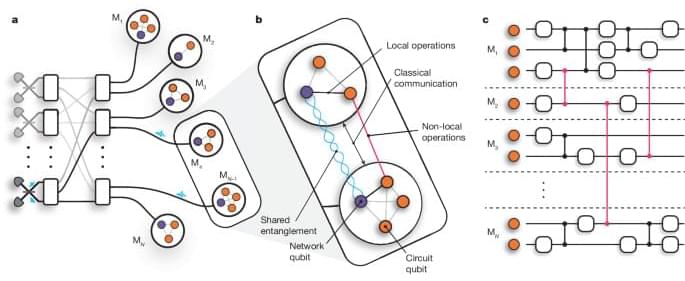
The distribution of quantum computations is demonstrated between two photonically interconnected trapped-ion modules, using repeatable, deterministic teleported controlled-Z gates to perform Grover’s search algorithm.


If left unchecked, powerful AI systems may pose an existential threat to the future of humanity, say UC Berkeley Professor Stuart Russell and postdoctoral scholar Michael Cohen.
Society is already grappling with myriad problems created by the rapid proliferation of AI, including disinformation, polarization and algorithmic bias. Meanwhile, tech companies are racing to build ever more powerful AI systems, while research into AI safety lags far behind.
Without giving powerful AI systems clearly defined objectives, or creating robust mechanisms to keep them in check, AI may one day evade human control. And if the objectives of these AIs are at odds with those of humans, say Russell and Cohen, it could spell the end of humanity.
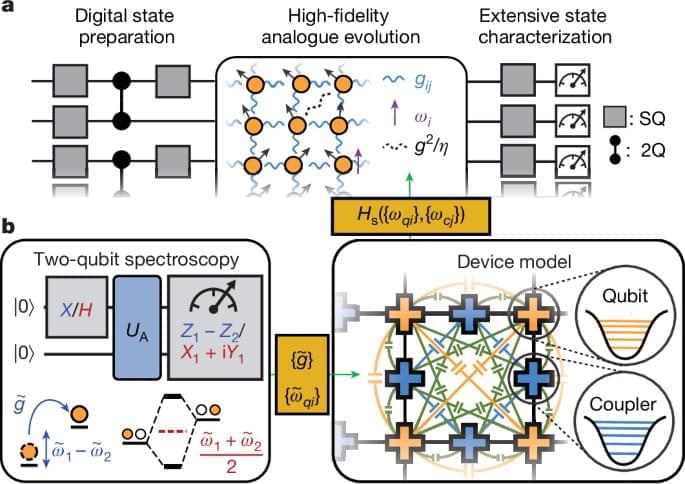
The advent of quantum simulators in various platforms8,9,10,11,12,13,14 has opened a powerful experimental avenue towards answering the theoretical question of thermalization5,6, which seeks to reconcile the unitarity of quantum evolution with the emergence of statistical mechanics in constituent subsystems. A particularly interesting setting is that in which a quantum system is swept through a critical point15,16,17,18, as varying the sweep rate can allow for accessing markedly different paths through phase space and correspondingly distinct coarsening behaviour. Such effects have been theoretically predicted to cause deviations19,20,21,22 from the celebrated Kibble–Zurek (KZ) mechanism, which states that the correlation length ξ of the final state follows a universal power-law scaling with the ramp time tr (refs. 3, 23,24,25).
Whereas tremendous technical advancements in quantum simulators have enabled the observation of a wealth of thermalization-related phenomena26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35, the analogue nature of these systems has also imposed constraints on the experimental versatility. Studying thermalization dynamics necessitates state characterization beyond density–density correlations and preparation of initial states across the entire eigenspectrum, both of which are difficult without universal quantum control36. Although digital quantum processors are in principle suitable for such tasks, implementing Hamiltonian evolution requires a high number of digital gates, making large-scale Hamiltonian simulation infeasible under current gate errors.
In this work, we present a hybrid analogue–digital37,38 quantum simulator comprising 69 superconducting transmon qubits connected by tunable couplers in a two-dimensional (2D) lattice (Fig. 1a). The quantum simulator supports universal entangling gates with pairwise interaction between qubits, and high-fidelity analogue simulation of a U symmetric spin Hamiltonian when all couplers are activated at once. The low analogue evolution error, which was previously difficult to achieve with transmon qubits due to correlated cross-talk effects, is enabled by a new scalable calibration scheme (Fig. 1b). Using cross-entropy benchmarking (XEB)39, we demonstrate analogue performance that exceeds the simulation capacity of known classical algorithms at the full system size.
