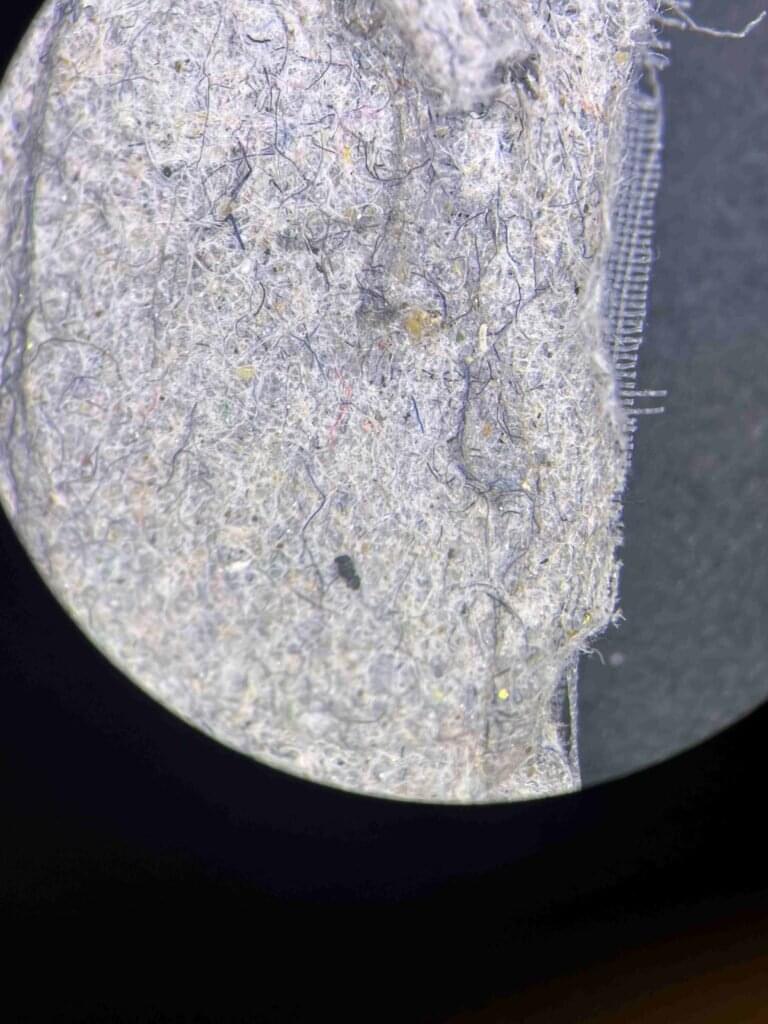
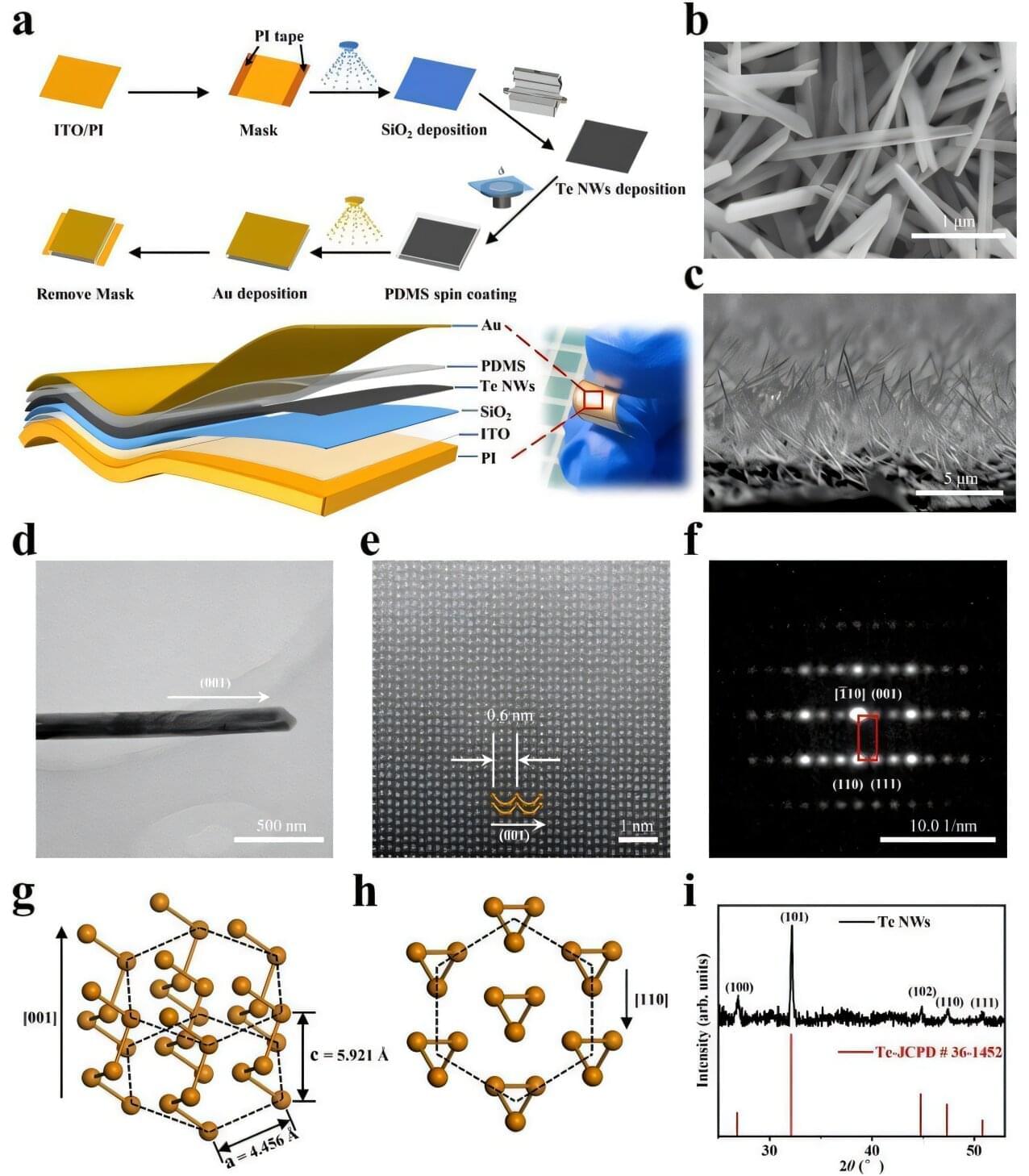
A single laundry load containing synthetic clothing can release thousands of plastic microfibers from nylon, acrylic and polyester materials. Lab testing of an SA-made washing machine filter at Flinders University shows it can be a useful new way to help protect waterways from polyester and other synthetic microparticles.
Flinders researchers are also developing a novel approach to enhance nanoplastic capture on cellulose filters using a plasma polymer coating.
Microplastics are plastic particles less than 5 mm wide, and they break down further to nanoparticles.