A hidden form of evolution inside aging sperm may quietly raise genetic risks for the next generation.

A small group of volunteers will receive multiple injections of the experimental treatments next month, says Unlimited Bio.
Tim Gibson has been involved in cryonics for many years.

Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

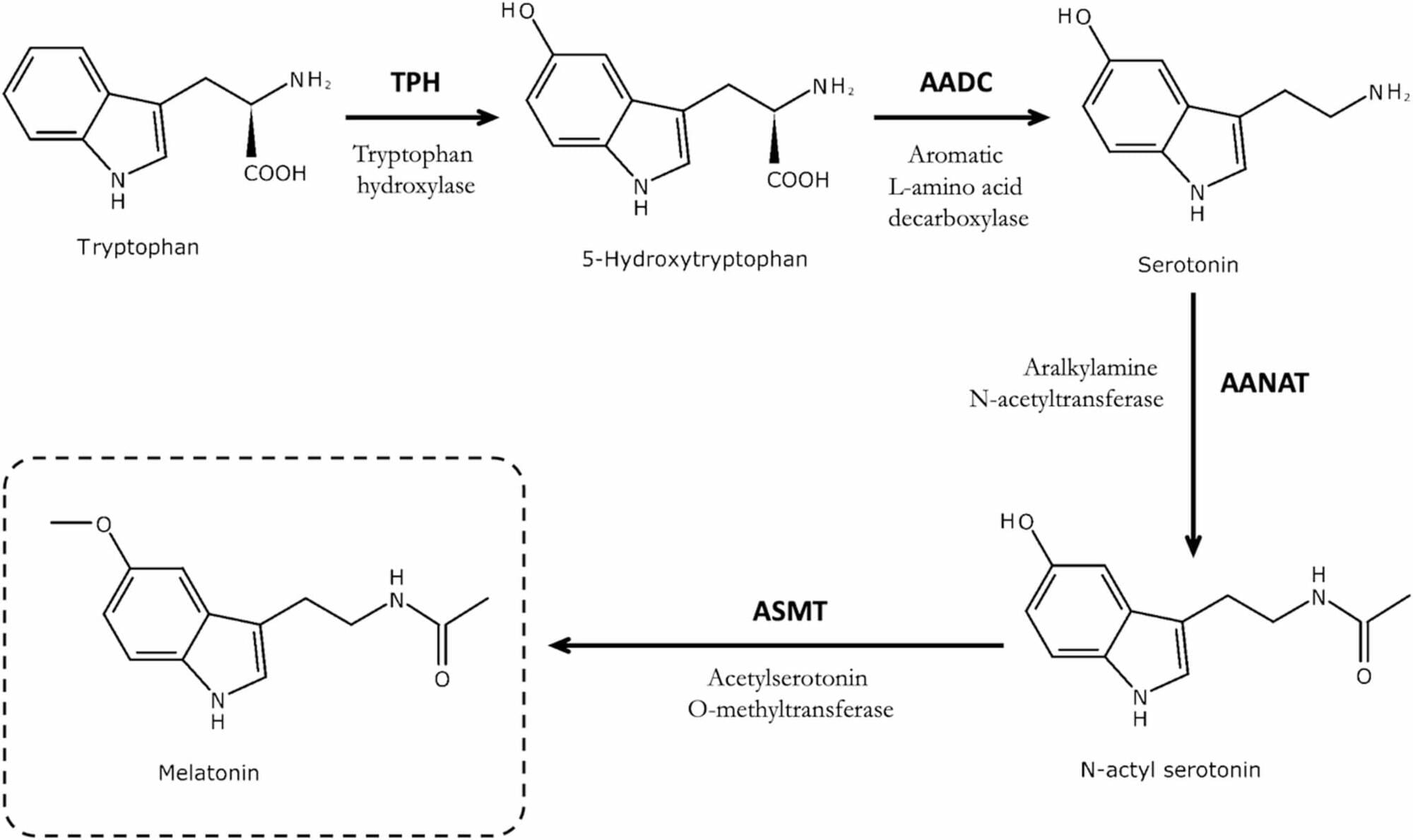
An ageing-related pathology has recently been described as one that develops and/or progresses with increasing chronological age, that is associated with, or contributes to, functional decline and that is evidenced by studies in humans. The pineal gland is a photo-neuroendocrine organ whose primary function is to produce and secrete melatonin in response to light-dark cycle environmental cues. The gland may undergo ageing-related structural and morphological changes, including calcification, gliosis, cyst formation, and reduced density of β-adrenergic receptors, which are hypothesised to reduce melatonin secretion.
