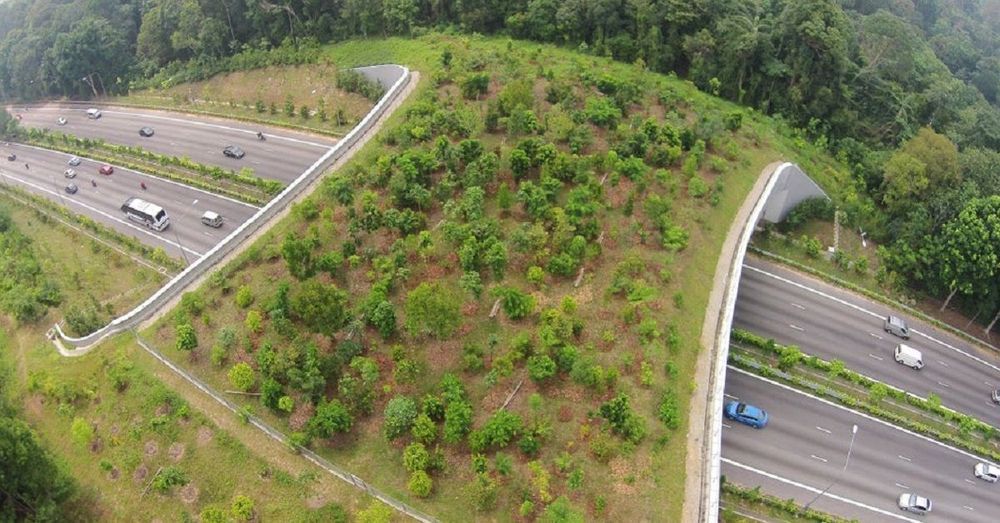
Scientists observed heavy metals escaping the atmosphere of football-shaped exoplanet.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Government to Enhance Six Central Forensic Labs to Help Probe Heinous Crimes
New Delhi: Six central forensic laboratories in the country will soon be upgraded for carrying out efficient and scientific investigation in serious and heinous crimes, officials said on Sunday.
The central forensic science laboratories (CFSLs) which will be upgraded with capacity enhancement are located at Chandigarh, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Bhopal, Pune and Guwahati.
“The Ministry of Home Affairs has decided to enhance the capacity of six CFSLs under the Directorate of Forensic Science Services in the area of forensic psychology involving external experts,” an official said.
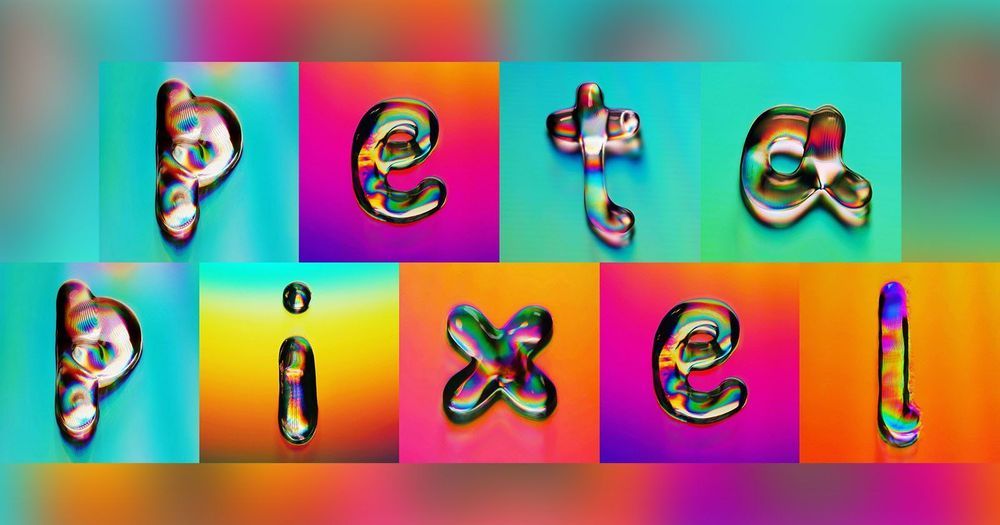
This Colorful Typography Was Made by Shooting Photos of Water on CDs
For his project Marmalade Type, Russian visual artist Rus Khasanov created colorful typography using his camera. The colors seen are due to interference patterns — not a single drop of paint was used in the project.
