Tag: dna
Harvard Rewinds the Biological Clock of Time
Investigators at Harvard Medical School have identified the key cellular mechanisms behind vascular aging and its effects on muscle health, and they have successfully reversed the process in animals.
The scientists used a chemical compound that’s an NAD+ booster called NMN which plays a critical role in repairing cellular DNA as well as maintaining cell vitality to test what would happen.
Could reversing the aging of blood vessels hold the key to restoring youthful vitality? If the old adage “you are as old as your arteries” reigns true then the answer is yes, at least in mice.
According to a new study by Harvard Medical School researchers, they have identified the cellular mechanisms that cause the aging of vascular arteries as well as the effects of such aging on the health of muscles. The Medical team was also able to successfully reverse this aging process.
What these findings seem to indicate is that there’s a glitch in the normal crosswalk between both muscles and blood vessels and keeping both tissues healthy. The scientists were also able reverse the demise of blood vessels and muscle atrophy in the aging mice by using the synthetic precursors of two molecules naturally present in the body. This boosted their exercise endurance in the process.
The Medical team is excited because such a breakthrough will now pave the way to identifying new therapies for humans.
Study senior investigator David Sinclair, professor in the Department of Genetics at Harvard Medical School and co-director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for the Biology of Aging at Harvard Medical School stated “we’ve discovered a way to reverse vascular aging by boosting the presence of naturally occurring molecules in the body that augment the physiological response to exercise.”
Because there are some very important differences in biology between humans and mice there’s a possibility that this treatment may not have the same effect in humans. Nonetheless, the research team plans to follow through with human clinical trials because the results of this experiment were important enough to prompt the research team in doing so.
Sinclair, who is also a professor at the University of New South Wales School of Medical Sciences in Sydney, Australia stated, “the approach stimulates blood vessel growth and boosts stamina and endurance in mice and sets the stage for therapies in humans to address the spectrum of diseases that arise from vascular aging.”
One of the side effects of aging is reduced blood flow and the compromise of oxygenation of organs and tissue because our tiniest blood vessels began to wither and die. Cardiac and neurologic conditions, muscle loss, impaired wound healing and overall frailty, and among other things are the results of vascular aging. As these blood vessels die there’s a loss of blood flow to organs and tissues which causes toxins build-up and a loss of oxygen.
For quite some time scientists have known the essential role that endothelial cells, which line blood vessels, play in the health and growth of blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich and nutrient-loaded blood to organs and tissues. Unfortunately, as with all things on the human body, these endothelial cells age having a detrimental effect on the body. New blood vessels fail to form, blood vessels atrophy, and the overall blood flow to most parts of the body diminishes. This has a powerful impact on muscles, which heavily rely on robust blood supply to function because they’re heavily vascularized.
Typically we exercise in hopes of slowing down sarcopenia, but unfortunately even that doesn’t last forever. Gradually our muscles grow weaker and begin to shrivel as part of the aging process.
What precisely curtails the blood flow and precipitates this unavoidable decline? Why does even exercise lose its protective power to sustain muscle vitality? Is this process reversible? There were some of the leading questions Sinclair and team had.
The Experiment/Results:
Sinclair and his team discovered through a series of experiments that the flow of blood is reduced as endothelial cells start to lose a critical protein known as sirtuin1, or SIRT1. SIRT1 delays aging and extends life in yeast and mice as shown in previous studies.
Research done previously by Sinclair and others has shown that NAD+ boosts the activity of SIRT1. SIRT1 loss is a result of the loss of NAD+, which is a key regulator of protein interactions and DNA repair that was identified more than a century ago. As NAD+ declines with age so does the protein SIRT1.
The results showed that the critical interface that enables the conversation between endothelial cells in the walls of blood vessels and muscle cells is provided by NAD+ and SIRT1.
SIRT1 signaling is activated and generates new capillaries, the tiniest blood vessels in the body that supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs in young mice muscles. As the mice aged, however, the study found that muscle tissue was left nutrient-deprived and oxygen-starved as a result in the diminishment of NAD+ and SIRT1.
The researchers hope that their findings may pave the way to therapeutic advances that hold promise for the millions of older people for whom regular physical activity is not an option.
