Researchers have developed an injectable hydrogel that could help repair and prevent further damage to the heart muscle after a heart attack event.


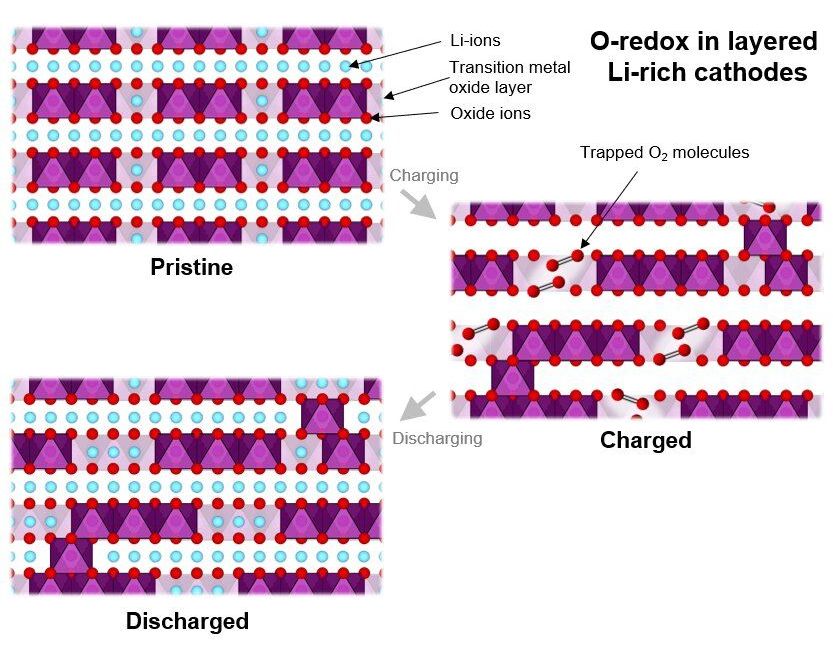
Scientists based at the University of Oxford as part of the Faraday Institution CATMAT project researching next-generation cathode materials have made a significant advance in understanding oxygen-redox processes involved in lithium-rich cathode materials. The paper, published in Nature Energy, proposes strategies that offer potential routes to increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries.
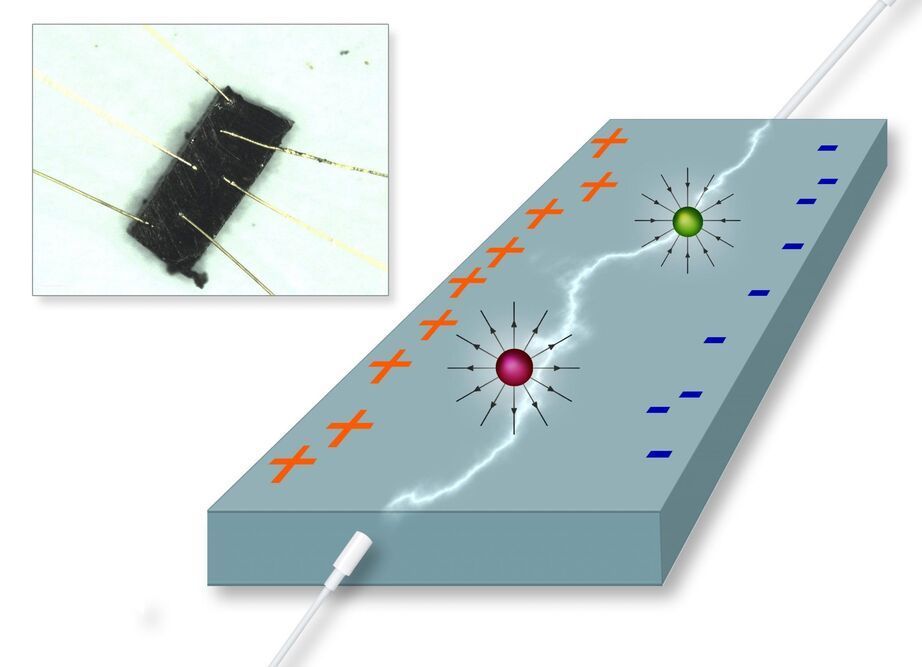
Surprise in solid-state physics: The Hall effect, which normally requires magnetic fields, can also be generated in a completely different way – with extreme strength.
