The animal brain consists of tens of billions of neurons or nerve cells that perform complex tasks like processing emotions, learning, and making judgments by communicating with each other via neurotransmitters. These small signaling molecules diffuse—move from high to low concentration regions—between neurons, acting as chemical messengers.
Scientists believe that this diffusive motion might be at the heart of the brain’s superior function. Therefore, they have aimed to understand the role of specific neurotransmitters by detecting their release in the brain using amperometric and microdialysis methods. However, these methods provide insufficient information, necessitating better sensing techniques.
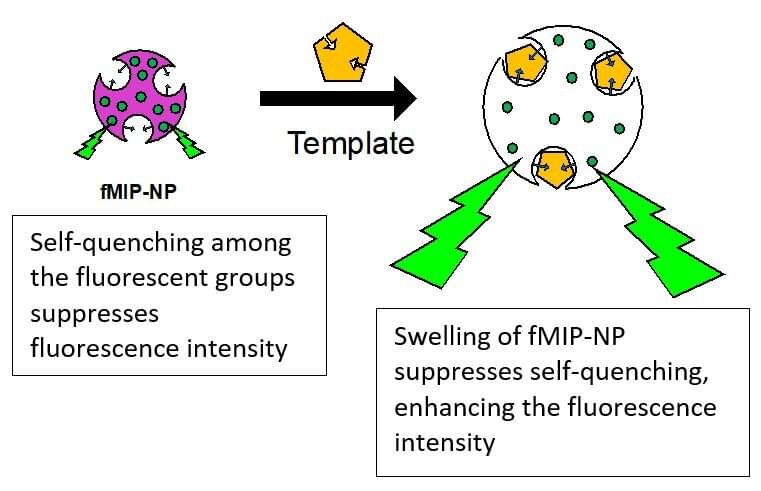
To this end, scientists developed an optical imaging method wherein protein probes change their fluorescence intensity upon detecting a specific neurotransmitter. Recently, a group of researchers from Shibaura Institute of Technology in Japan led by Professor Yasuo Yoshimi has taken this idea forward. They have successfully synthesized fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (fMIP-NPs) that serve as probes to detect specific neurotransmitters–serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine.