face_with_colon_three Year 2021
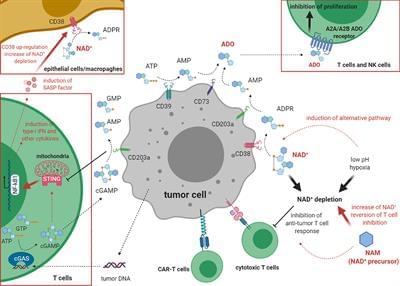
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an important molecule that functions as a co-enzyme in numerous metabolic processes. Generated both through de novo synthesis and via salvage pathways, NAD+ is the substrate for a variety of NAD+-consuming enzymes. Among them is CD38, a cell surface ecto-enzyme widely expressed on different types of cells and endowed with the function of cADP-ribose synthases/NAD+ glycohydrolase. Surface CD38 expression is increased in different hematological and solid tumors, where it cooperates with other ecto-enzymes to produce the immunosuppressive molecule adenosine (ADO). Few studies have explored the correlation of NAD+ levels with T-cell mediated anti-tumor response in preclinical models. We therefore discuss these novel findings, examining the possible contribution of NAD+ depletion, along with ADO production, in the immunosuppressive activities of CD38 in the context of human tumors. Lastly, we discuss the use of pharmacological inhibitors of CD38 and supplementation of different NAD+ precursors to increase NAD+ levels and to boost T cell responses. Such molecules may be employed as adjuvant therapies, in combination with standard treatments, for cancer patients.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and its reduced/phosphorylated forms (NADH, NADP+ and NADPH) are key molecules in cellular metabolism and energy production, acting as hybrid-accepting and hybrid-donating co-enzymes in different biological reactions. NAD+ and NADH are then inter-converted by hybrid transfer and not consumed. NAD+ can be generated de novo starting from tryptophan, which is converted to N-formylkynurenine by indoleamine dioxygenase or tryptophan dioxygenase. Other enzymes are involved in converting N-formylkynurenine to nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN), which is adenylated by adenyl-transferases to generate nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD), finally converted to NAD+ by NAD+ synthetase. NAD+ can also be obtained through different salvage pathways, starting from nicotinic acid (Na) which is converted to NaMN by Na phosphoribosyltransferase (Naprt) or starting from nicotinamide (Nam) and nicotinamide riboside (NR).









Comments are closed.