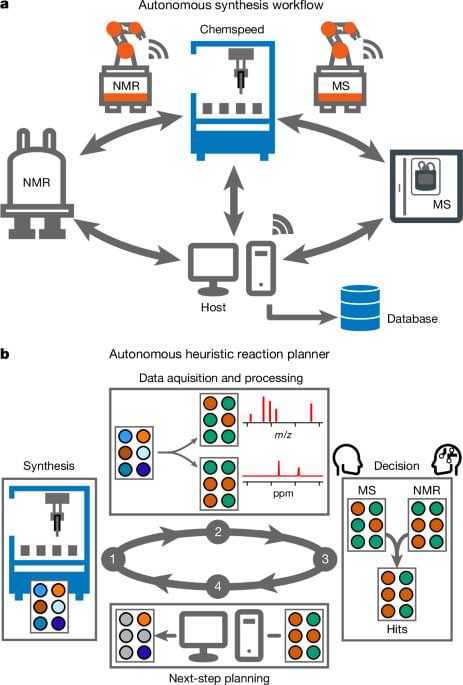
Autonomous laboratories can accelerate discoveries in chemical synthesis, but this requires automated measurements coupled with reliable decision-making.
Much progress has been made towards diversifying automated synthesis platforms4,5,19 and increasing their autonomous capabilities9,14,15,20,21,22. So far, most platforms use bespoke engineering and physically integrated analytical equipment6. The associated cost, complexity and proximal monopolization of analytical equipment means that single, fixed characterization techniques are often favoured in automated workflows, rather than drawing on the wider array of analytical techniques available in most synthetic laboratories. This forces any decision-making algorithms to operate with limited analytical information, unlike more multifaceted manual approaches. Hence, closed-loop autonomous chemical synthesis often bears little resemblance to human experimentation, either in the laboratory infrastructure required or in the decision-making steps.
We showed previously11 that free-roaming mobile robots could be integrated into existing laboratories to perform experiments by emulating the physical operations of human scientists. However, that first workflow was limited to one specific type of chemistry—photochemical hydrogen evolution—and the only measurement available was gas chromatography, which gives a simple scalar output. Subsequent studies involving mobile robots also focused on the optimization of catalyst performance12,13. These benchtop catalysis workflows11,12,13 cannot carry out more general synthetic chemistry, for example, involving organic solvents, nor can they measure and interpret more complex characterization data, such as NMR spectra. The algorithmic decision-making was limited to maximizing catalyst performance11, which is analogous to autonomous synthesis platforms that maximize yield for a reaction using NMR23 or chromatographic10,24 peak areas.
Here we present a modular autonomous platform for general exploratory synthetic chemistry. It uses mobile robots to operate a Chemspeed ISynth synthesis platform, an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS) and a benchtop NMR spectrometer. This modular laboratory workflow is inherently expandable to include other equipment, as shown here by the addition of a standard commercial photoreactor.