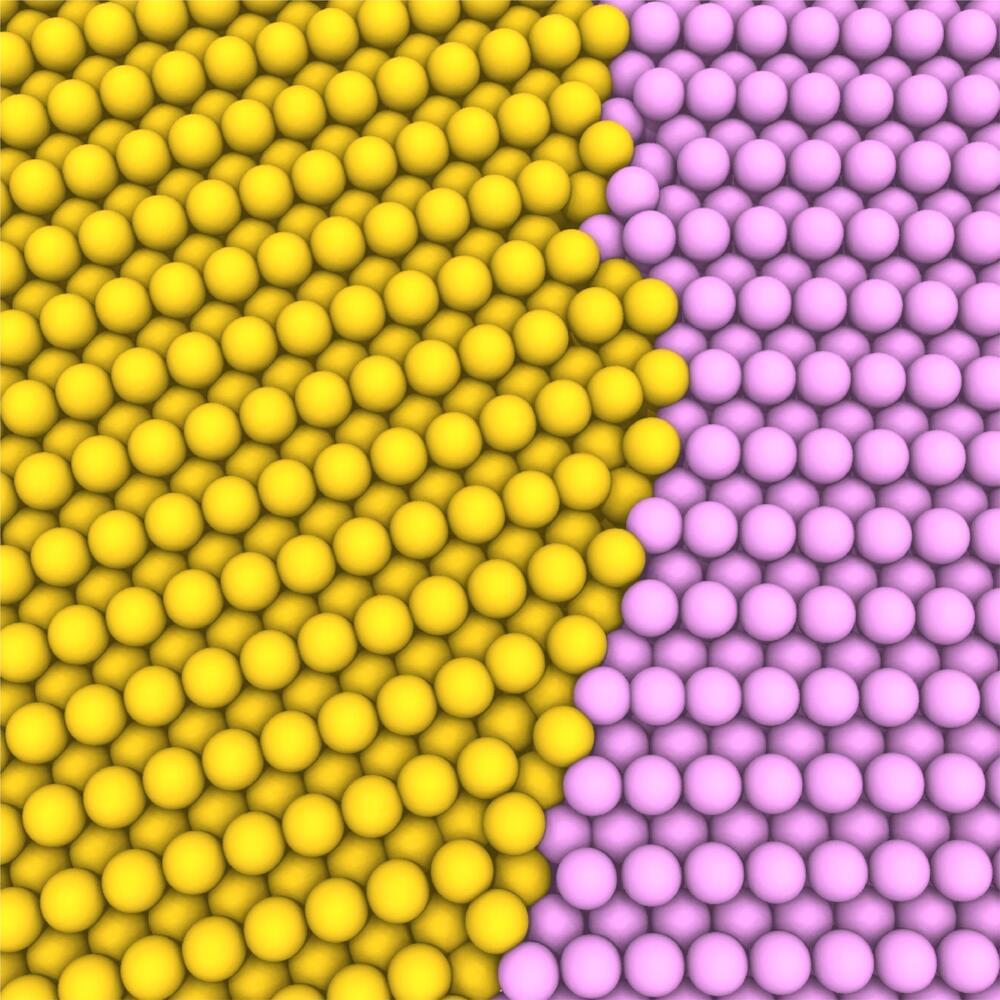
The secret sauce? An improved manufacturing process that eliminates corrosive carbon dioxide gas.
There’s a better way to build solid-state lithium batteries, scientists say. By studying the battery manufacturing process, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Upton, New York-based Brookhaven National Laboratory have eliminated a tiny (but crucial) contamination issue, which could cut down on the complexity in future battery designs.
Solid-state batteries are widely considered to be the next great thing in rechargeable battery design. With an energy capacity at least two times greater than traditional lithium-ion batteries with flammable liquid electrolytes, solid-state batteries are safer, as well as more efficient—a huge pair of selling points for electric consumer vehicles in particular.
So what’s stopping solid-state lithium batteries from fully revolutionizing the industry? There are two issues: conductivity, and instability where the materials join. The first is easy to explain: volatile liquid electrolytes allow electrons to move freely, which is more challenging within a solid material with less particle mobility.