Abhirup Das, the studies first author, who conducted the work as a post-doctoral fellow in Sinclair’s lab, currently a visiting scholar in genetics at Harvard Medical School and a post-doctoral research fellow at the University of South New Wales School of Medical Sciences, said that “we reasoned that declining NAD+ levels reduce SIRT1 activity and thus interfere with aging mice’s ability to grow new blood vessels.”
The researchers then set their sights on the NAD+, which is a critical coenzyme for enzymes that fuel reduction-oxidation reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, and as a cosubstrate for other enzymes such as the sirtuins and poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerases.
The scientists used a chemical compound that’s an NAD+ booster called NMN (no not m&m!) which plays a critical role in repairing cellular DNA as well as maintaining cell vitality to test what would happen.
One of the results showed that treatment from NMN caused endothelial cells from humans and mice to have strong growth capacity and reduced cell death.
The team then wondered what would happen to a group of mice that were 20 months old—the rough equivalent of 70 in human years given NMN. After a 2 month time span the results showed that NMN treatment restored the number of blood capillaries and capillary density to those seen in younger mice. Blood flow to the muscles also increased and was significantly higher than blood supply to the muscles seen in same-age mice that didn’t receive NMN.
That wasn’t the most surprising result to the researchers however. What they discovered was that the aging mice showed in comparison to the entreated mice that they regained the capacity to exercise by 56 and 80% more. The untreated mice could only run 240 meters, or 780 feet, on average whereas the mice treated with NMN could run 430 meters, or about 1,400 feet, on average. This treatment could be an answer to humans who have lost the capacity to exercise due to other disabilities or age-related diseases.
The next step for the researchers was to explore methods for boosting the activity of SIRT1. To do this the researchers added a second compound NaHS, sodium hydrosulfide, which is known to be a precursor of SIRT1.
For four weeks a group of mice that were 32-month-old mice—the rough equivalent to 90 in human years—receiving the combo treatment. The results were significant! Not only were the mice able to run longer and faster but they were able to outperform the untreated mice by a longshot. The treated mice ran 1.6 times further than the untreated mice.
Study co-author James Mitchell, associate professor of genetics and complex diseases at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health stated that “these are really old mice so our finding that the combo treatment doubles their running capacity is nothing short of intriguing.”
“This observation underscores the notion that age plays a critical role in the crosstalk between blood vessels and muscles and points to a loss of NAD+ and SIRT1 as the reason behind loss of exercise effectiveness after middle age,” Das said.
One of the ultimate goals for the team is to eventually move forward in developing small-molecule, NMN-based drugs that mimic the effects of exercise—enhanced blood flow and oxygenation of muscles and other tissues. Though they must first replicate their findings first. Such therapies could potentially help with new vessel growth of organs that suffer tissue-damaging loss of blood supply and oxygen, a common scenario in heart attacks and ischemic strokes, the team said.
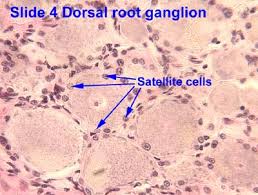
Human Skeletal Muscle Aging and Mutagenesis
Study based upon human skeletal muscle aging, mutagenesis, and the role of #satellite cells.
“A more comprehensive understanding of the interplay of stem cell–intrinsic and extrinsic factors will set the stage for improving cell therapies capable of restoring tissue homeostasis and enhancing muscle repair in the aged.”
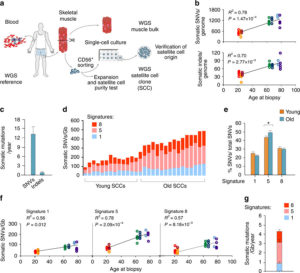
Human aging has multiple effects on the human body. One of the effects of human aging is the reduction in skeletal muscle (SkM) function and a reduction in the number and activity of satellite cells (SCs), the resident stem cells. The whole genome of single SC clones of the leg muscle vastus lateralis from healthy individuals of different ages (21–78 years) was analyzed, to study the specific connection between SC aging and muscle impairment. In healthy adult muscle rapid increase of SCs is consistent with the accumulation rate of 13 somatic mutations per genome per year. Mutations typically do not happen in SkM-expressed genes because they are protected. However, as mutations in exons and promoters increase, genes involved in SC activity and muscle function are targeted which results in aging. Exons are coding sections of an RNA transcript, or the DNA encoding it, that are translated into protein. Proteins are the synthesis of molecules. A change in of a single base pair that caused the substitution of a different amino acid in the resulting protein (missense mutation) that was propagated to the muscle and detected in association with SC mutations affecting the whole tissue. #Somatic mutagenesis in SCs as a result is the driving force in the age related decline of SkM function.
