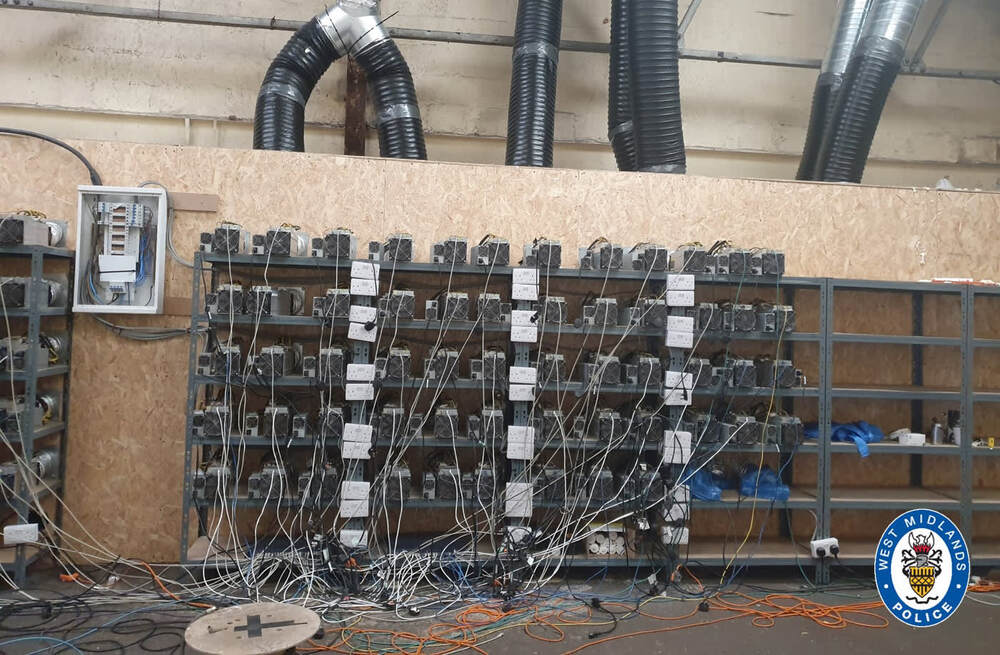
LONDON — An illegal bitcoin mine has been found by police in the U.K. who were looking for a cannabis farm.
The mine — located in an industrial unit on the outskirts of the English city of Birmingham — was stealing thousands of pounds worth of electricity from the mains supply, West Midlands Police said Thursday.
Police searched the unit in Sandwell on May 18 on the back of intelligence that led them to believe it was being used as a cannabis farm.