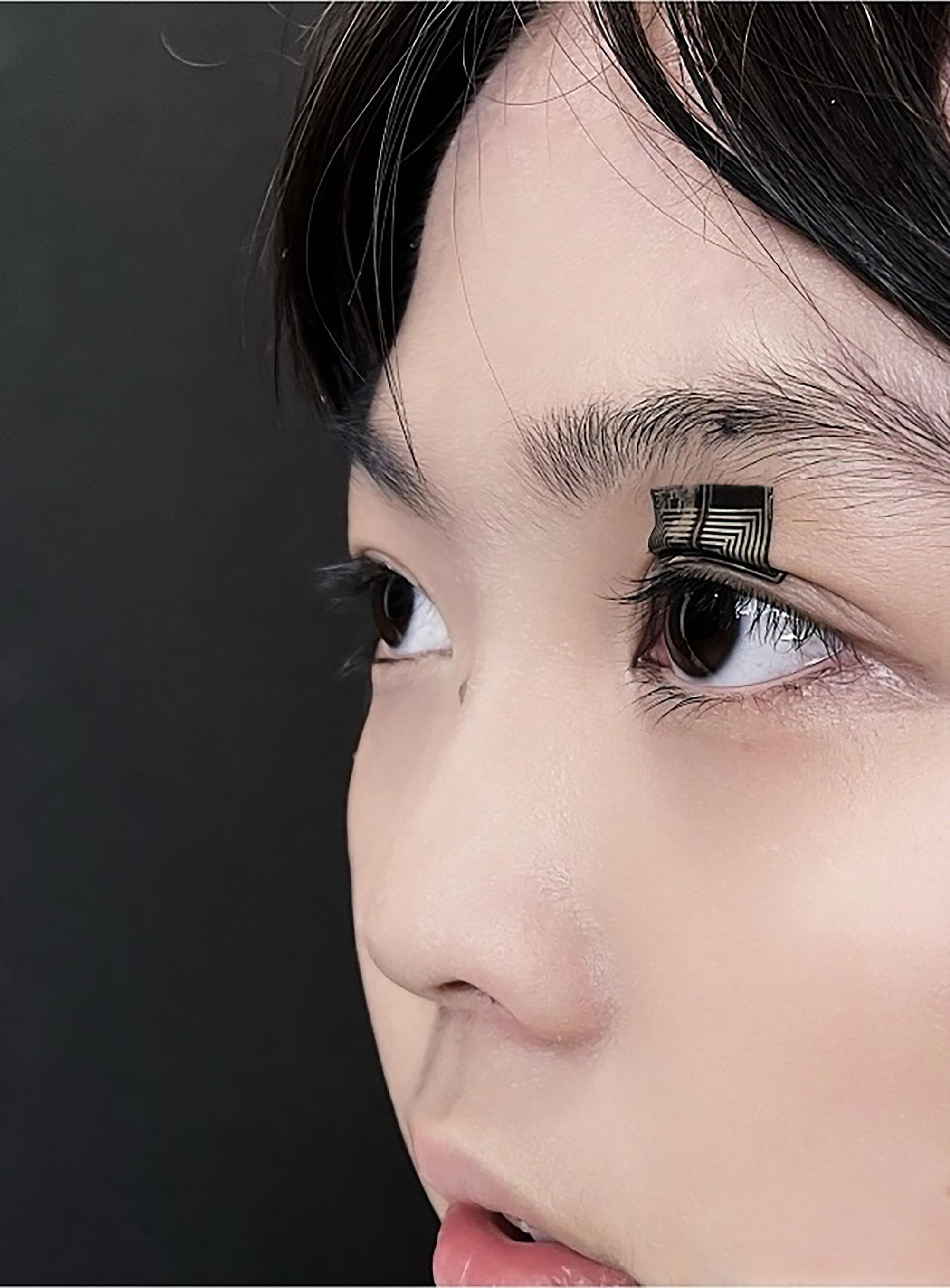
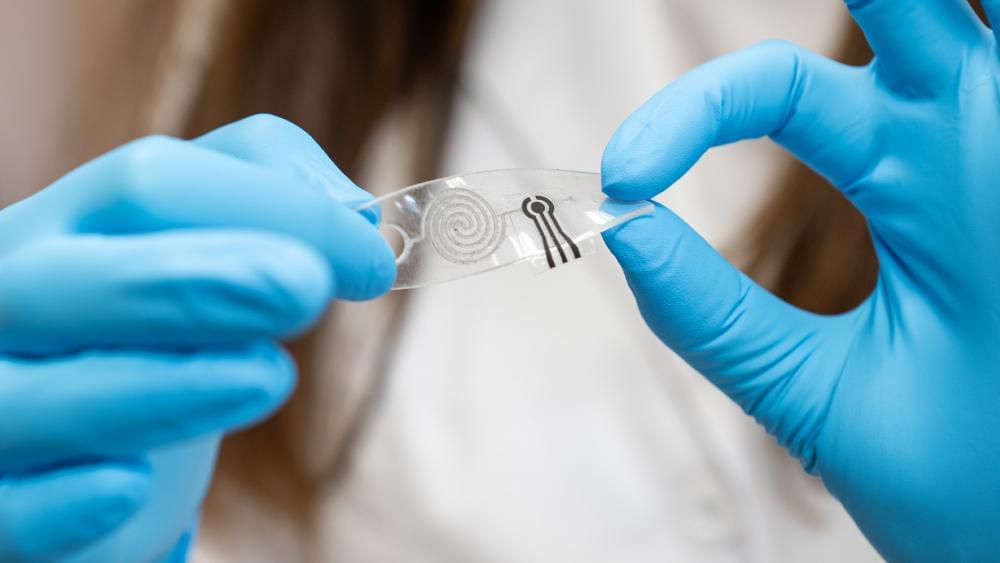
Over the past few decades, electronics engineers have developed increasingly sophisticated sensors that can reliably measure a wide range of physiological signals, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate and oxygen saturation. These sensors were used to create both biomedical and consumer-facing wearable devices, advancing research and the real-time monitoring of health-related metrics, such as sleep quality and physiological stress.
Fatigue, a mental state marked by a decline in performance due to stress, lack of sleep, excessive activity or other factors, has proved to be more difficult to reliably quantify. Most existing methods for measuring fatigue rely on surveys that ask people to report how tired they feel, a method to record the brain’s electrical activity known as electroencephalography (EEG) or camera-based systems.
Most of these approaches are unreliable or only applicable in laboratory settings, as they rely on subjective evaluations, bulky equipment or controlled environments. These limitations prevent their large-scale deployment in everyday settings.