Oops sry wrong group…😁✨🕊.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Quantum Computer: We’re Planning to Create One That Acts Like a Brain
The human brain has amazing capabilities making it in many ways more powerful than the world’s most advanced computers. So it’s not surprising that engineers have long been trying to copy it. Today, artificial neural networks inspired by the structure of the brain are used to tackle some of the most difficult problems in artificial intelligence (AI). But this approach typically involves building software so information is processed in a similar way to the brain, rather than creating hardware that mimics neurons.
My colleagues and I instead hope to build the first dedicated neural network computer, using the latest “quantum” technology rather than AI software. By combining these two branches of computing, we hope to produce a breakthrough which leads to AI that operates at unprecedented speed, automatically making very complex decisions in a very short time.
We need much more advanced AI if we want it to help us create things like truly autonomous self-driving cars and systems for accurately managing the traffic flow of an entire city in real-time. Many attempts to build this kind of software involve writing code that mimics the way neurons in the human brain work and combining many of these artificial neurons into a network. Each neuron mimics a decision-making process by taking a number of input signals and processing them to give an output corresponding to either “yes” or “no”.
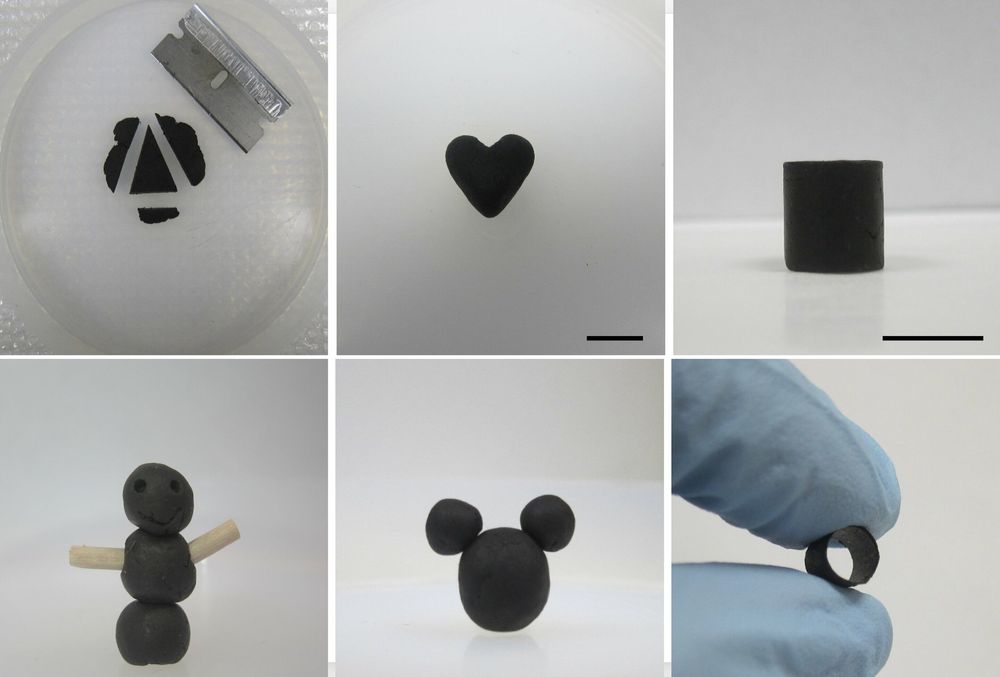
Self-assembling nanomaterial offers pathway to more efficient, affordable harnessing of solar power
Solar rays are a plentiful, clean source of energy that is becoming increasingly important as the world works to shift away from power sources that contribute to global warming. But current methods of harvesting solar charges are expensive and inefficient—with a theoretical efficiency limit of 33 percent. New nanomaterials developed by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) at The Graduate Center of The City University of New York (CUNY) could provide a pathway to more efficient and potentially affordable harvesting of solar energy.

AI Finds Traces of a Lost Species in Human DNA
Buried deep within the DNA of Asian individuals is a genetic clue pointing to the existence of an unknown human ancestor. Remarkably, it wasn’t a human who reached this startling conjecture, but rather an artificially intelligent algorithm. Welcome to archaeology in the 21st century.
New research published last week in Nature Communications suggests a yet-to-be discovered hominid interbred with modern humans tens of thousands of years ago. This mystery species eventually went extinct, but an AI developed by researchers from the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE) and several other European institutions found traces of its existence in the DNA of present-day people with Asian ancestry. A press release issued by the Centre for Genomic Regulation said it’s the first time deep learning has been used to explain human history, “paving the way for this technology to be applied in other questions in biology, genomics and evolution.”



Analysis: “The Era of Deep Learning Is Coming to an End”
Many of the new developments in artificial intelligence that we hear about nowadays are actually just applications of machine learning techniques that have been hammered out for years.
And as the research community’s attention shifts from deep learning, it remains unclear what will take its place, according to MIT Tech. In the past, older types of artificial intelligence that didn’t really take off when they were first developed later resurfaced and taken off with new life. For instance, scientists first developed machine learning decades ago, but it only became commonplace about a decade ago.
MIT Tech didn’t predict what will come next. It may be that some form of existing technology will finally hits its stride, but it’s also possible that an AI engineer will develop some brand-new type of AI that’ll shape the future.