cargo ship on the horizon, the low hum of engines and gulls complaining overhead. Yet under that flat grey surface, survey vessels are tracing invisible lines, mapping the seabed for something that sounds like science fiction: a high‑speed train that will dive under the Baltic and emerge on another continent.
On deck, an engineer in a neon jacket points to the radar screen like someone tracing the outline of a new city. He talks about boring through rock, laying tracks where only fish and submarines have passed. His words hang in the cold air.
Soon, a train will cross here faster than most people cross a city.