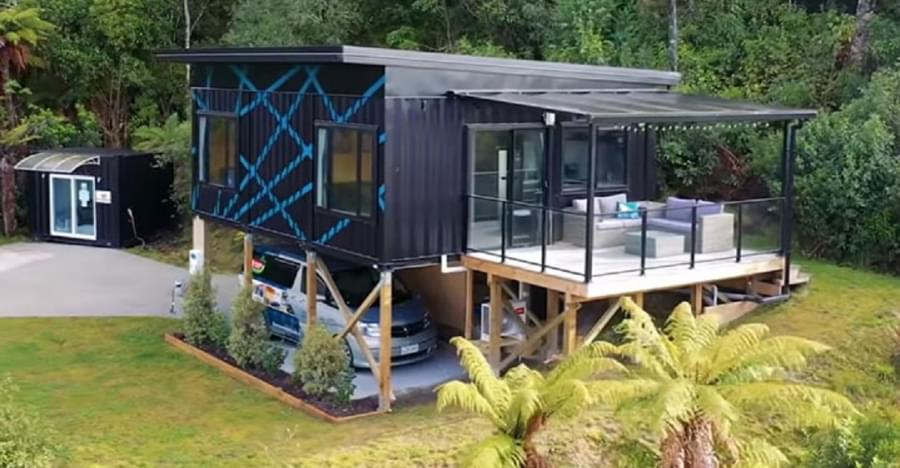
This magnificent shipping container container home near Lake Taupo, New Zealand, is worth checking out. This compact shipping container house was designed and built by Brenda Kelly of IQ Container Homes, and it has been raised to provide views of Lake Taupo. Three 20-foot shipping containers were used to form the tiny house’s design. Inside, there’s an open living area and kitchen that take use of the views, as well as a sliding door that leads to a deck with stairs leading down to the yard. This amazing concept, which includes covered parking beneath the container home design and a covered terrace with amazing views of the surrounding area, is guaranteed to inspire you.
The living area and kitchen are open-plan in the shipping container home. A plywood accent wall, which matches the living room wall and serves as a backdrop for the bed, can be found. A closet with sliding mirrored doors is on the opposite wall, and the bed lifts to show even additional storage. A plywood accent wall might be found in a tiny bedroom. When visitors come to visit, the shipping container home contains a home office with a wide desk that can be converted into a bed.
The IQ Container houses are made of non-corrosive Corten steel, are built to last, and are 100% recyclable when they are no longer needed. They can work with you on a custom design that matches your needs, or they can use eco-principles like passive solar and cross ventilation in their basic practical designs. Off-site building reduces waste and disruption on the job site.