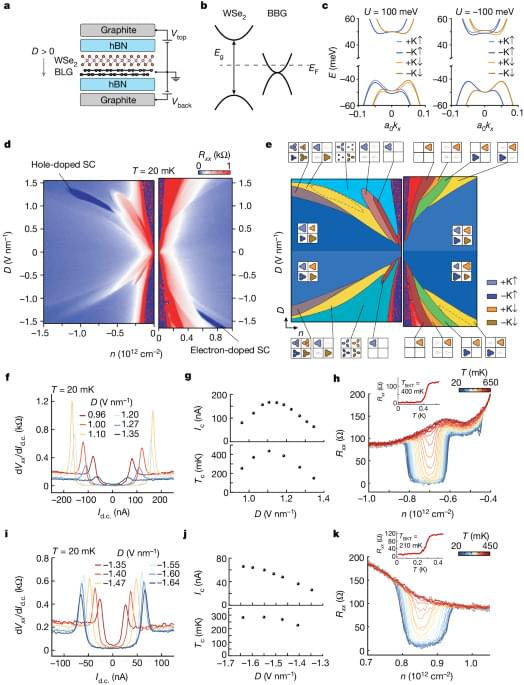
Tunable superconductivity and a series of flavour-symmetry-breaking phases are observed in electron-and hole-doped Bernal bilayer graphene.

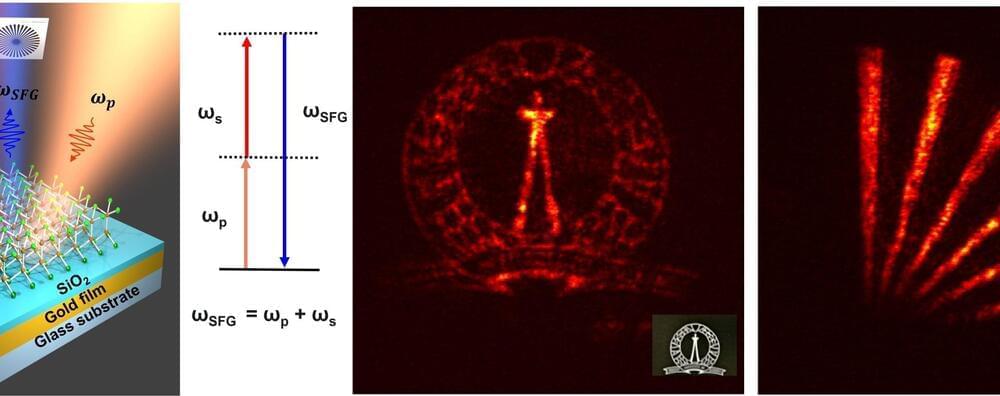
The human eye can only see light at certain frequencies (called the visible spectrum), the lowest of which constitutes red light. Infrared light, which we can’t see, has an even lower frequency than red light. Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have now fabricated a device to increase or “up-convert” the frequency of short infrared light to the visible range.
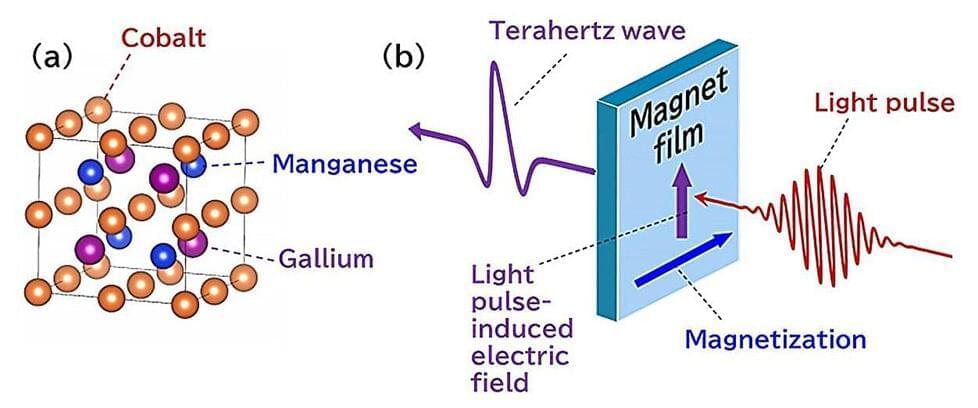
Terahertz waves are being intensely studied by researchers around the world seeking to understand the “terahertz gap.” Terahertz waves have a specific frequency that puts them somewhere between microwaves and infrared light. This range is referred to as a “gap” because much remains unknown about these waves.