Satellite Cells
Satellite cells (SCs) are a heterogeneous population of stem and progenitor cells. These cells play an important role in the growth and development of myofiber. The enlargement, regeneration, and remodeling in skeletal muscle (SkM) is the pivotal role of satellite cells. Satellite cells are dormant until they become activated through exercise or SkM injury. Upon injury skeletal muscle have a remarkable ability to recover from injury. Skeletal muscle goes through a sophisticated degeneration and regenerative process that takes place at the tissue, cellular, and molecular levels. This regenerative process relies upon the dynamic interplay between satellite cells and their environment (stem cell niche). SCs multiply further when committed to myogenic differentiation. As SCs proliferate further they begin to combine with existing SkM fibers and supply new nuclei to the growing and regenerating fibers. The declining of numbers of proliferative potential of SCs is one sign of aging in human SkMs.
A flawed SC compartment is foreseen as a major contributor for age-related deficiencies such as, skeletal muscle tissue having restricted mobility and voluntary functions. The results of such defects include a reduced capacity to respond to hypertrophic stimuli such as exercise and impaired recovery from muscle disuse and injury and the disruption of muscle tissue homeostasis. Moreover, the SCs of nonactive adult animals have been shown to contribute to differentiated fibers in non-injured muscles. Less important is the basal turnover of nuclei in adult fibers in the protection from sarcopenia. This hypothesis was tested and showed that lifelong reduction of satellite cells neither accelerated nor exacerbated sarcopenia and that satellite cells did not contribute to the maintenance of muscle size or fiber type composition during aging, but that their loss may contribute to age-related muscle fibrosis. The progressive loss of SkM mass and function known as sarcopenia affects up to 29% of the population aged 85 years. The accumulation of sarcopenia causes a highly disabling condition. It is essential, nonetheless, that the characterization of SCs in human pathology be further explored. SCs are a key factor in limiting the occurrence of fibrosis in the SkM of mice affected by sarcopenia.
The progressive loss of SkM mass and function known as sarcopenia affects up to 29% of the population aged 85 years. The accumulation of sarcopenia causes a highly disabling condition. It is essential, nonetheless, that the characterization of SCs in human pathology be further explored. Scs are key in limiting the occurrence of fibrosis in the SkM of mice affected by sarcopenia. Genome integrity is essential for the function of stem-cells. But there still must be some stability of the genome. Genetic mutations in the soma has diverse physiological roles and pathological consequences, such as the decline of stem-cell functions. Starting from the first division of the embryo, modifications in the genome extend from single-base changes (single-nucleotide variants (SNVs)) to insertions or deletions of a few bases (indels) to chromosomal rearrangements and occur during the whole life. Somatic variants are not propagated to the whole individual but to a subpopulation of cells in the body, which is strikingly different from germline variants. Adult human tissues become a mosaic of genetically different cells as a result. Furthermore, as a result of the buildup of errors taking place either during cell-division or because of environmental induced DNA damage, somatic mutation burden increases, causing age-related disease. Currently, somatic mutation burden in human SCs or SkM is unknown.
The purpose of the investigation of genetic alterations that occur with aging in the genome of human adult SCs is to use the results to clearly explain mutational processes and SC replication rate occurring in vivo in adult human muscles. The prediction of global consequences on muscle aging and sarcopenia was done by evaluating the functional effects of somatic mutations on SC proliferation and differentiation.
Results
- An accumulation of 13 mutations per genome per year that results in a 2–3-fold higher mutation load in active genes and promoters in aged SCs.
- High mutation burden correlates with defective SC function. • The accumulation of somatic mutations as an intrinsic factor contributing to impaired muscle function with aging.
- The accumulation of somatic mutations as an intrinsic factor contributing to impaired muscle function with aging.
Resources:
“Somatic mutagenesis in satellite cells associates with human skeletal muscle aging.”
Nature Communications volume 9, Article number: 800(2018) Full Abstract Study
“Satellite Cells and the Muscle Stem Cell Niche.”
Physiological Reviews Volume 93, No.1 (2013) Physiological Reviews
“Tissue-specific mutation accumulation in human adult stem cells during life.”
