Nice.
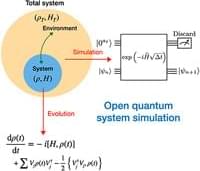
A novel quantum algorithm, which exploits the relation between the Lindblad master equation, stochastic differential equations, and Hamiltonian simulations, is proposed to simulate open quantum systems on a quantum computer.
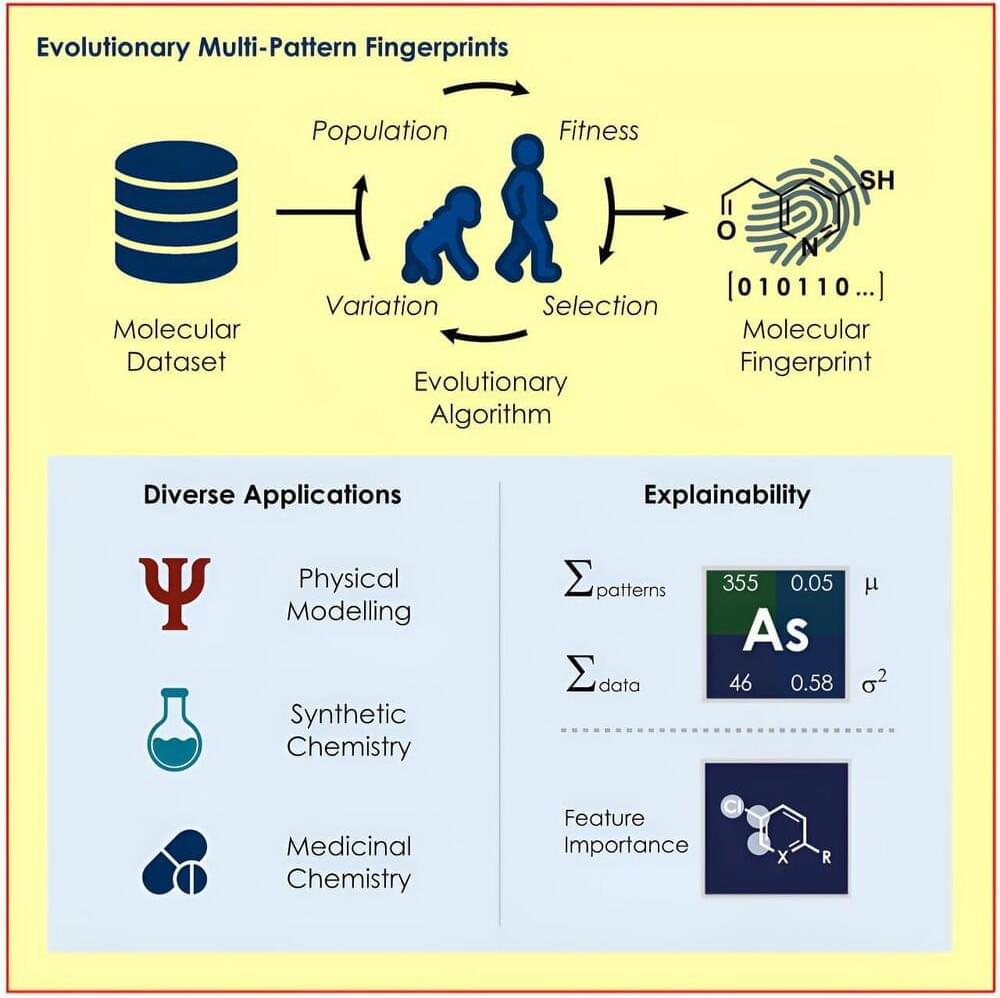
A team led by Prof Frank Glorius from the Institute of Organic Chemistry at the University of Münster has developed an evolutionary algorithm that identifies the structures in a molecule that are particularly relevant for a respective question and uses them to encode the properties of the molecules for various machine-learning models.

