When materials reach extremely small size scales, strange things begin to happen. One of those phenomena is the formation of mesocrystals.

A group of researchers from the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society and the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin have found out that a semiconductor can be converted to a metal and back by light more easily and more quickly than previously thought. This discovery may increase the processing speed and simplify the design of many common technological devices.



An international team led by researchers of Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) has managed to manipulate the magnetic state of a magnetic material by optically shaking it. The whole process happens within an extremely short time frame of less than a few picoseconds. In times of stalling efficiency trends of current technology, such atomically-driven ultrafast control of magnetism opens broad new vistas for information technology. The results, which have been published in Nature Materials, could eventually lead to fast and energy-efficient data processing technologies, which are essential to keep up with our data hunger.
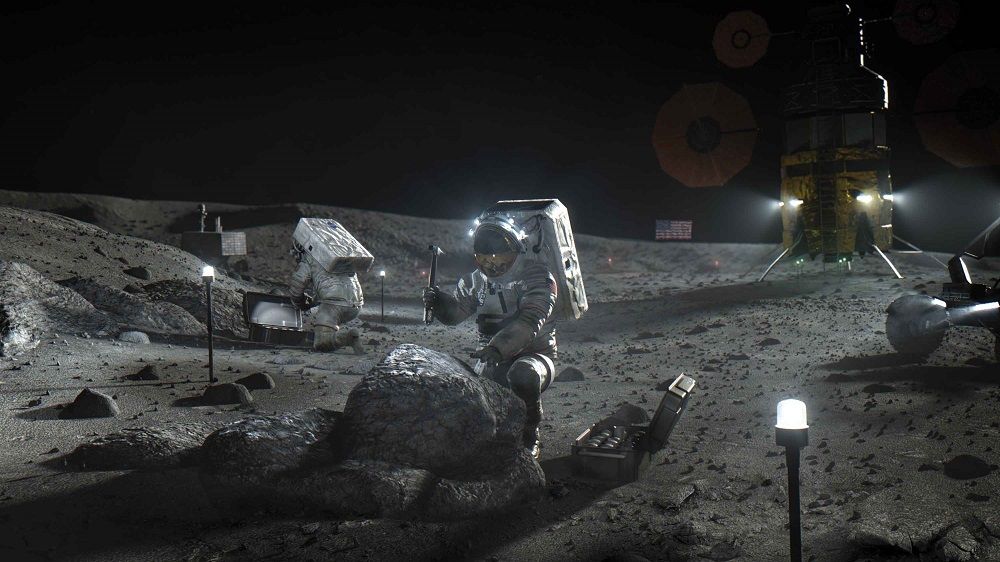



WASHINGTON — The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency wants to hear from the space industry about their capabilities to manufacture large structures on the moon.
This is a new project that DARPA announced Feb. 5 called “Novel Orbital and Moon Manufacturing, Materials and Mass-efficient Design.”

Plastics are among the most successful materials of modern times. However, they also create a huge waste problem. Scientists from the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and the East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST) in Shanghai produced different polymers from lipoic acid, a natural molecule. These polymers are easily depolymerized under mild conditions. Some 87 percent of the monomers can be recovered in their pure form and re-used to make new polymers of virgin quality. The process is described in an article that was published in the journal Matter on 4 February.