How One Mineral May Slow Brain Aging and Lower Dementia Risk.



Antler blastema progenitor cells (ABPCs) are a distinct population of skeletal mesenchymal stem cells found in regenerating deer antlers, with strong stemness and renewal capacity in vitro. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as potential therapeutic candidates that can mediate donor cells’ beneficial effects. Here, we tested the effects of ABPC-derived EVs (EVsABPC) on aging in mice and rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). We identified a variety of unique factors in EVsABPC and showed that in vitro, EVsABPC attenuated phenotypes of senescence in bone marrow stem cells. In aged mice and macaques, EVsABPC substantially increased femoral bone mineral density. Further, intravenous EVsABPC improved physical performance, enhanced cognitive function and reduced systemic inflammation in aged mice, while reversing epigenetic age by over 3 months. In macaques, EVABPC treatment was also neuroprotective, reduced inflammation, improved locomotor function and reduced epigenetic age by over 2 years. Our findings position ABPCs as an emerging and practical source of EVs with translational value for healthy aging interventions.
Inspired by the regenerative capacity of deer antlers, Hao and colleagues report that antler blastema progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicle treatment counteracts bone loss and epigenetic aging and is neuroprotective in mice and macaques.
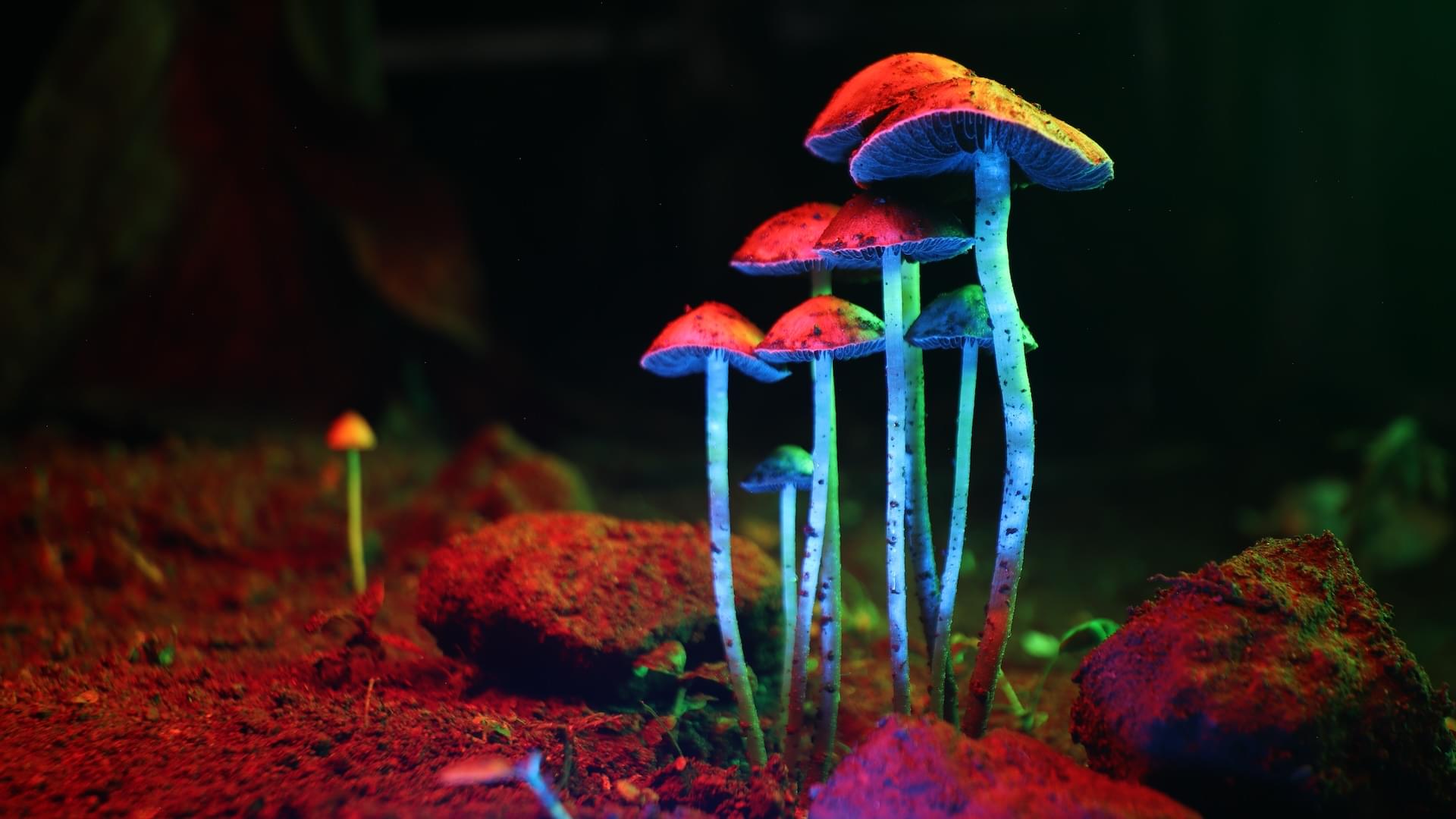


Psilocybin, the main psychoactive ingredient in magic mushrooms, extends the lifespan of human cells, a lab study suggests. Researchers also found that the psychedelic compound slows certain hallmarks of aging in older mice while improving their fur quality.
The findings, published July 8 in the journal npj Aging, provide the first experimental evidence of psilocybin’s potential anti-aging properties.

IN A NUTSHELL 🌿 Lignin-based separators improve the safety and extend the life of lithium-ion batteries by 60 percent. 🔥 These separators remain stable at temperatures up to 572°F, significantly reducing the risk of thermal runaway. 🌍 The use of a solvent-free dry process ensures eco-friendly and scalable battery production with zero waste. 🔋 This



Memczak, S., Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. & Graepel, T. Escaping ageing through Cell Annealing—a phenomenological model. Cell Res (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-025-01138-z.