Stroke is the leading cause of serious long-term disability in the US with approximately 17 million individuals experiencing it each year. About 8 out of 10 stroke survivors suffer from “hemiparesis”, a paralysis that typically impacts the limbs and facial muscles on one side of their bodies, and often causes severe difficulties walking, a loss of balance with an increased risk of falling, as well as muscle fatigue that quickly sets in during exertions. Oftentimes, these impairments also make it impossible for them to perform basic everyday activities.
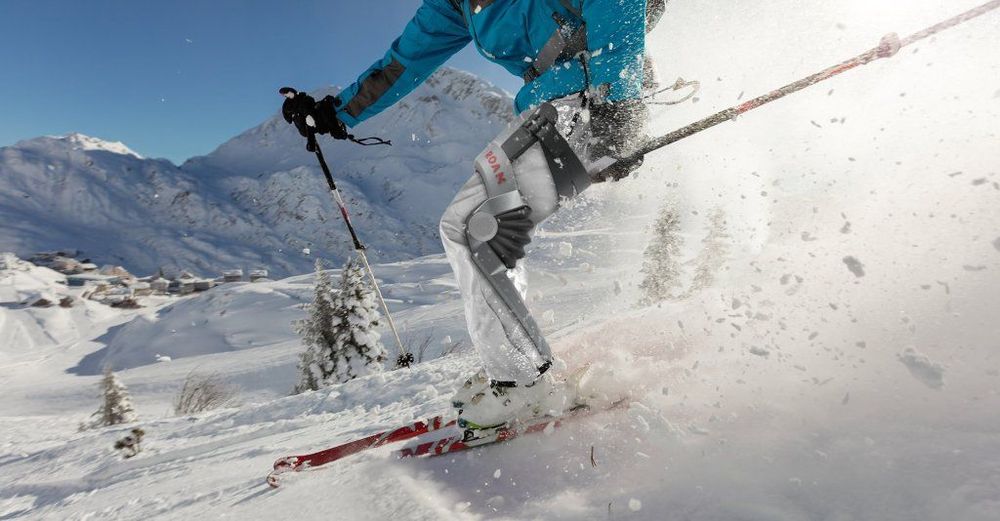
To allow stroke patients to recover, many rehabilitation centers have looked to robotic exoskeletons. But although there are now a range of exciting devices that are enabling people to walk again who initially were utterly unable to do so, there remains significant active research trying to understand how to best apply wearable robotics for rehabilitation after stroke. Despite the promise, recent clinical practice guidelines now even recommend against the use of robotic therapies when the goal is to improve walking speed or distance.
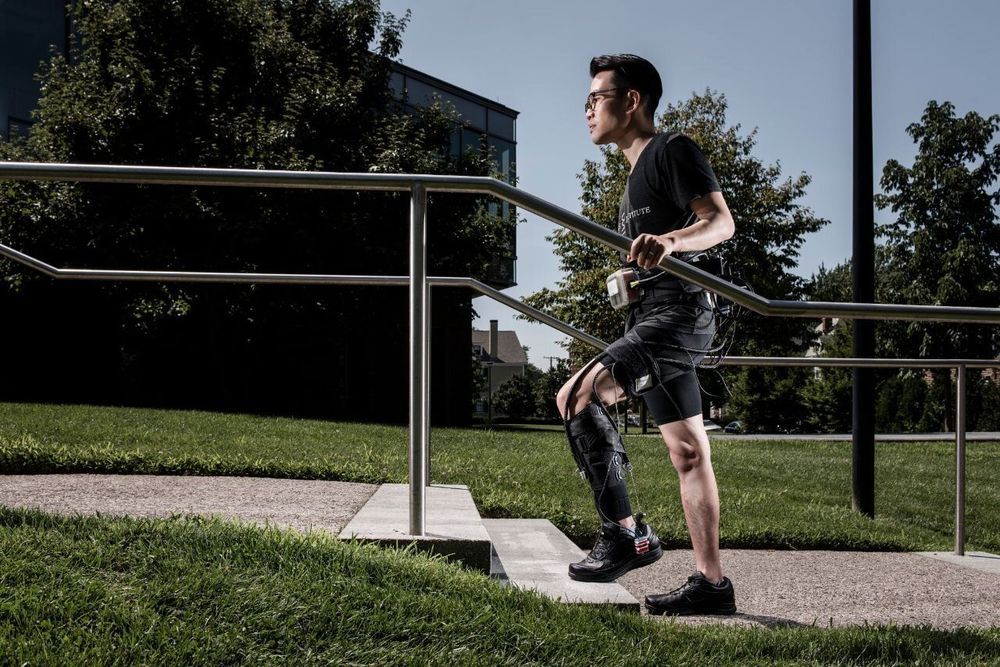
In 2017, a multidisciplinary team of mechanical and electrical engineers, apparel designers, and neurorehabilitation experts at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), and Boston University’s (BU) College of Health & Rehabilitation Sciences: Sargent College showed that an ankle-assisting soft robotic exosuit, tethered to an external battery and motor, was able to significantly improve biomechanical gait functions in stroke patients when worn while walking on a treadmill. The cross-institutional and cross-disciplinary team effort was led by Wyss faculty members Conor Walsh, Ph.D. and Lou Awad, P.T., D.P.T., Ph.D, together with Terry Ellis, Ph.D., P.T., N.C.S. from BU.