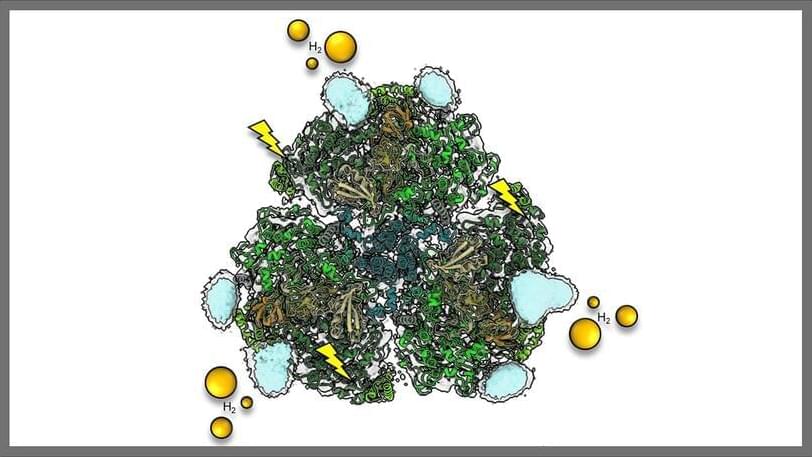
Photosynthesis is one of the most efficient natural processes for converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy vital for life on earth. Proteins called photosystems are critical to this process and are responsible for the conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
Combining one kind of these proteins, called photosystem I (PSI), with platinum nanoparticles, microscopic particles that can perform a chemical reaction that produces hydrogen — a valuable clean energy source — creates a biohybrid catalyst. That is, the light absorbed by PSI drives hydrogen production by the platinum nanoparticle.
In a recent breakthrough, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Yale University have determined the structure of the PSI biohybrid solar fuel catalyst. Building on more than 13 years of research pioneered at Argonne, the team reports the first high-resolution view of a biohybrid structure, using an electron microscopy method called cryo-EM. With structural information in hand, this advancement opens the door for researchers to develop biohybrid solar fuel systems with improved performance, which would provide a sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources.
Argonne and Yale researchers shed light on the structure of a photosynthetic hybrid for the first time, enabling advancements in clean energy production.