Scientists have discovered that a two graphene layers can conduct electrons showing superconductivity if the two hexagonal nets are twisted against each other at a 1.1 degree angle.
Category: materials – Page 254
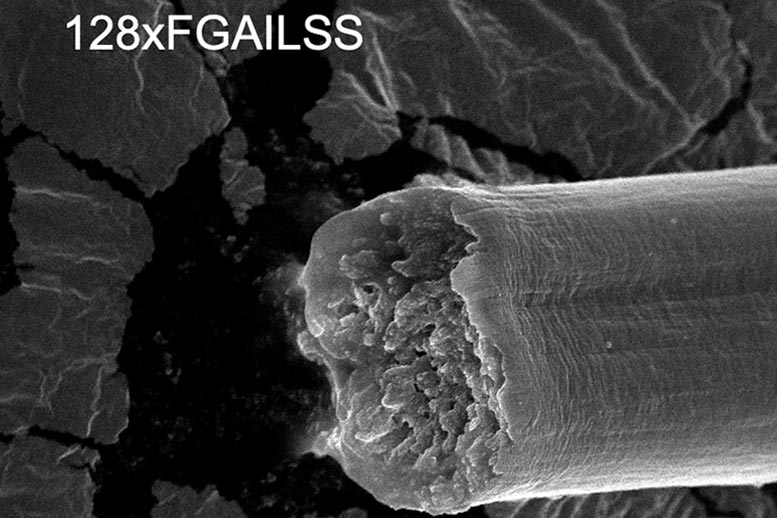
Incredible Fibers Produced by Engineered Bacteria: Stronger Than Steel, Tougher Than Kevlar
Artificially designed, amyloid-silk hybrid protein developed in Zhang lab even outperforms some spider silks.
Spider silk is said to be one of the strongest, toughest materials on the Earth. Now engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have designed amyloid silk hybrid proteins and produced them in engineered bacteria. The resulting fibers are stronger and tougher than some natural spider silks.
Their research was published in the journal ACS Nano.
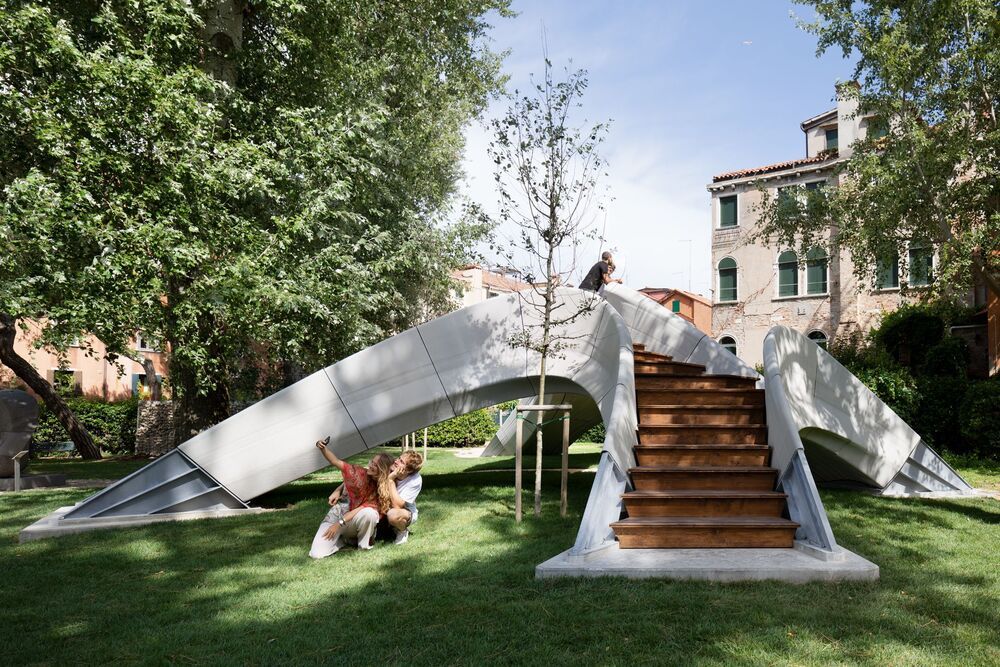

World’s first unreinforced 3D-printed concrete bridge displayed in Venice
A first-of-its-kind 3D-printed concrete bridge has been unveiled in Venice, Italy. The bridge is a demonstration of a new 3D printing method resulting in a structure requiring no mortar or steel reinforcement.
