Typically, when a neutron decays, it splits into three particles: a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. However, there’s another possible decay path involving just two particles: a hydrogen atom and a neutrino.


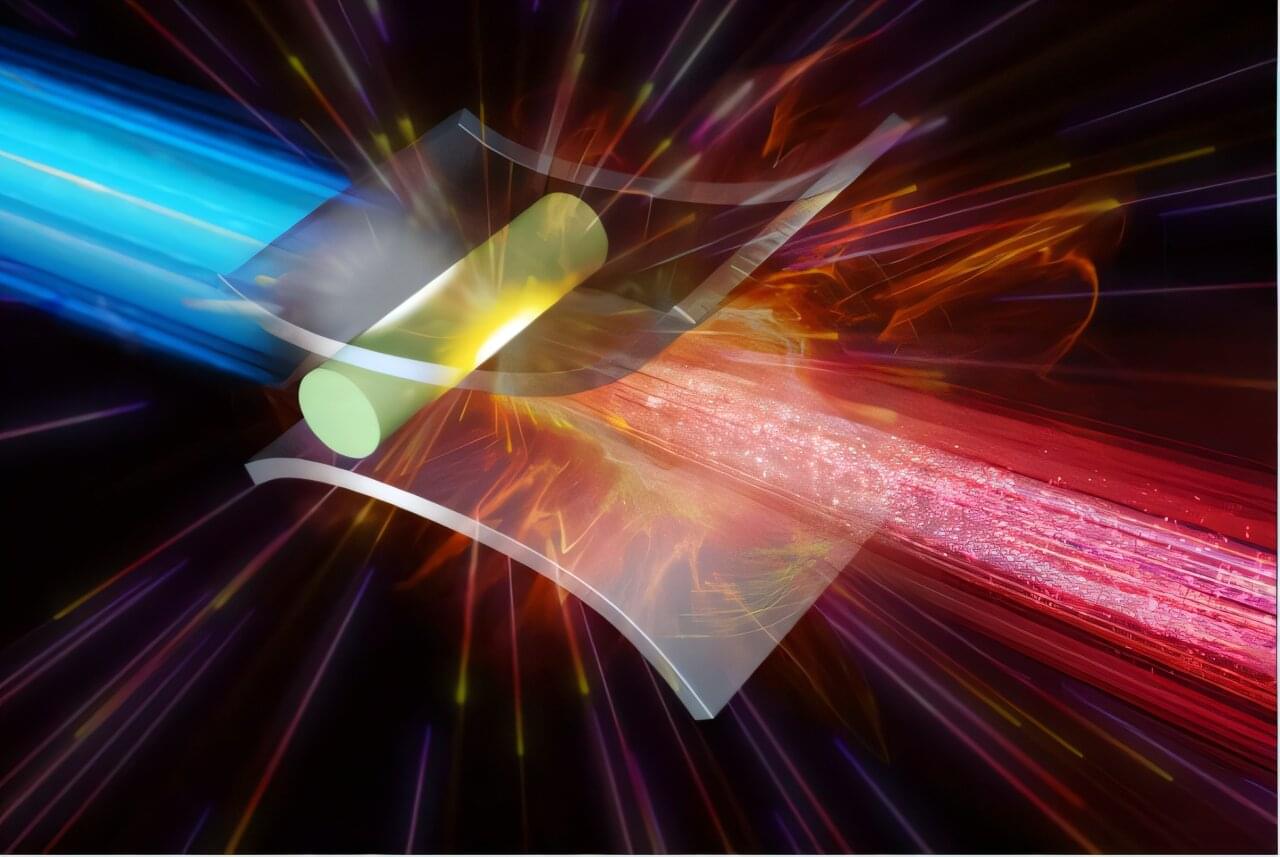
Proton beams with giga-electron-volt (GeV) energies—once thought to be achievable only with massive particle accelerators—may soon be generated in compact setups thanks to a breakthrough by researchers at The University of Osaka.
A team led by Professor Masakatsu Murakami has developed a novel concept called micronozzle acceleration (MNA). By designing a microtarget with tiny nozzle-like features and irradiating it with ultraintense, ultrashort laser pulses, the team successfully demonstrated—through advanced numerical simulations—the generation of high-quality, GeV-class proton beams: a world-first achievement.
The article, “Generation of giga-electron-volt proton beams by micronozzle acceleration,” was published in Scientific Reports.