Nature International Journal of Science volume 538, pages 260–264 (13 October 2016) Abstract Study
“When stem cells grow old: phenotypes and mechanisms of stem cell aging”
Development for advances in developmental biology and stem cells Development 2016 143: 314 Abstract Study “Clock-like mutational processes in human somatic cells.”
Nature Genetics volume 47, pages 1402–1407 (2015) Abstract Study


Bioquark Inc. and Lakmus LLC Announce Research Collaboration to Study Novel Biopharmaceuticals for Healthy Longevity Enhancement
Philadelphia, PA, USA / Moscow, Russia — Bioquark, Inc., (www.bioquark.com) a life sciences company focused on the development of novel bio-products for regeneration, disease reversion, and healthy aging, and Moscow based, Lakmus LLC, a diversified investment company with business interests in pharmacies, restaurants, and real estate, announced a multi-disciplinary research collaboration with the FSBI Zakusov Institute of Pharmacology, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (http://www.academpharm.ru/), and the Pavlov Institute of Physiology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (http://www.infran.ru/), to jointly study the pharmacotherapeutic longevity enhancement properties of its combinatorial regenerative biologic candidates.
“We are very excited about this continued collaboration with Lakmus,” said Ira S. Pastor, CEO, Bioquark Inc. “The disciplined development of our combinatorial biologic candidates (Bioquantines) for healthy longevity enhancement, represents another important step in our continued evolution as a company focused on a broad range of therapeutic products and services in the regenerative healthcare space.”
Throughout the 20th century, natural products formed the basis for a majority of all pharmaceuticals, biologics, and consumer healthcare products used by patients around the globe, generating trillions of dollars of wealth. However, many scientists believe we have only touched the surface with what the natural world, and its range of organisms, which from a health and wellness perspective are much further advanced than human beings, has to teach us.
The integration of a complex set of newer research disciplines, including interkingdom signaling, semiochemical communication, and evolutionary biology, as well as significant recent activity in the areas of the microbiome, are highlighting a myriad of new ways that non-human bio-products can affect the human genome for positive transitions in health and wellness dynamics.
“Bioquark has spent several years studying the natural ability of many species to turn back biological time in order to maintain health, fitness, and survival, developing a broad understanding of the combinatorial biochemical approaches they use to control nested hierarchies of disease (i.e. gene, cell, tissue, organism, environment),” said Dr. Sergei Paylian, Founder, CSO, and President, Bioquark Inc. “This research initiative is one more step in the path in allowing humans to recapture these capabilities to effectively counter our unfortunate progression into aging, disease and degeneration.”
About Bioquark, Inc.
Bioquark Inc. is focused on the development of natural biologic based products, services, and technologies, with the goal of curing a wide range of diseases, as well as effecting complex regeneration. Bioquark is developing both biological pharmaceutical candidates, as well as products for the global consumer health and wellness market segments.
Want to Get 70 Billion Copies of Your Book In Print? Print It In DNA
I have been meaning to read a book coming out soon called Regenesis: How Synthetic Biology Will Reinvent Nature and Ourselves. It’s written by Harvard biologist George Church and science writer Ed Regis. Church is doing stunning work on a number of fronts, from creating synthetic microbes to sequencing human genomes, so I definitely am interested in what he has to say. I don’t know how many other people will be, so I have no idea how well the book will do. But in a tour de force of biochemical publishing, he has created 70 billion copies. Instead of paper and ink, or pdf’s and pixels, he’s used DNA.
Much as pdf’s are built on a digital system of 1s and 0s, DNA is a string of nucleotides, which can be one of four different types. Church and his colleagues turned his whole book–including illustrations–into a 5.27 MB file–which they then translated into a sequence of DNA. They stored the DNA on a chip and then sequenced it to read the text. The book is broken up into little chunks of DNA, each of which has a portion of the book itself as well as an address to indicate where it should go. They recovered the book with only 10 wrong bits out of 5.27 million. Using standard DNA-copying methods, they duplicated the DNA into 70 billion copies.
Scientists have stored little pieces of information in DNA before, but Church’s book is about 1,000 times bigger. I doubt anyone would buy a DNA edition of Regenesis on Amazon, since they’d need some expensive equipment and a lot of time to translate it into a format our brains can comprehend. But the costs are crashing, and DNA is a far more stable medium than that hard drive on your desk that you’re waiting to die. In fact, Regenesis could endure for centuries in its genetic form. Perhaps librarians of the future will need to get a degree in biology…