The bridge was developed as part of a collaboration between ETH Zurich and Zaha Hadid Architects’ Computation and Design Group. The unreinforced structure was created by 3D-printing concrete blocks using a novel type of concrete ink produced by a company called Holcim.
“This precise method of 3D concrete printing allows us to combine the principles of traditional vaulted construction with digital concrete fabrication to use material only where it is structurally necessary without producing waste,” explains Philippe Block, a researcher from ETH Zurich.
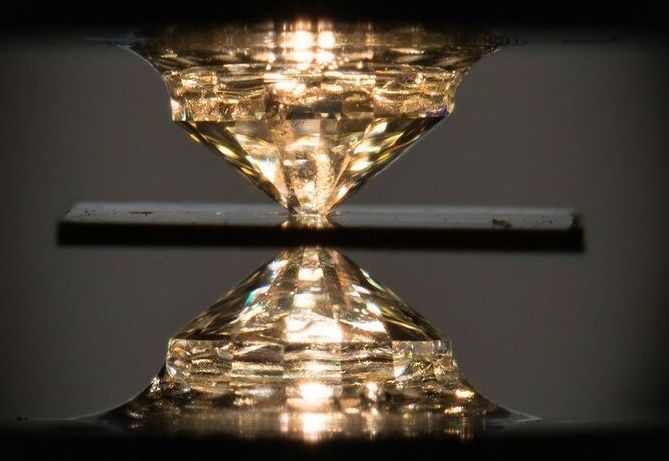

Scientists Discover the First Room-Temperature Superconductor
A novel metallic compound of hydrogen, carbon, and sulfur exhibited superconductivity at a balmy 59 degrees Fahrenheit—when pressurized between a pair of diamond anvils.
Via Quanta Magazine9 months ago.
Physicists finally achieved the long-sought goal, but there’s a catch: Their compound requires crushing pressures to keep from falling apart.
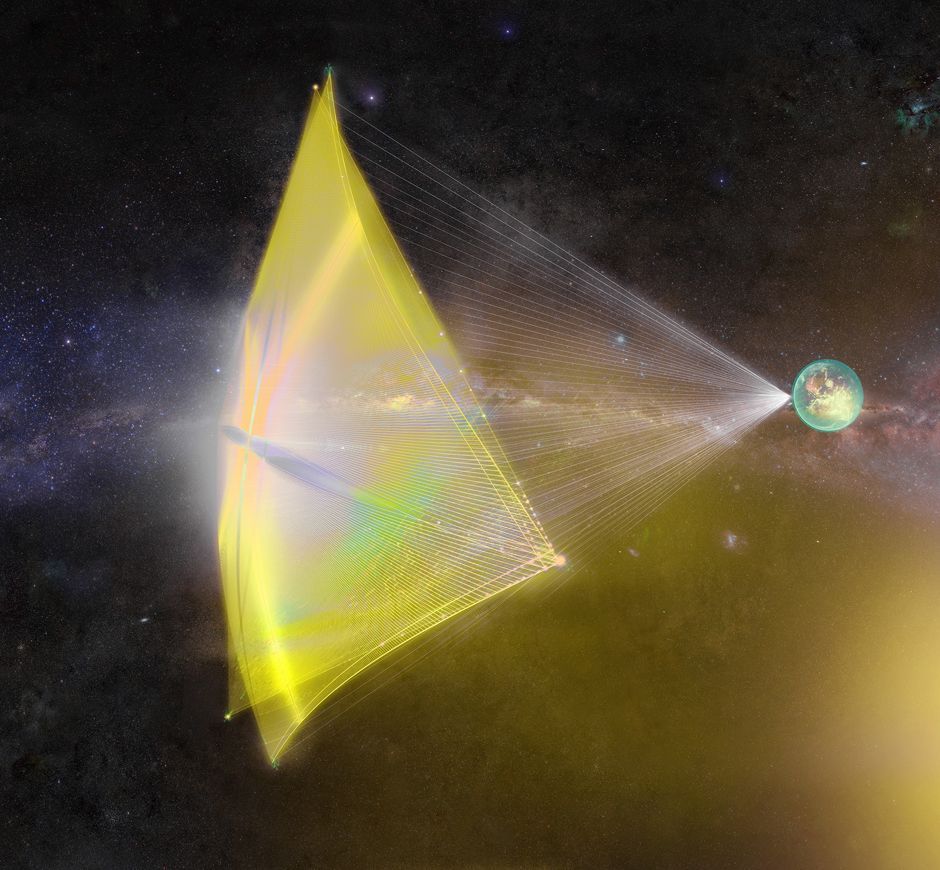
Forget About Interstellar Flights. Tiny Light Sails Could be Used to Explore the Solar System Today
Solar sails have been receiving a lot of attention lately. In part that is due to a series of high profile missions that have successfully proven the concept. It’s also in part due to the high profile Breakthrough Starshot project, which is designing a solar sail powered mission to reach Alpha Centauri. But this versatile third propulsion system isn’t only useful for far flung adventures – it has advantages closer to home as well. A new paper by engineers at UCLA defines what those advantages are, and how we might be able to best utilize them.
The literal driving force behind some solar sail projects are lasers. These concentrated beams of light are perfect to provide a pushing force against a solar sail. However, they are also useful as weapons if scaled up too much, vaporizing anything in its path. As such, one of the main design constraints for solar sail systems is around materials that can withstand a high power laser blast, yet still be light enough to not burden the craft it is attached to with extra weight.
For the missions that graduate student Ho-Ting Tung and Dr. Artur Davoyan of UCLA’s Mechanical Engineering Department envision that weight is miniscule. They expect any sailing spacecraft to weigh less than 100 grams. That 100 grams would include a sail array that measures up to 10 cm square.
‘Next-Generation’ Total Artificial Heart Successfully Transplanted into First US Patient
