Circa 2009
March 19, 2009 Researchers at the University of Miami and at the Universities of Tokyo and Tohoku, Japan, have been able to prove the existence of a “spin battery,” that could have significant applications including much faster, less expensive and use less energy consuming computer hard drives with no moving parts, and could even be developed to power cars.
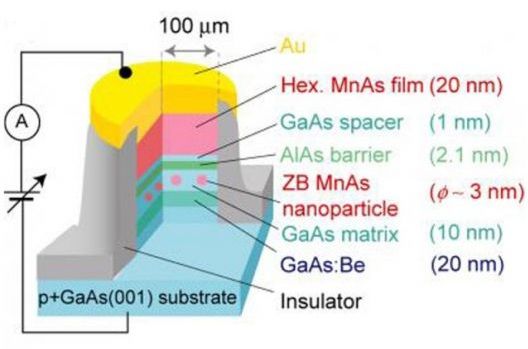
A “spin battery” is “charged” by applying a large magnetic field to nano-magnets in a device called a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). Like a toy car, the spin battery is “wound up” by applying a large magnetic field — no chemistry involved.
The secret behind this technology is the use of nano-magnets to induce an electromotive force. It uses the same principles as those in a conventional battery, except in a more direct fashion. The energy stored in a battery, be it in an iPod or an electric car, is in the form of chemical energy. When something is turned “on” there is a chemical reaction, which occurs and produces an electric current. The new technology converts the magnetic energy directly into electrical energy, without a chemical reaction. The electrical current made in this process is called a spin polarized current and finds use in a new technology called “spintronics.” Also known as magnetoelectronics, this is an emerging technology, which exploits the intrinsic spin of electrons and its associated magnetic movement, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices.









Comments are closed.