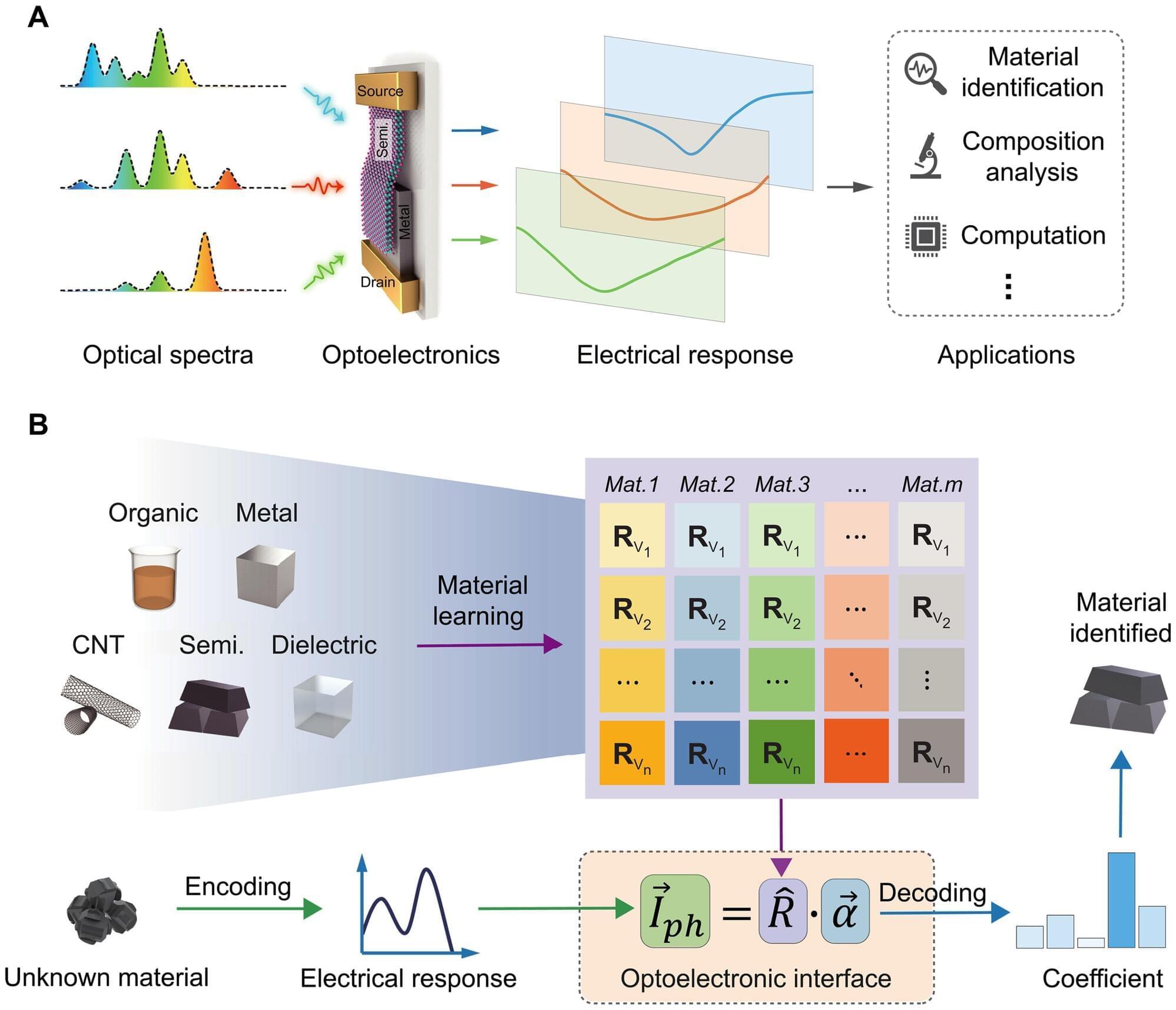
Imagine smartphones that can diagnose diseases, detect counterfeit drugs or warn of spoiled food. Spectral sensing is a powerful technique that identifies materials by analyzing how they interact with light, revealing details far beyond what the human eye can see.