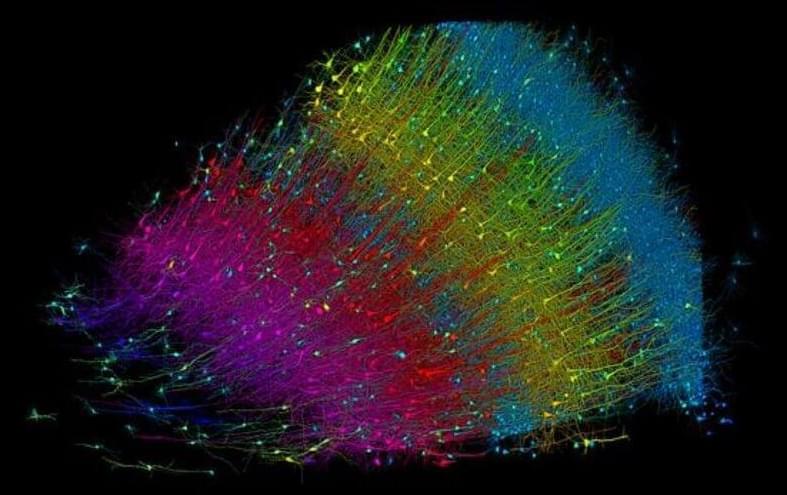
Summary: Researchers created the largest 3D reconstruction of human brain tissue at synaptic resolution, capturing detailed images of a cubic millimeter of human temporal cortex. This tiny piece of brain contains 57,000 cells, 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and 150 million synapses, which amounts to 1,400 terabytes of data.
This research is part of a broader effort to map an entire mouse brain’s neural wiring, with hopes of advancing our understanding of brain function and disease. The technology combines high-resolution electron microscopy and AI-powered algorithms to meticulously color-code and map out the complex neural connections.


Inspired by the tetromino shapes in the classic video game Tetris, researchers in the US have designed a simple radiation detector that can monitor radioactive sources both safely and efficiently. Created by Mingda Li and colleagues at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the device employs a machine learning algorithm to process data, allowing it to build up accurate maps of sources using just four detector pixels.
\r \r.
Wherever there is a risk of radioactive materials leaking into the environment, it is critical for site managers to map out radiation sources as accurately as possible.
Dive into the deepest quantum mystery: how do we transition from a haze of possibilities to the concrete reality we experience? Does the answer require a profusion of universes, each shaped by different quantum outcomes?
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participants:
Sean Carroll.
Moderator:
Brian Greene.
00:00 — Introduction.
03:38 — Sean Carroll Introduction.
04:09 — The Quantum Measurement Problem.
08:33 — The GRW Theory.
11:18 — What would be predicted with the Schrödinger equation?
15:10 — Many Worlds Theory.
17:42 — What are the implications of the many worlds theory?
22:37 — Quantum Entanglement.
29:05 — What does the future of Quantum Mechanics look like?
31:26 — Embracing the Many Worlds Concept.
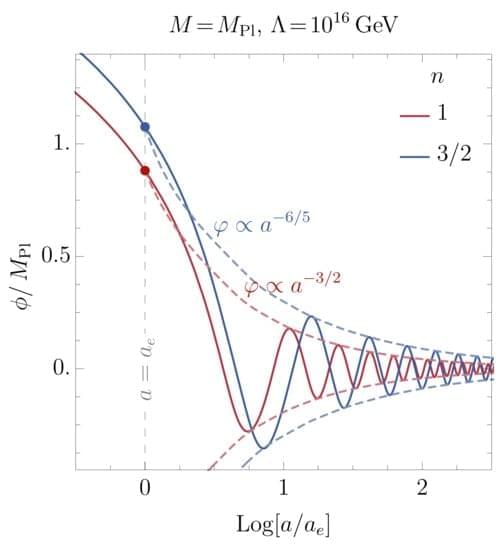
We discuss a perturbative and non-instantaneous reheating model, adopting a generic post-inflationary scenario with an equation of state w. In particular, we explore the Higgs boson-induced reheating, assuming that it is achieved through a cubic inflaton-Higgs coupling ϕ|H|2. In the presence of such coupling, the Higgs doublet acquires a ϕ-dependent mass and a non-trivial vacuum–expectation–value that oscillates in time and breaks the Standard Model gauge symmetry. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the non-standard cosmologies and the inflaton-induced mass of the Higgs field modify the radiation production during the reheating period. This, in turn, affects the evolution of a thermal bath temperature, which has remarkable consequences for the ultraviolet freeze-in dark matter production.