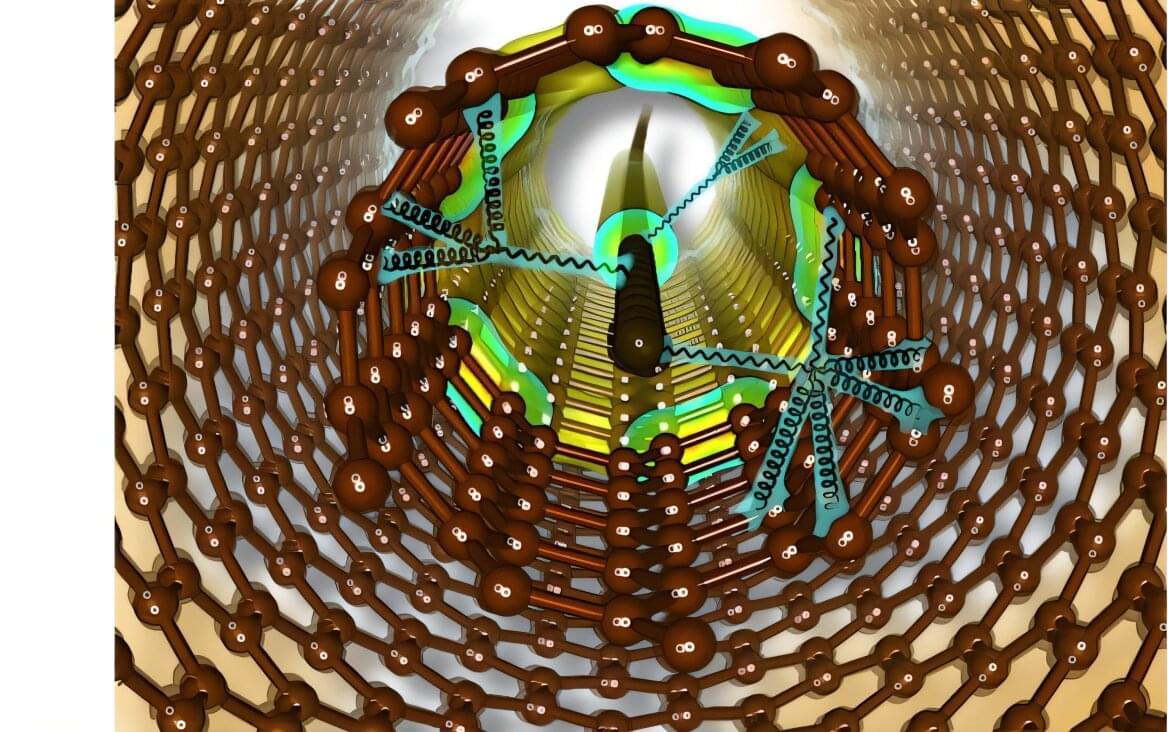
For the design of future materials, it is important to understand how the individual atoms inside a material interact with each other quantum mechanically. Previously inexplicable vibrational states between carbon chains (carbyne) and nanotubes have puzzled materials scientists.
Researchers from Austria, Italy, France, China and Japan led by the University of Vienna have now succeeded in getting to the bottom of this phenomenon with the help of Raman spectroscopy, innovative theoretical models and the use of machine learning. The results, published in Nature Communications, show the universal applicability of carbyne as a sensor due to its sensitivity to external influences.
For the design of future materials, it is important to understand how matter interacts on an atomic scale. These quantum mechanical effects determine all macroscopic properties of matter, such as electrical, magnetic, optical or elastic properties. In experiments, scientists use Raman spectroscopy, in which light interacts with matter, to determine the vibrational eigenstates of the atomic nuclei of the samples.
An AI scanning billions of particle collisions at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider has detected something extraordinary — a mysterious particle decay at 4.8 TeV that doesn’t match any known physics. While scientists aren’t calling it official yet, this anomaly could be our first glimpse of a fifth fundamental force of nature.
🔬 What We Cover:
The real AI discovery behind the viral headlines.
How machine learning found what human scientists missed.
Why this 2.9-sigma anomaly has top physicists watching closely.


Somewhere in our galaxy are engines capable of driving atomic fragments to velocities that come within a whisker of lightspeed.
The explosive deaths of stars seems like a natural place to search for sources of these highly energetic cosmic bullets, yet when it comes to the most powerful particles, researchers have had their doubts.
Numerical simulations by a small international team of physicists may yet save the supernova theory of cosmic ray emissions at the highest of energies, suggesting there is a brief period where a collapsing star could still become the Universe’s most extreme accelerator.

Very soon after the Big Bang, the universe enjoyed a brief phase where quarks and gluons roamed freely, not yet joined up into hadrons such as protons, neutrons and mesons. This state, called a quark-gluon plasma, existed for a brief time until the temperature dropped to about 20 trillion Kelvin, after which this “hadronization” took place.
Now a research group from Italy has presented new calculations of the plasma’s equation of state that show how important the strong force was before the hadrons formed. Their work is published in Physical Review Letters.
The equation of state of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) represents the collective behavior of particles that experience the strong force—a gas of strongly interacting particles at equilibrium, with its numbers and net energy unchanging. It’s analogous to the well-known, simple equation of state of atoms in a gas, PV=nRT, but can’t be so simply summarized.

Organic light emitting diodes, or OLEDs, are a type of photoluminescence device that utilizes organic compounds to produce light. Compared to traditional LEDs, OLEDs have shown to be more efficient, can be built into super-thin and flexible materials, and have higher dynamic range in image quality. To further develop better OLEDs, researchers around the world work to understand the fundamental chemistry and physics behind the technology.
Now, researchers at Kyushu University have developed a new analytical model that details the kinetics of the exciton dynamics in OLED materials. The findings, published in Nature Communications, have the potential to enhance the lifetime of OLED devices, and accelerate the development of more advanced and efficient materials.
Fluorescence devices like OLEDs light up because of excited electrons, or excitons. When you add energy into atoms, their electrons get excited and jump to a higher energy state. When they come back down to their regular energy state, they produce fluorescence.