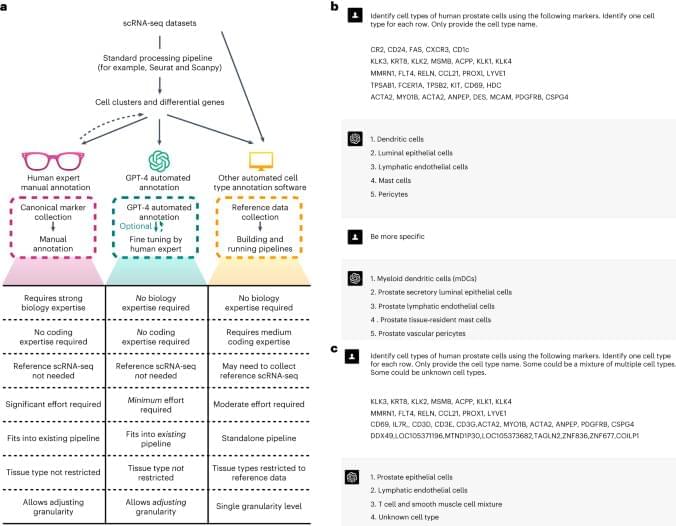
With no biology expertise, GPT-4 performs as good or better than human experts for single-cell RNA-seq cell annotation.
This study evaluates the performance of GPT-4 in single-cell type annotation.
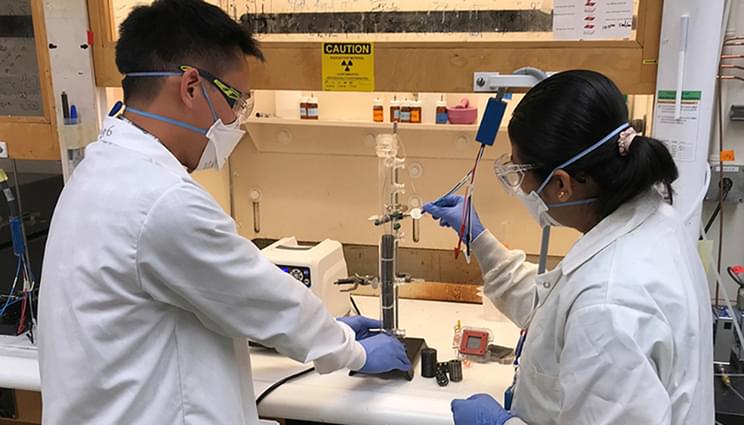

Four Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have partnered with Los Angeles-based SoCalGas and Munich, Germany-based Electrochaea to develop an electrobioreactor to allow excess renewable electricity from wind and solar sources to be stored in chemical bonds as renewable natural gas.
When renewable electricity supply exceeds demand, electric-utility operators intentionally curtail production of renewable electricity to avoid overloading the grid. In 2020, in California, more than 1.5 million megawatt hours of renewable electricity were curtailed, enough to power more than 100,000 households for a full year.
This practice also occurs in other countries. The team’s electrobioreactor uses the renewable electricity to convert water into hydrogen and oxygen. The microbes then use the hydrogen to convert carbon dioxide into methane, which is a major component of natural gas. Methane can then be moved around in natural gas pipelines and can be stored indefinitely, allowing the renewable energy to be recovered when it is most needed.

Probabilistic computing with stochastic devices.
In recent decades, artificial intelligence has been successively employed in the fields of finance, commerce, and other industries. However, imitating high-level brain functions, such as imagination and inference, pose several challenges as they are relevant to a particular type of noise in a biological neuron network. Probabilistic computing algorithms based on restricted Boltzmann machine and Bayesian inference that use silicon electronics have progressed significantly in terms of mimicking probabilistic inference. However, the quasi-random noise generated from additional circuits or algorithms presents a major challenge for silicon electronics to realize the true stochasticity of biological neuron systems. Artificial neurons based on emerging devices, such as memristors and ferroelectric field-effect transistors with inherent stochasticity can produce uncertain non-linear output spikes, which may be the key to make machine learning closer to the human brain. In this article, we present a comprehensive review of the recent advances in the emerging stochastic artificial neurons (SANs) in terms of probabilistic computing. We briefly introduce the biological neurons, neuron models, and silicon neurons before presenting the detailed working mechanisms of various SANs. Finally, the merits and demerits of silicon-based and emerging neurons are discussed, and the outlook for SANs is presented.
Keywords: brain-inspired computing, artificial neurons, stochastic neurons, memristive devices, stochastic electronics.

Neuromorphic computing is an emerging solution for companies specializing in small, energy-efficient edge computing devices and robotics, striving to improve their products. There has been a paradigm shift in computing since the advent of neuromorphic chips. With the potential to unlock new levels of processing speed, energy efficiency, and adaptability, neuromorphic chips are here to stay. Industries from robotics to healthcare are exploring the potential of neuromorphic chips in various applications.
What is Neuromorphic Computing?
Neuromorphic computing is a field within computer science and engineering that draws inspiration from the structure and operation of the human brain. Its goal is to create computational systems, including custom hardware replicating the neural networks and synapses in biological brains. These custom computational systems are commonly known as neuromorphic chips or neuromorphic hardware.
In cells, like the snowflake yeast in this image byTony Burnetti, proteins are translated and folded into very specific, three-dimensional shapes. | Cell And Molecular Biology.

In a recent study published in Nature Communications, researchers developed a modular synthetic biology toolkit for Aspergillus oryzae, an edible fungus used in fermented foods, protein production, and meat alternatives.
Study: Edible mycelium bioengineered for enhanced nutritional value and sensory appeal using a modular synthetic biology toolkit. Image Credit: Rattiya Thongdumhyu/Shutterstock.com.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7x…

Hydrogen gas is a clean fuel. It burns with oxygen in the air to provide energy with no CO2. Hydrogen is a key to sustainable energy for the future. Though humans are just now coming to realize the benefits of hydrogen gas (H2 in chemical shorthand), microbes have known that H2 is a good fuel for as long as there has been life on Earth. Hydrogen is ancient energy.
A small research group from the University of Michigan has developed a three-legged skating/shuffling robot called SKOOTR that rolls as it walks, can move along in any direction and can even rise up to overcome obstacles.
The idea for the SKOOTR – or SKating, Omni-Oriented, Tripedal Robot – project came from assistant professor Talia Y. Moore at the University of Michigan’s Evolution and Motion of Biology and Robotics (EMBiR) Lab.
“I came up with this idea as I was rolling around on my office chair between groups of students,” said Moore. “I realized that the passively rolling office chair could easily spin in any direction, and I could use my legs to perform a variety of maneuvers while staying remarkably stable. I realized that this omnidirectional maneuverability is similar to how brittle stars change directions while swimming.”