This is the most practical advice we’ve heard for changing the world.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
New role for brain’s support cells in controlling circadian rhythms
This new study, led by the MRC’s Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) in Cambridge, used microscopic imaging to observe the detailed internal molecular clock timing of the astrocytes and neurons of the SCN. Surprisingly, this showed that although both types of cell have their own circadian clocks, they are differently regulated and were seen to be active at different times of the day. This delicate interplay was found to be critical in keeping the entire SCN clockwork ticking.
A new study has found that astrocytes, previously thought of as just supporting neurons in regulating circadian rhythms, can actually lead the tempo of the body’s internal clock and have been shown for the first time to be able to control patterns of daily behavior in mammals.
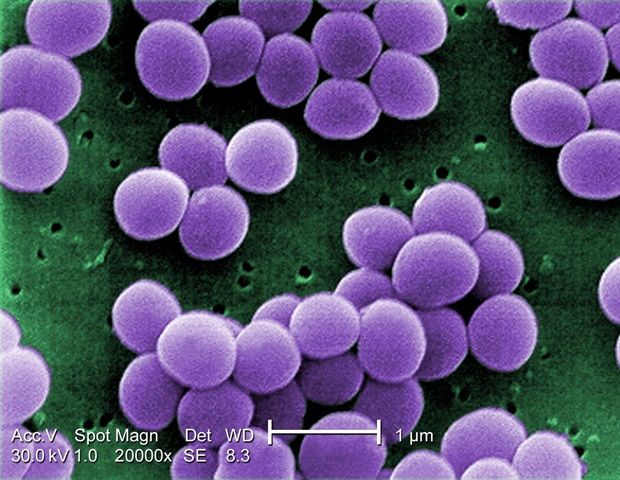
Staphylococcus aureus: Study describes development of resistance to antibiotic for the first time
The Staphylococcus aureus bacterium is one of the commonest pathogens and can even cause sepsis. The new antibiotic dalbavancin is very effective against many bacterial pathogens. However, resistance to the antibiotic was seen to develop during the long-term treatment of a patient with an infection caused by an implanted cardiac device. A team of researchers led by infectiologists from the Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine within the Department of Medicine I at MedUni Vienna, Manuel Kussmann and Heimo Lagler, have now described the phenotypical and genotypical mechanism of this development of resistance for the first time. The study was published in leading journal “Emerging Microbes & Infections”.
Staphylococci are bacteria and are part of the normal flora on the skin of humans and animals. Approximately 20% of the Austrian population permanently carry the germ, which is often located in the nasal cavity. There are harmless variants, which only cause mild symptoms, if any at all. In serious cases, the pathogen can find its way into the bloodstream and cause endocarditis and sepsis.
A problematic strain is Staphylococcus aureus, which can be acquired outside hospital but also in hospital as a so-called “hospital-acquired infection”. There are multi-resistant forms of it, which do not necessarily cause serious illness in healthy people. However, in weakened hospital patients or where the natural skin barrier is damaged, infection can result in complications. Nowadays dalbavancin, a latest generation antibiotic, is one of the drugs successfully used to treat multi-resistant bacteria. One of the advantages of this drug is its very long half-life of approximately nine days, so that intravenous treatment can be given on an outpatient basis. However, clinical experience has shown that, sooner or later, resistance develops to any therapeutic use of new antibiotics, so it was just a matter of time with this one.
Create beautiful network visualizations of your thoughts, ideas, and writing
Abstract constellations of thought. Visualize your ideas and texts as a network, generate interesting insights along the way.
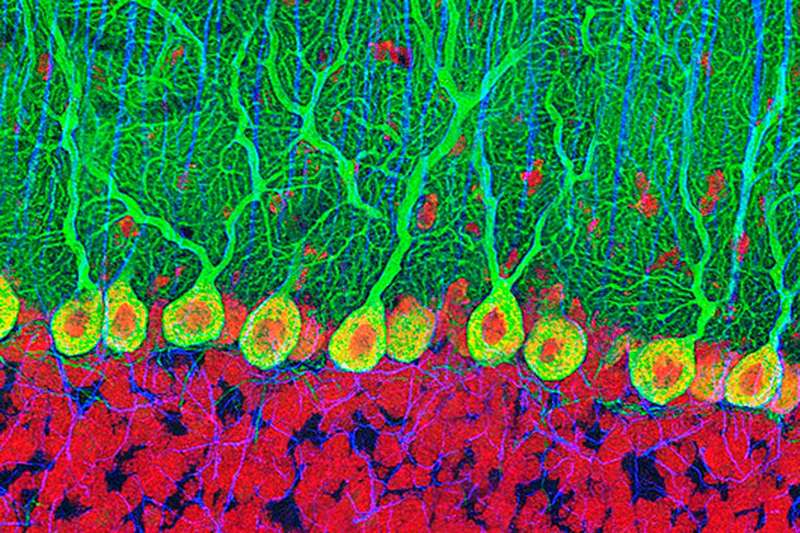
Old people can produce as many new brain cells as teenagers
By Helen Thomson
Old age may have its downsides, but losing the ability to grow new brain cells isn’t one: healthy people in their seventies seem to produce just as many new neurons as teenagers.
The discovery overturns a decades-old theory about how our brains age and could provide clues as to how we can keep our minds sharper for longer.
3D Atomic Quantum Chips and Advance to Eventual Large Scale Quantum Tech
Australia’s New South Wales scientists have adapted single atom technology to build 3D silicon quantum chips – with precise interlayer alignment and highly accurate measurement of spin states. The 3D architecture is considered a major step in the development of a blueprint to build a large-scale quantum computer.
They aligned the different layers in their 3D device with nanometer precision – and showed they could read out qubit states with what’s called ‘single shot’, i.e. within one single measurement, with very high fidelity.
“This 3D device architecture is a significant advancement for atomic qubits in silicon,” says Professor Simmons.