Year 2021 viable fusion reactor in a z pinch device which is compact enough to fit in a van or airplane ✈️ 😀
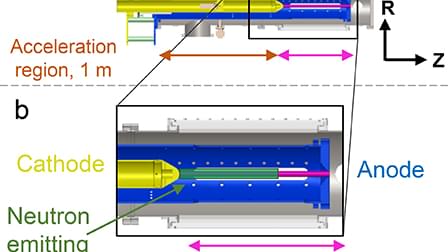
The fusion Z-pinch experiment (FuZE) is a sheared-flow stabilized Z-pinch designed to study the effects of flow stabilization on deuterium plasmas with densities and temperatures high enough to drive nuclear fusion reactions. Results from FuZE show high pinch currents and neutron emission durations thousands of times longer than instability growth times. While these results are consistent with thermonuclear neutron emission, energetically resolved neutron measurements are a stronger constraint on the origin of the fusion production. This stems from the strong anisotropy in energy created in beam-target fusion, compared to the relatively isotropic emission in thermonuclear fusion. In dense Z-pinch plasmas, a potential and undesirable cause of beam-target fusion reactions is the presence of fast-growing, “sausage” instabilities. This work introduces a new method for characterizing beam instabilities by recording individual neutron interactions in plastic scintillator detectors positioned at two different angles around the device chamber. Histograms of the pulse-integral spectra from the two locations are compared using detailed Monte Carlo simulations. These models infer the deuteron beam energy based on differences in the measured neutron spectra at the two angles, thereby discriminating beam-target from thermonuclear production. An analysis of neutron emission profiles from FuZE precludes the presence of deuteron beams with energies greater than 4.65 keV with a statistical uncertainty of 4.15 keV and a systematic uncertainty of 0.53 keV. This analysis demonstrates that axial, beam-target fusion reactions are not the dominant source of neutron emission from FuZE. These data are promising for scaling FuZE up to fusion reactor conditions.
The authors would like to thank Bob Geer and Daniel Behne for technical assistance, as well as Amanda Youmans, Christopher Cooper, and Clément Goyon for advice and discussions. The authors would also like to thank Phil Kerr and Vladimir Mozin for the use of their Thermo Fisher P385 neutron generator, which was important in verifying the ability to measure neutron energy shifts via the pulse integral technique. The information, data, or work presented herein was funded in part by the Advanced Research Projects Agency—Energy (ARPA-E), U.S. Department of Energy, under Award Nos. DE-AR-0000571, 18/CJ000/05/05, and DE-AR-0001160. This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344 and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231. U.