Proteins are the molecular machines that sustain every cell and organism, and knowing what they look like will be critical to untangling how they function normally and malfunction in disease. Now researchers have taken a huge stride toward that goal with the development of new machine learning algorithms that can predict the folded shapes of not only proteins but other biomolecules with unprecedented accuracy.
In a paper published today in Nature, Google DeepMind and its spinoff company Isomorphic Labs announced the latest iteration of their AlphaFold program, AlphaFold3, which can predict the structures of proteins, DNA, RNA, ligands and other biomolecules, either alone or bound together in different embraces. The findings follow the tail of a similar update to another deep learning structure-prediction algorithm, called RoseTTAFold All-Atom, which was published in March in Science.
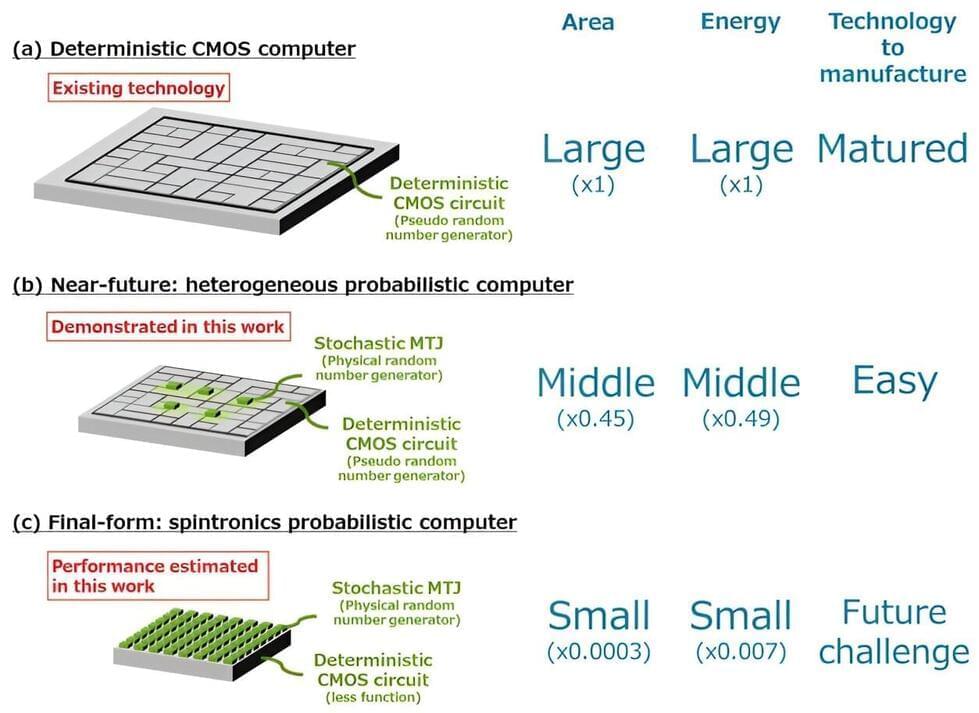
In this study, graduate student Keito Kobayashi and Professor Shunsuke Fukami from Tohoku University, along with Dr. Kerem Camsari from the University of California, Santa Barbara, and their colleagues, developed a near-future heterogeneous version of a probabilistic computer tailored for executing probabilistic algorithms and facile manufacturing.
“Our constructed prototype demonstrated that excellent computational performance can be achieved by driving pseudo random number generators in a deterministic CMOS circuit with physical random numbers generated by a limited number of stochastic nanomagnets,” says Fukami. “Specifically speaking, a limited number of probabilistic bits (p-bits) with a stochastic magnetic tunnel junction (s-MTJ), should be manufacturable with a near-future integration technology.”
The researchers also clarified that the final form of the spintronics probabilistic computer, primarily composed of s-MTJs, will yield a four-order-of-magnitude reduction in area and a three-order-of-magnitude reduction in energy consumption compared to the current CMOS circuits when running probabilistic algorithms.