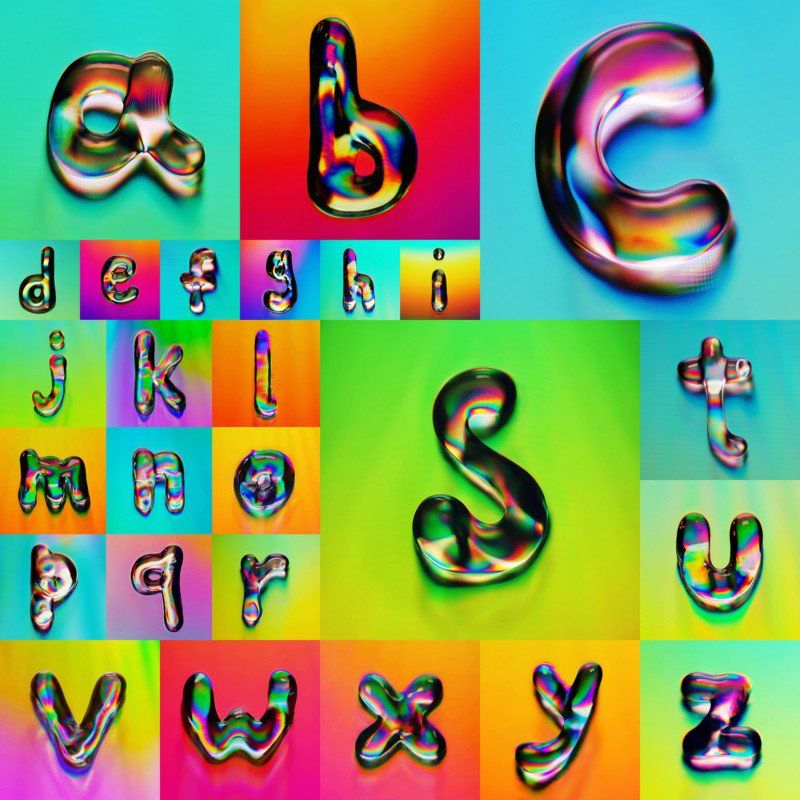
For a previous project titled Disctortion, Khasanov took CDs and DVDs and destroyed them in various ways (e.g. freezing, tearing, coating, bending). His goal was to see the way the colors and textures react to his alterations.
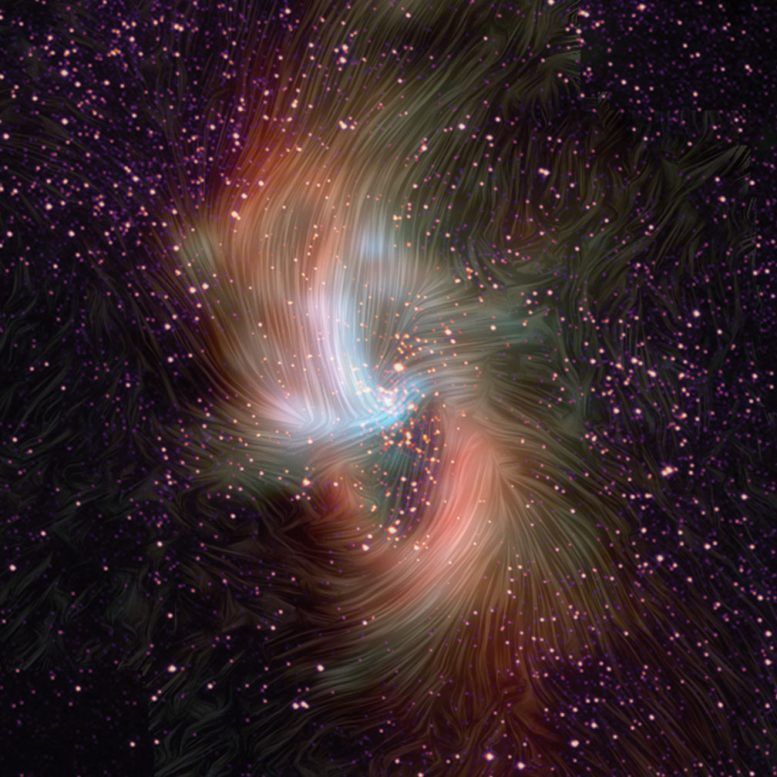


SOFIA Reveals What May Be Keeping Milky Way’s Black Hole Quiet
Supermassive black holes exist at the center of most galaxies, and our Milky Way is no exception. But many other galaxies have highly active black holes, meaning a lot of material is falling into them, emitting high-energy radiation in this “feeding” process. The Milky Way’s central black hole, on the other hand, is relatively quiet. New observations from NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, SOFIA, are helping scientists understand the differences between active and quiet black holes.


