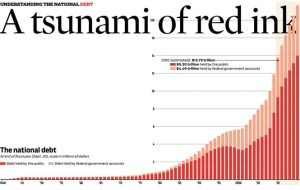
At the end of 2015, the US national debt will be 18.6 trillion dollars. With such a big number, it’s tempting to put it in perspective by comparing it with things more easily envisioned. Alas, I can not think of anything that puts such an oppressive and unfair burden into perspective, except to this:
US debt represents a personal obligation of $60,000 for each American citizen. And it is rising quickly. Most of our GDP is used simply to pay down interest on that debt. Few pundits see a way out of this hole.
 In my opinion, that hole was facilitated in August 1971, when the US modified the Bretton Woods Agreement and unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold. By forcibly swapping every dollar in every pocket and bank account with the promise of transient legislators, individual wealth was suddenly based on fiat instead of something tangible or intrinsic.
In my opinion, that hole was facilitated in August 1971, when the US modified the Bretton Woods Agreement and unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold. By forcibly swapping every dollar in every pocket and bank account with the promise of transient legislators, individual wealth was suddenly based on fiat instead of something tangible or intrinsic.
Feds Meet: No interest rate hike
The benchmark interest rate set by the US Federal Reserve Board is currently between 0 and 0.25%. It has been at or near zero since 2006.
By now, Lifeboat readers know that 20 hours ago, the US Federal Reserve board decided to not hike the benchmark interest rate. The Fed did, however, signal that they still intend to raise interest rates at a future meeting—perhaps in October or December.
The announcement came just after US equity markets closed. But, in what has become a most odd news coverage of a non-event, the immediate reaction was to lift the Asian stock markets, which were still open during the announcement.
I am a frequent contributor to Quora. I field many questions on economics, politics, law, and even physics. You might be inclined to check out my credentials as pundit of macro-economics. Don’t bother…There are none! I am an armchair economist (this is the same as saying: “I am not an economist”). But I certainly follow these things closely, and have an informed opinion.
Today, I was asked this:
What would happen if the fed had raised interest rates?
The question asked specifically about the effect on other interest rates, but a more interesting exercise might be to speculate on the state of the economy. Here then, is a comon-sense response…
If we could freeze all other conditions and avoid the effects of public confidence, likely change in debt, debt rating, etc… If we ignore these things, then the direct result of raising the interest rate for a given national currency is to attract outside money. That is, we would see an increase in foreign conversion into dollars and a movement of US assets from stocks and bonds into currency or currency equivalents. This is a simple result of the higher payout that one would expect after a raise in interest rates.
In theory, the sift of international assets and investment into dollars does four things:
- It strengthens the value of the dollar, thereby increasing the take-home potential of US workers and the number of things US residence buy from overseas (because a slightly higher fraction of organizations seek dollars)
- It increases income for anyone tied to published interest rates, such as many senior citizens.
- It increases interest payments from anyone tied to published interest rates. For anyone deeply in debt on instruments such as credit cards or home equity, this can have a devastating impact—causing minimum payments to rise by many times the interest rate hike.
- It increases US national debt, because so much of the economy is built on forward loans in the form of Treasury notes. With an interest rate increase, the US must pay more on both new debt and the financing of massive outstanding debts.
This is all theoretical, of course. In practice, one of the first effects is for individuals and institutions to wonder: “How can the US possibly pay out on debt at an increased rate?”. [possible answer]*
One very obvious effect is that many individuals will further lose confidence in the American economy or the will of American’s to honor the national debt. Because of this, the effect of raising the interest rate (for the first time in 9 years) is not easy to predict. Despite massive uptake on US debt, the Chinese and energy producing nations have limits to what they can believe. A subtle switch in their investment activity (or the determination to move away from a dollar-based reserve) will have massive repercussions, especially for the US.
_____________
* Some pundits argue that US debt and payments can continue to grow, because the ability to accommodate these things are protected by these things:
- a recovering economy
- increased activity from the new investors
- need for producer nations to seize on a massive consumer market
- need for producer nations to invest their gains
But, a growing number of economists, investors, analysts, credit bureaus, and citizens don’t buy this argument! They point out that it kicks-the-can down the road and foists untenable debt on future generations. They would prefer that the US reign in spending and pay down debt.
In this regard, being the world’s reserve currency has helped hook the US on debt, and it has ballooned out of control. Transitioning to a firmly capped currency that is not controlled by legislation or a reserve board would help the country avoid massive debts (those that exceed the willingness of bond holders to finance) and to do what it must do.
In my take, the real question is not “What if the Fed has raised interest rates?” The real question is:
Does the U.S. have the courage to link its currency to something durable
— and beyond control of transient political winds and a debt pyramid?”
Sure, we must still honor the excess of the past 40 years. But with gold, or Bitcoin, at least we will have solid underpinnings and incentives to spend within our means.
Philip Raymond is a member the New Money Systems Board
at Lifeboat. He is Co-chair of Cryptocurrency Standards
Association and editor at A Wild Duck.