Year 2016 face_with_colon_three
In the future, can humans control computer-operated machines by simply “thinking”?



The neuroscience of perception has recently been revolutionized with an integrative modeling approach in which computation, brain function, and behavior are linked across many datasets and many computational models. By revealing trends across models, this approach yields novel insights into cognitive and neural mechanisms in the target domain. We here present a systematic study taking this approach to higher-level cognition: human language processing, our species’ signature cognitive skill. We find that the most powerful “transformer” models predict nearly 100% of explainable variance in neural responses to sentences and generalize across different datasets and imaging modalities (functional MRI and electrocorticography). Models’ neural fits (“brain score”) and fits to behavioral responses are both strongly correlated with model accuracy on the next-word prediction task (but not other language tasks). Model architecture appears to substantially contribute to neural fit. These results provide computationally explicit evidence that predictive processing fundamentally shapes the language comprehension mechanisms in the human brain.
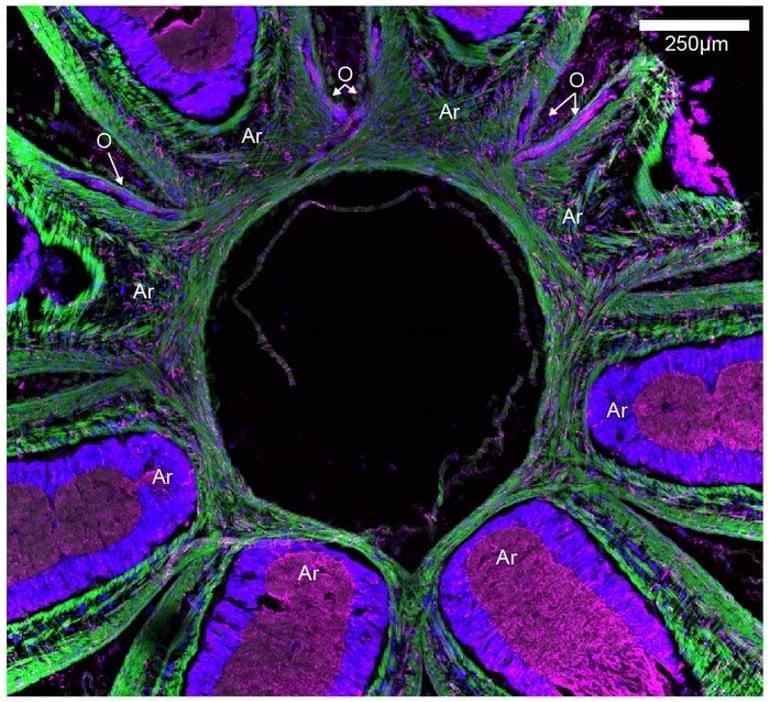
Summary: Researchers discovered a structure within the octopus nervous system by which the intramuscular nerve cords, which help the cephalopod to sense its arm movements, connect arms on the opposite side of the animal.
Source: University of Chicago.
Octopuses are not much like humans — they are invertebrates with eight arms, and more closely related to clams and snails. Still, they have evolved complex nervous systems with as many neurons as in the brains of dogs, and are capable of a wide array of complicated behaviors.
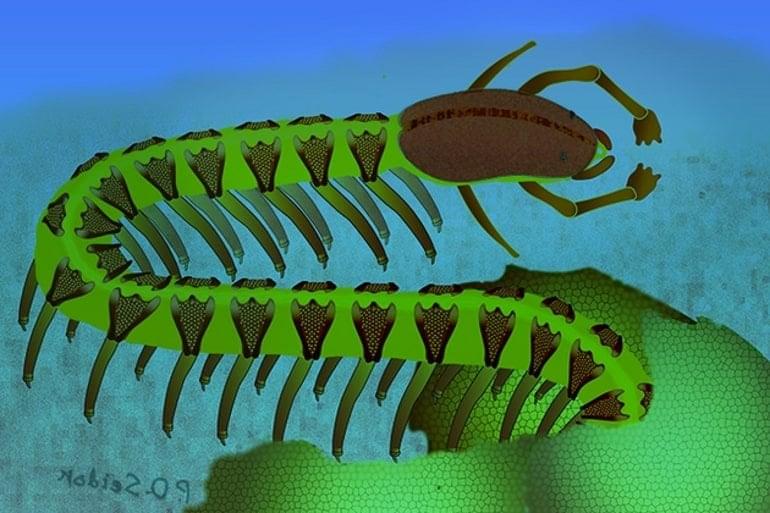

Summary: The fossil of a 525-million-year-old tiny sea creature with a preserved nervous system may solve a century-long debate about how the brains of arthropods evolved.
Source: University of Arizona.
Fossils of a tiny sea creature that died more than half a billion years ago may compel a science textbook rewrite of how brains evolved.
Quantum mechanics, which developed in the early 20th century, has been a serious blow to materialism.
There is no way to make sense of it if immaterial entities like information, observation, or the mind are not real. Theoretical physicist Sabine Hossenfelder struggles against the effects of this fact.
In a recent video, she asks, “Does Consciousness Influence Quantum Effects?” (November 19, 2022).
Year 2011 face_with_colon_three
UC Berkeley scientists have developed a system to capture visual activity in human brains and reconstruct it as digital video clips. Eventually, this process will allow you to record and reconstruct your own dreams on a computer screen.