Traditionally, this technology required bulky, expensive systems confined to laboratories and industrial applications. But what if this capability could be miniaturized to fit inside a smartphone or wearable device?
Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have combined miniaturized hardware and intelligent algorithms to create a powerful tool that is compact, cost-effective, and capable of solving real-world problems in areas such as health care, food safety and autonomous driving. The research is published in the journal Science Advances.

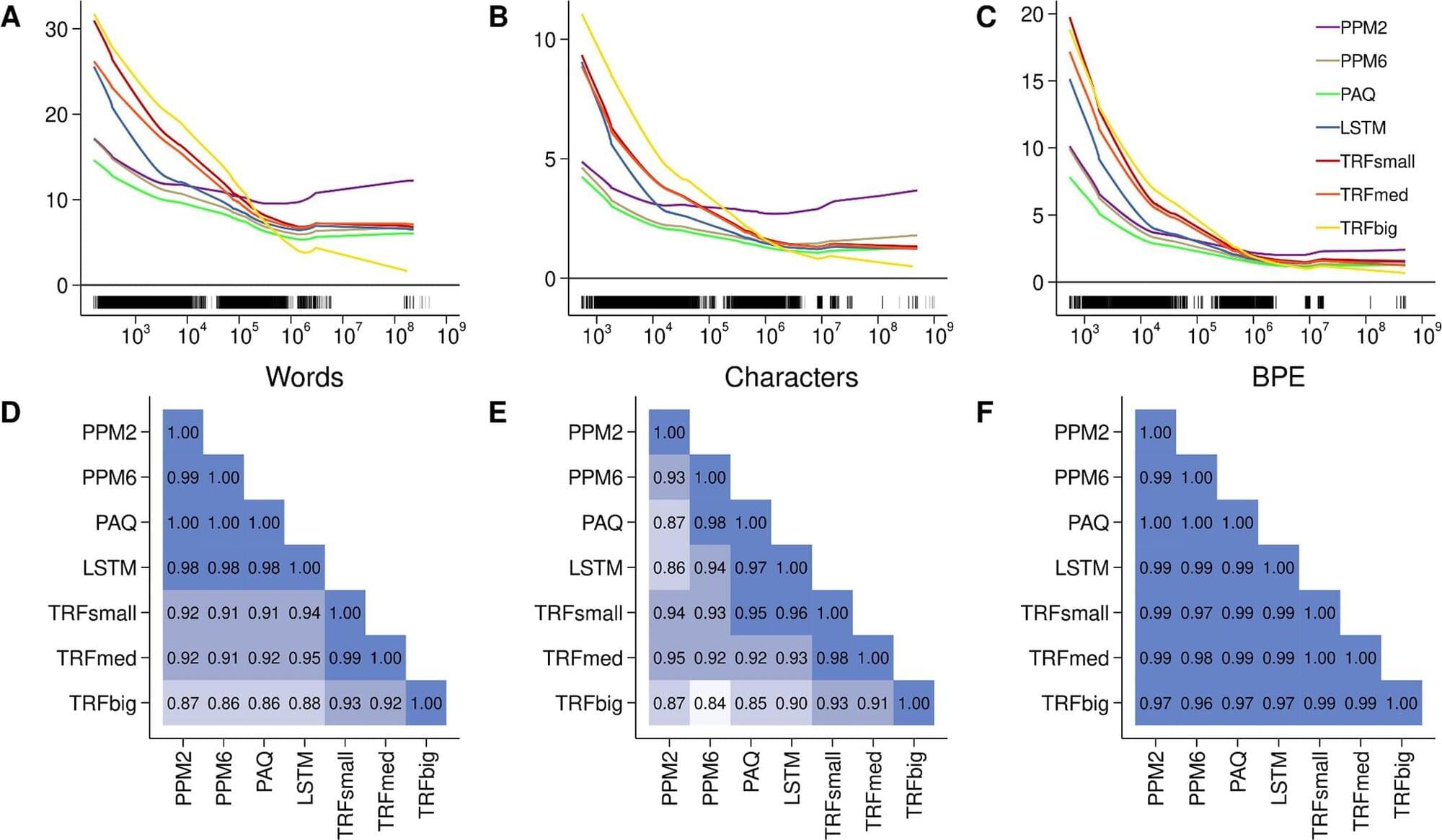
A new study published in PNAS Nexus reveals that large language models, which are advanced artificial intelligence systems, demonstrate a tendency to present themselves in a favorable light when taking personality tests. This “social desirability bias” leads these models to score higher on traits generally seen as positive, such as extraversion and conscientiousness, and lower on traits often viewed negatively, like neuroticism.
