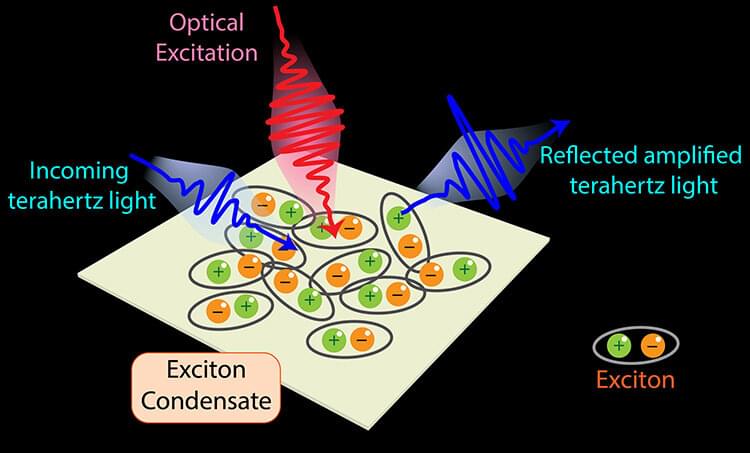
The discovery of superconductivity more than a century ago has significantly changed our world.
The story began in 1911 when the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes observed that the electrical resistance of mercury abruptly dropped to zero when it was cooled to a temperature of about 4 Kelvin (approximately 269°C)—a bit colder than the boiling point of liquid helium.
The practical applications of this remarkable effect were realized much later, in 1986, when a class of high-temperature superconductors was discovered. These high-Tc materials have a critical temperature below the boiling point of liquid nitrogen, about −196°C, which reduces the complexity and cost of their operation.