Electric current is deflected by a magnetic field – in conducting materials this leads to the so-called Hall effect. This effect is often used to measure magnetic fields. A surprising discovery has now been made at TU Wien, in collaboration with scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute (Switzerland), McMater University (Canada), and Rice University (USA): an exotic metal made of cerium, bismuth, and palladium was examined and a giant Hall effect was found to be produced by the material, in the total absence of any magnetic field. The reason for this unexpected result lies in the unusual properties of the electrons: They behave as if magnetic monopoles were present in the material. These discoveries have now been published in the scientific magazine PNAS.
A voltage perpendicular to the current.
Pulsed lasers repeatedly emit light for a short period of time as if blinking. They have the advantage of focusing more energy than a continuous wave laser, whose intensity is kept unchanged over time. If digital signals are loaded in a pulsed laser, each pulse can encode one bit of data. In this respect, the higher the repetition rate, the more the amount of data that can be transmitted. However, conventional optical-fiber-based pulsed lasers have typically had a limitation in increasing the number of pulses per second above the MHz level.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research team led by Senior Researcher Dr. Yong-Won Song at the Center for Opto-Electronic Materials and Devices was able to generate laser pulses at a rate at least 10000 times higher than the state of the art. This achievement was accomplished by inserting an additional resonator containing graphene into a fiber-optic pulsed–laser oscillator that operates in the domain of femtoseconds (10-15 seconds). The data transmission and processing speeds are expected to increase significantly by applying this method to data communications.
The KIST research team noted that the characteristics of the wavelength and intensity of laser light that change over time are correlated (Fourier transform). If a resonator is inserted into the laser oscillator, the wavelength of the pulsed laser is periodically filtered, thereby modifying the pattern of laser intensity change. Based on this background research, Principal Researcher Song synthesized graphene, which has the characteristics of absorbing and eliminating weak light and amplifying the intensity by passing only strong light into the resonator. This allows the laser intensity change to be accurately controlled at a high rate, and thus the repetition rate of pulses could be increased to a higher level.
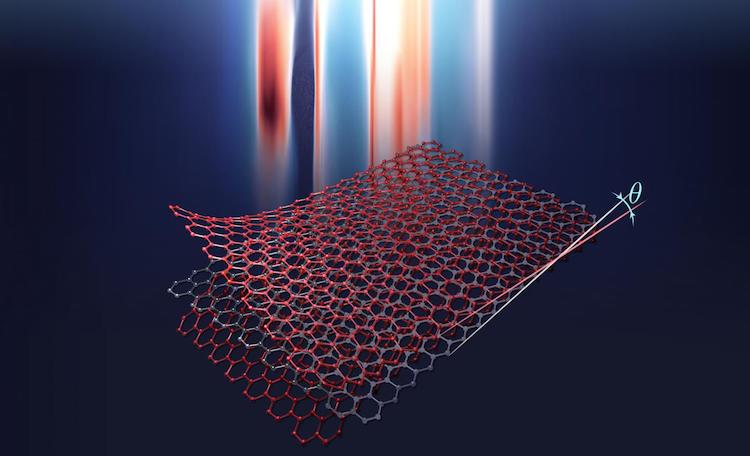
Two’s company, but three’s a crowd – unless you’re trying to make graphene superconduct at higher temperatures. That is the finding of researchers at Harvard University in the US, who discovered that the superconducting state in three stacked and twisted layers of graphene is more robust to temperature increase than the equivalent state in two-layer graphene. The researchers also found evidence that superconductivity in the trilayer system comes from strong interactions between electrons, rather than weak ones as in most conventional superconductors – corroborating a result reported a few days earlier by a separate team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
A sheet of graphene consists of a simple repetition of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice. When two sheets of graphene are placed atop each other and slightly misaligned, they form a moiré pattern, or “stretched” superlattice that dramatically changes the electronic interactions in the material compared to its pristine counterpart. The misalignment angle is critical: in 2018, the MIT group, led by Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, discovered a so-called “magic” angle of 1.1° where the material switches from an insulator to a superconductor. This means the twisted graphene can carry electrical current with no resistance below a superconducting transition temperature, Tc, of 1.7 K.
A group of researchers from the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society and the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin have found out that a semiconductor can be converted to a metal and back by light more easily and more quickly than previously thought. This discovery may increase the processing speed and simplify the design of many common technological devices.