Late last year, a French company called Carmat received approval in Europe for its total artificial heart. It’s exactly what it sounds like: a heart made of synthetic and biological materials intended for implantation into people who need heart transplants. Now, just half a year later, the first US patient has received one of the hearts.
The transplant took place last week in a 39-year-old man at Duke University Hospital in North Carolina. The man didn’t go to the hospital expecting to have a heart transplant, but it ended up saving his life.
After experiencing unexpected heart failure, he was diagnosed with advanced coronary artery disease (when plaque builds up in the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood to heart) and went in for bypass surgery (which implants a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to redirect blood around a blocked artery).

World’s first 3D-printed steel bridge debuts in Amsterdam’s Red Light District
Amazing.
While Venice may be home to the first 3D-printed concrete footbridge to be constructed entirely sans reinforcement or mortar, the similarly canal laced city of Amsterdam, not to be outdone, has unveiled the world’s first 3D-printed steel pedestrian bridge. The long-awaited project, first announced in 2015, was dedicated on the Oudezijds Achterburgwal canal in the city’s Red Light District on July 15. The ceremony was attended by Her Majesty the Queen of the Netherlands, Máxima, who was assisted by a ribbon-cutting robot during the festivities.
Spanning nearly 40 feet across the canal, the curving 6-ton stainless steel structure was constructed by Amsterdam-based 3D metal printing technology company MX3D using a wire arc additive manufacturing process that marries advanced robotics with welding. With the aid of four robots, the entire printing process took just six months. The completed bridge, designed by Joris Laarman Lab with Arup serving as lead engineer, was first unveiled in October 2018 during Dutch Design Week. Several load-testing rounds followed, the last of which was carried out in the fall of 2019 with plans to install the structure in early 2020. However, ongoing site prep work at the canal delayed the factory-produced bridge’s installation to just last week.
As reported by the Associated Press, the stainless steel structure, dubbed the MX3D Smart Bridge, will remain in place for at least two years while the footbridge that previously spanned the canal undergoes renovation.