The so-called Casimir force or Casimir effect is a quantum mechanical phenomenon resulting from fluctuations in the electromagnetic field between two conducting or dielectric surfaces that are a short distance apart. Studies have shown that this force can be either be attractive or repulsive, depending on the dielectric and magnetic properties of the materials used in experiments.
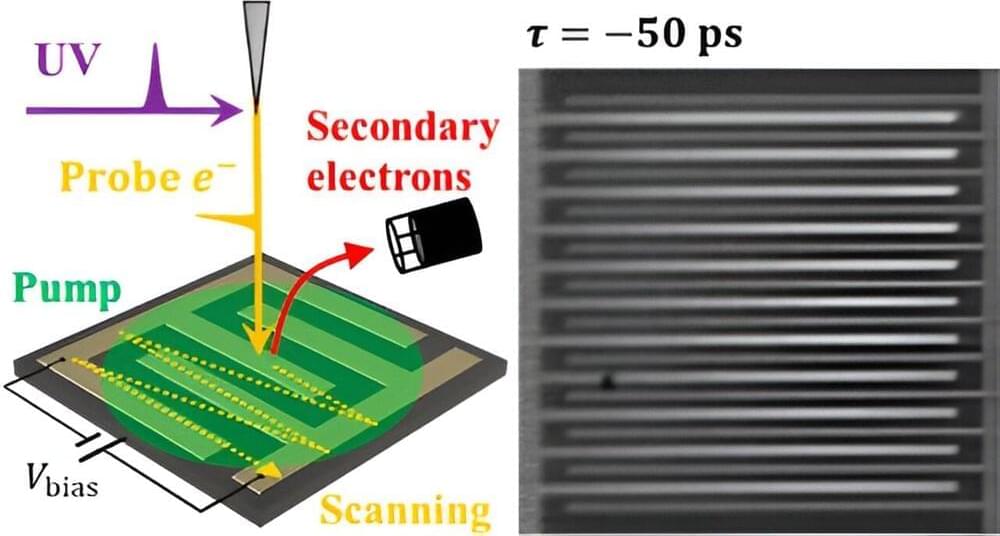
Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed an ultrafast time-resolved scanning electron microscopy instrument by integrating a scanning electron microscope with a femtosecond laser. This innovative system facilitates the observation of the instantaneous states of various materials. Their paper is published in the journal ACS Photonics.

UCLA researchers have created a new type of imager that can capture features much smaller than the limitations of traditional optical systems. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize fields like bioimaging, lithography and material science. The research is published in the journal eLight.
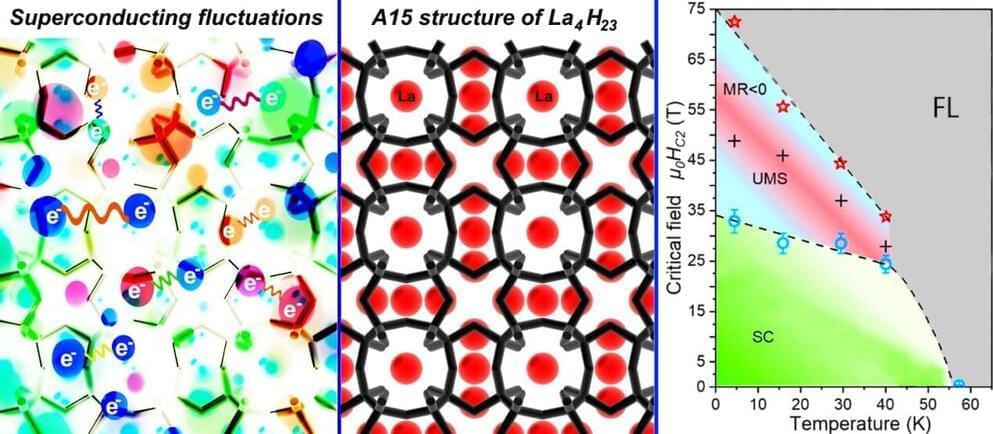
Researchers from Skoltech, Jilin University and Beijing HPSTAR in China, and their German colleagues have synthesized and studied a new type of hydrogen-rich superconductor. Technically referred to as an A15-type lanthanum superhydride, with the formula La4H23, it shows superconductivity below minus 168 degrees Celsius at a pressure of 1.2 million atmospheres. The research results were published in the National Science Review.
