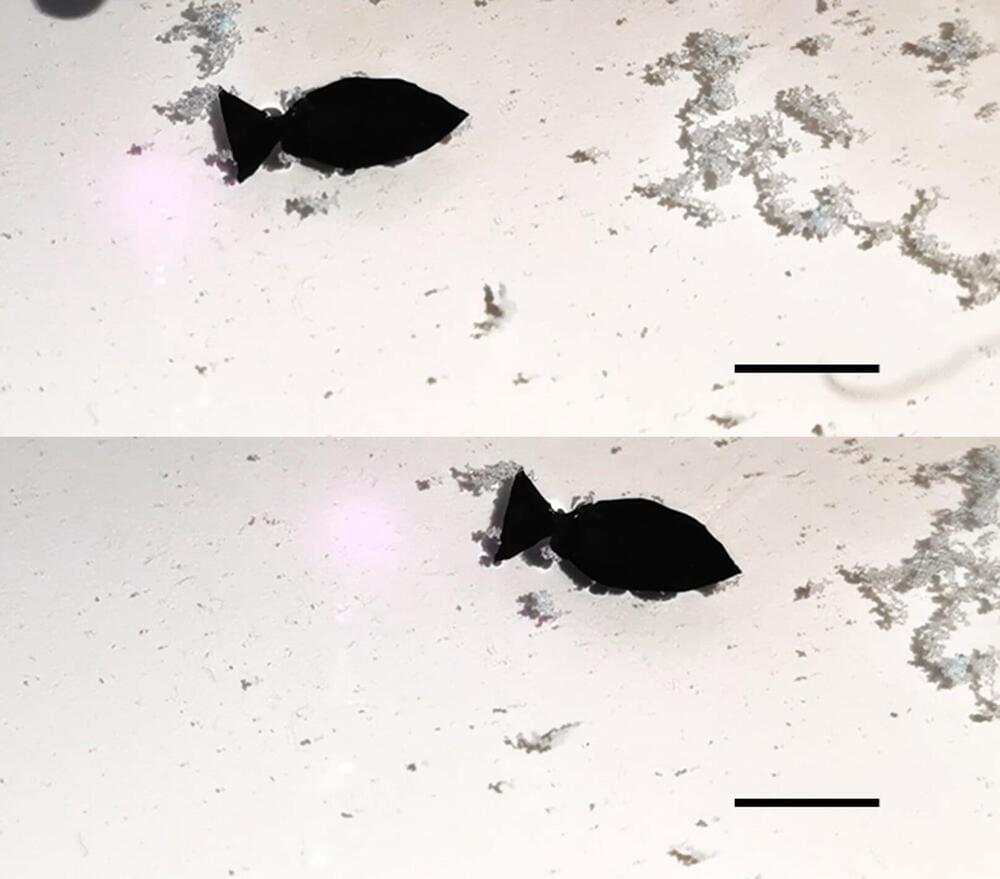
Researchers in the US, Poland and Korea have observed photon avalanching – a chain-reaction-like process in which the absorption of a single photon triggers the emission of many – in tiny crystals just 25–30 nm in diameter. This highly nonlinear phenomenon had previously only been seen in bulk materials, and team leader James Schuck says that replicating it in nanoparticles could lead to “revolutionary new applications” in imaging, sensing and light detection (Nature 589 230).
Photon avalanching involves a process known as upconversion, whereby the energy of the emitted photons is higher than the energy of the photons that triggered the avalanche. Materials based on lanthanides (chemical elements with atomic numbers between 57 and 71) can support this process in part because their internal atomic structure enables them to store energy for long periods of time. Even so, achieving photon avalanching in lanthanide systems is difficult because high concentrations of lanthanide ions are needed to keep the avalanche going, and the relatively large volume of material required has previously restricted applications.
In the latest work, Schuck and colleagues at Columbia University, together with collaborators at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the Polish Academy of Sciences and Sungkyunkwan University, observed photon avalanching in lanthanide nanocrystals after exciting them with a laser at near-infrared wavelengths of either 1,064 or 1450 nm. The crystals are based on sodium yttrium fluoride in which 8% of the yttrium ions have been replaced with thulium. This doping fraction is much higher than the 0.2–1% typically found in previous work on photon avalanching.