By now, every interested news-junkie is aware that Bitcoin plummeted from $15,000 to $13,000 (USD exchange rate) on January 11, 2018. This morning, every news outlet and armchair analyst attributes the drop to the Korean government signaling that it will ban Bitcoin trading among its citizens.
With Donald Trump and Kim Jong Un butting heads over nuclear missile tests and the upcoming Winter Olympics, you would think that South Korea has other priorities than banning Bitcoin.
As with all news—except accidents—the Korean plans were known by a few insiders (in this case, government bureaucrats), and so the influence on value was bigger than the drop that occurred after the news story. In the days before this “event”, it was probably responsible for a drop of about $4500 in exchange value.
Listen up Wild Ducks! We have heard this before. On Sept 11, China announced the exact same thing. I wrote about it in the most popular article of my 7 years as Blogger: Bad News is Good News for Bitcoin Investors.
As an investor, am I worried? Not on your sweet bippy. I am ecstatic! There are some things that governments cannot ban: the mating of feral cats; water from seeping into cellars; communications networks that are distributed and permissionless. Ineffective and unenforceable regulation always spells opportunity.  When I hear of such “bans” (or learn about Jamie Dimon claiming that Bitcoin is a ‘pyramid scheme’ before having all the facts), I become confused and excited…
When I hear of such “bans” (or learn about Jamie Dimon claiming that Bitcoin is a ‘pyramid scheme’ before having all the facts), I become confused and excited…
Investors often fail to recognize the way in which toothless government edicts work. I am confused that anyone would act on such flawed information. I am excited that they do. Why?—Because each time Bitcoin makes a quick dive due to crazy or irrelevant news, it makes an even bigger upward jump within days. In this case, the reverse correction has already begun.
I created the chart, below, for my presentation at the Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai during the last days of October. During this 3 day conference, Bitcoin jumped from $6000 to 6500 because these days followed a hard fork that scared analysts. Within 5 weeks of the conference, Bitcoin touched $20,000, depending on the exchange from which you get quotes. But here’s an odd thing (not so odd, to me): With sudden market accessibility in the past 30 days, why is Bitcoin falling? [continued below]…
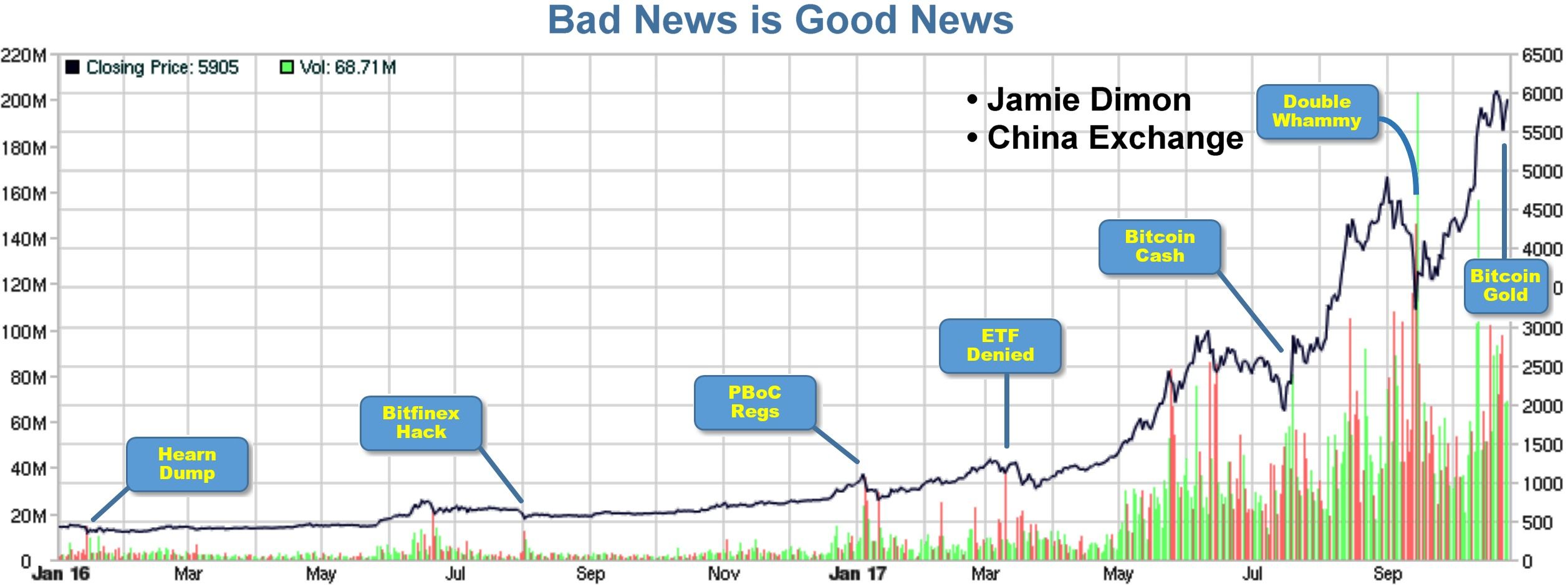
In the past month (Dec 10 2017~Jan 10 2018), Bitcoin and Bitcoin futures are finally becoming accessible to traditional brokers using familiar investment instruments. As a result of market accessibility, everyone and his brother is getting into Bitcoin. Since it is still difficult to take a negative position, you might expect this fresh interest to drive up value. This expectation is reinforced by my own anecdotal observation: Based on the large number of old acquaintances asking me to help them buy Bitcoin, it certainly feels like the sentiment is bullish. But no! Existing stakeholders are dumping their positions!
It’s not just because of yesterday’s news. Rather, it’s because anyone who has seen Bitcoin triple in just 3 months, feels that their personal stake experienced a “lucky” gain. They want to turn that paper gain into a profit before it tanks.
But then, there are the cognoscenti. That’s us…We are the individuals who have a feel for the natural, intrinsic value of Bitcoin. We understand that value does not require a redemption guarantee from Caesar. We have a reasonable vision of currency, inflation, economics, history, the role of government—and especially, of distributed trust. Just as important, we understand why an altcoin is unlikely to replace Bitcoin—even if it solves some of Bitcoin’s frustrating technical and governance issues.
Governments tend to react to perceived threats before understanding opportunities, motives and that which is fait accompli. There is a role for government in all of this, but it is not to ban what cannot be banned. That is simply good news for us stakeholders.
Related Reading:
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, publishes A Wild Duck and hosts the New York Bitcoin Event. He is keynote speaker at the Cryptocurrency Expo in India this month. Click Here to inquire about a presentation or consulting engagement.









 When I hear of such “bans” (or learn about Jamie Dimon claiming that Bitcoin is a ‘pyramid scheme’ before having all the facts), I become confused and excited…
When I hear of such “bans” (or learn about Jamie Dimon claiming that Bitcoin is a ‘pyramid scheme’ before having all the facts), I become confused and excited…