Polyhydrides are a novel class of compounds synthesized at about 1 million times the normal atmospheric pressure on Earth. They can exhibit unique superconducting properties with record-high critical temperatures of up to-23 C in lanthanum decahydride LaH10, critical magnetic fields reaching 300 tesla, and critical current densities.
Even compared to other similar hydrides, the newly discovered La4H23 behaves unusually: It has a negative temperature coefficient of electrical resistance in a certain pressure range. That is, unlike ordinary metals, with a decrease in temperature its electrical resistance does not decrease but grows, the way it happens in semiconductors and many unconventional superconductors, such as cuprates.

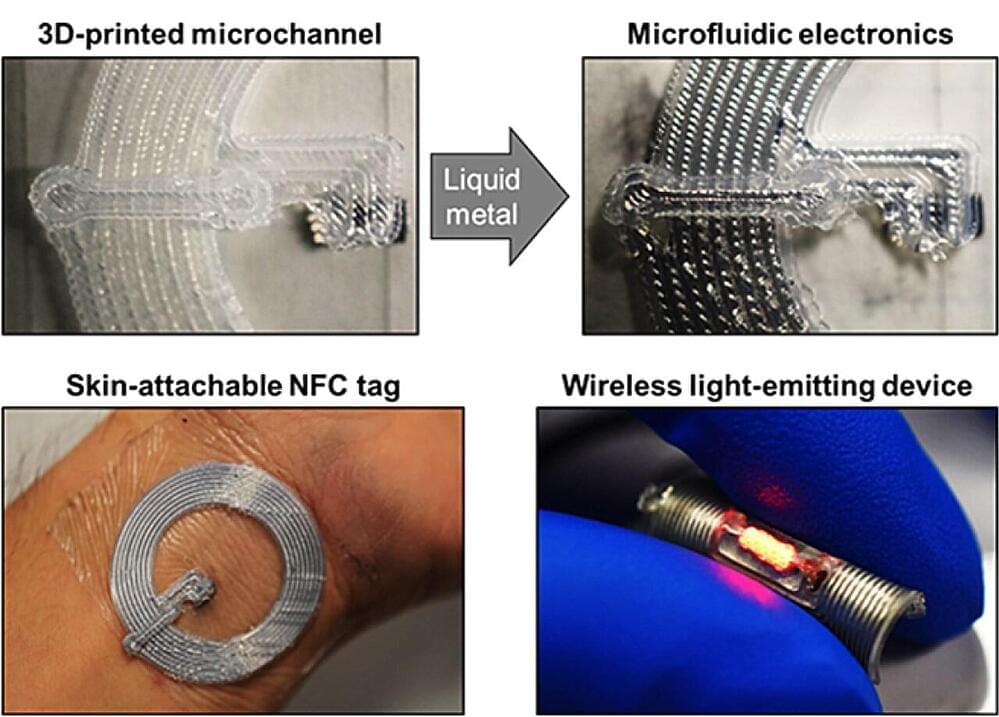
The transition from traditional 2D to 3D microfluidic structures is a significant advancement in microfluidics, offering benefits in scientific and industrial applications. These 3D systems improve throughput through parallel operation, and soft elastomeric networks, when filled with conductive materials like liquid metal, allowing for the integration of microfluidics and electronics.