The language systems seem to “know” when they are being tested and then try to look better than they might otherwise appear. This bias is consistent across various models, including GPT-4, Claude 3, Llama 3, and PaLM-2, with more recent and larger models showing an even stronger inclination towards socially desirable responses.
Large language models are increasingly used to simulate human behavior in research settings. They offer a potentially cost-effective and efficient way to collect data that would otherwise require human participants. Since these models are trained on vast amounts of text data generated by humans, they can often mimic human language and behavior with surprising accuracy. Understanding the potential biases of large language models is therefore important for researchers who are using or planning to use them in their studies.
How do languages balance the richness of their structures with the need for efficient communication? To investigate, researchers at the Leibniz Institute for the German Language (IDS) in Mannheim, Germany, trained computational language models on a vast dataset covering thousands of languages.
They found that languages that are computationally harder to process compensate for this increased complexity with greater efficiency: more complex languages need fewer symbols to encode the same message. The analyses also reveal that larger language communities tend to use more complex but more efficient languages.
Language models are computer algorithms that learn to process and generate language by analyzing large amounts of text. They excel at identifying patterns without relying on predefined rules, making them valuable tools for linguistic research. Importantly, not all models are the same: their internal architectures vary, shaping how they learn and process language. These differences allow researchers to compare languages in new ways and uncover insights into linguistic diversity.
An international team of researchers, led by physicists from the University of Vienna, has achieved a breakthrough in data processing by employing an “inverse-design” approach. This method allows algorithms to configure a system based on desired functions, bypassing manual design and complex simulations. The result is a smart “universal” device that uses spin waves (“magnons”) to perform multiple data processing tasks with exceptional energy efficiency.
