The F.B.I. should follow the example of European law enforcement and help victims of ransomware decrypt their data.
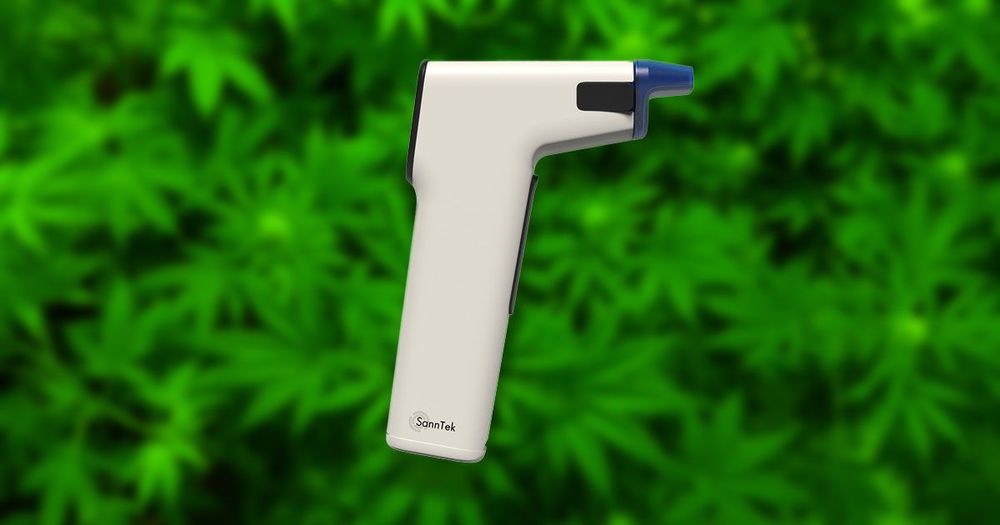




If a police officer suspects you’ve had too much to drink before getting behind the wheel of your car, they can use a breathalyzer to estimate your blood alcohol level on the spot.
But if a cop thinks you’re driving stoned, they currently don’t have any evidence-based way to immediately confirm their suspicions — they typically have to rely on subjective roadside sobriety tests.
Now, though, Canadian startup SannTek Labs says it’s developed a marijuana breathalyzer — and it’s caught the eye of top startup accelerator Y Combinator.
THE INSTITUTE Teenager Ari Firester watched on television last year as members of a youth soccer team were saved from a flooded cave in Chiang Rai Province, Thailand. The two-week-long effort, which left one rescuer dead, inspired Firester to create a technology that might prevent such a tragedy from occurring again.
Firester, 16, a junior at Hunter College High School in New York City, created “Wormbot,” an earthworm-inspired robot capable of maneuvering in narrow spaces. The project was displayed at Intel’s annual International Science and Engineering Fair, held in May in Phoenix. His invention earned him the US $10,000 IEEE Presidents’ Scholarship, which is given at the fair.
Controlled by an Arduino microcontroller and built with off-the-shelf items, the robot makes wormlike movements by using eight retractable claws along its length to grip its surroundings and prevent it from slipping. The modular robot is powered by compressed air. The control and power components are connected to the robot through a thin, plastic air tube. By using inflatable actuators, its body can be lengthened, shortened, or bent.
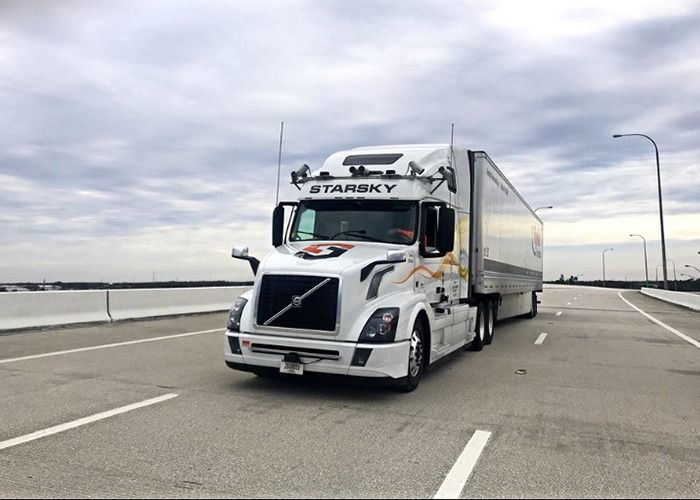

This week, two companies say that their technologies were able to work together successfully broker and transport a load without any human help.
On Thursday, July 8, Starsky Robotics and Loadsmart issued an announcement about the trucking industry’s first autonomous dispatch and delivery.
The companies say that this “marks the first time an autonomous company and a digital broker have collaborated to price, book and load a shipment without any human involvement.”
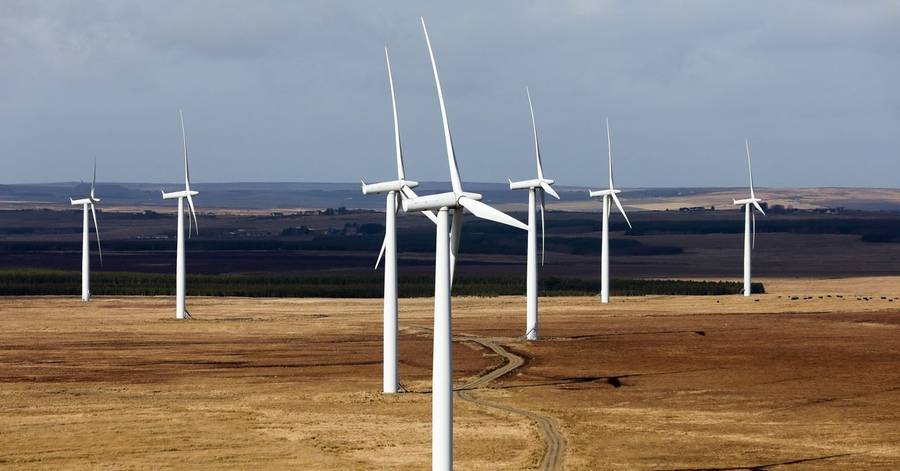

A global wave of investment in high-capacity batteries is poised to transform the market for renewable energy in coming years, making it more practical and affordable to store wind and solar power and deploy it when needed.
Government-owned utilities and companies are buying batteries that can be larger than shipping containers. Some like…
To Read the Full Story.

When Fortnite reached stratospheric popularity early last year, there were undoubtedly an awful lot of VCs on the sidelines looking enviously at the massive platform and wondering what opportunities could be gleaned from its rapid rise.
Epic Games went on to raise later that year at a nearly $15 billion valuation so some of those investors decided to invest directly in the Fortnite creator’s continued ascent, but others have been looking to get in on the ground floor of new operations that are aiming to rethink the line between video games and social networks.
Today, Andreessen Horowitz announced that it’s leading the $16.5 million Series A of a stealthy gaming startup called Singularity 6. The startup’s ex-Riot Games co-founders claim their venture is less focused on building a button-mashing competitive shooter than it is a “virtual society” where users can develop relationships with in-game characters powered by “complex AI”.
New research, published today in Nature, reveals how increasing brain stiffness as we age causes brain stem cell dysfunction, and demonstrates new ways to reverse older stem cells to a younger, healthier state.
The results have far reaching implications for how we understand the ageing process, and how we might develop much-needed treatments for age-related brain diseases.
As our bodies age, muscles and joints can become stiff, making everyday movements more difficult. This study shows the same is true in our brains, and that age-related brain stiffening has a significant impact on the function of brain stem cells.
The invention is an improved piston engine, either two stroke or four stroke. In one, two stroke, one cylinder embodiment, the improvement comprises two springs connecting between the piston and the base of the piston. These springs are relatively relaxed when the crank is at top dead center. Then during the power/intake stroke, some of the fuel’s energy is delivered to the crankshaft and some is used to compress the springs. The stored energy in the springs is delivered to the crankshaft during the exhaust/compression stroke while the springs return to their relatively relaxed condition. As a result, energy is delivered to the crankshaft during both strokes of the cycle, and the engine runs smooth.
In one, four stroke, two cylinder embodiment, each cylinder has springs as described above, the cranks of each cylinder are aligned, and the cam sets one cylinder in the power stroke while the other is in the intake stroke. As a result, the engine runs smooth because energy is delivered to the crankshaft during all four strokes of the cycle, during two of the strokes by the burning fuel and during the other two by the release of energy in the springs. In both embodiments, a heavy crankshaft is not needed because of the more uniform power delivery.
Ok, I saw this on Gizmodo (unexpectedly), and despite the fact that I’ve been blogging for five years now I’ve never actually seen something this amazing – the famous magnetic motor spinning by itself indefinitely, like this video shows.
Now, I don’t think there’s any trick involved, there couldn’t be, could it? Just watch the whole movie. If you see anything suspicious, let me know.
Magnetic motors have always fascinated me. I’ve even endorsed schematics of magnetic motors hoping that someday, someone will find the proper recipe and post it on youtube without being called names and accused of scamming people.