Published in Nature Electronics, this innovation marks a transformative advance in unconventional computing, with significant potential for next-generation telecommunications, computing, and neuromorphic systems.
Modern electronics face critical challenges, including high energy consumption and increasing design complexity. In this context, magnonics—the use of magnons, or quantized spin waves in magnetic materials —offers a promising alternative. Magnons enable efficient data transport and processing with minimal energy loss.
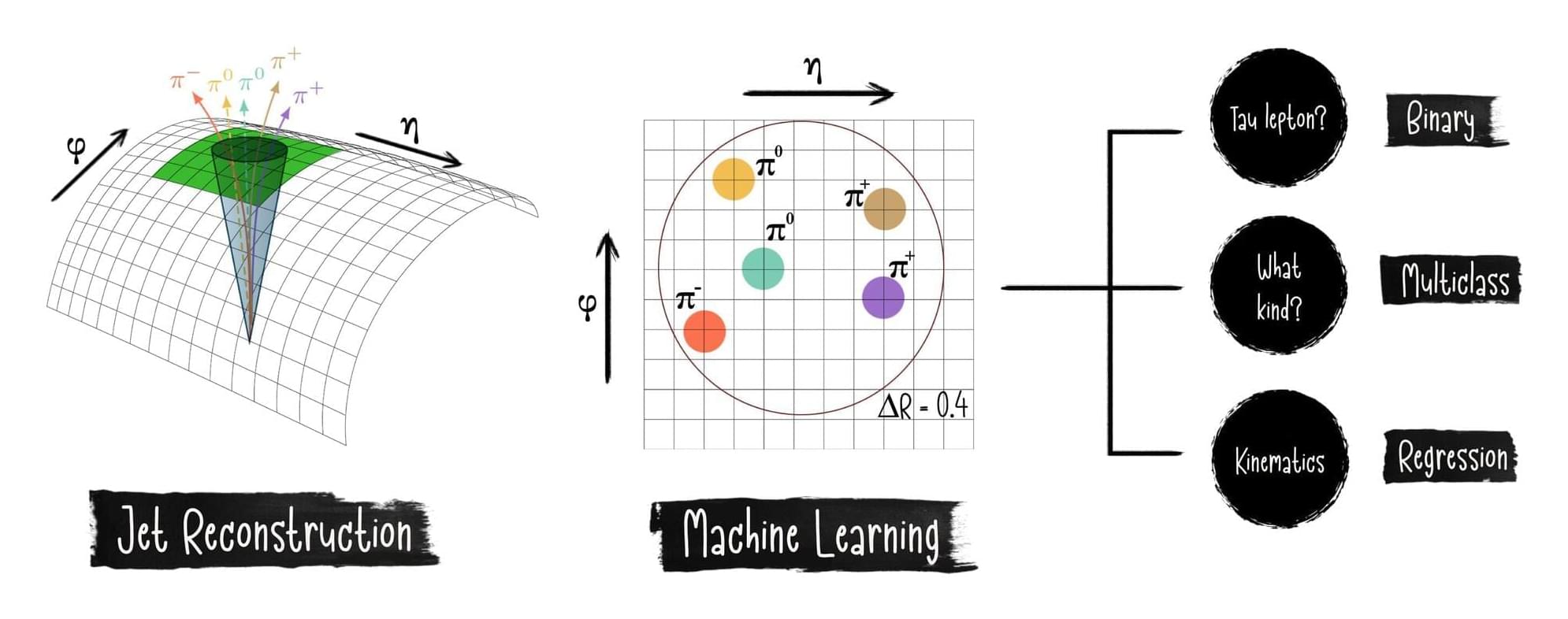
In order to find rare processes from collider data, scientists use computer algorithms to determine the type and properties of particles based on the faint signals that they leave in the detector. One such particle is the tau lepton, which is produced, for example, in the decay of the Higgs boson.
The tau lepton leaves a spray or jet of low-energy particles, the subtle pattern of which in the jet allows one to distinguish them from jets produced by other particles. The jet also contains information about the energy of the tau lepton, which is distributed among the daughter particles, and on the way is decayed. Currently, the best algorithms use multiple steps of combinatorics and computer vision.
ChatGPT has shown much stronger performance in rejecting backgrounds than computer-vision based methods. In this paper, researchers showed that such language-based models can find the tau leptons from the jet patterns, and also determine the energy and decay properties more accurately than before.
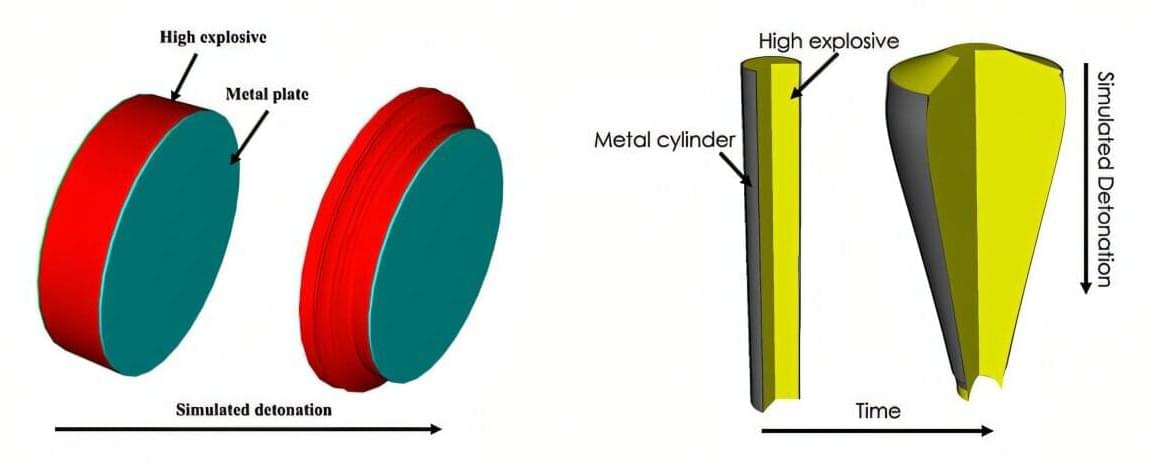
For the first time, a team of researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) quantified and rigorously studied the effect of metal strength on accurately modeling coupled metal/high explosive (HE) experiments, shedding light on an elusive variable in an important model for national security and defense applications.
The team used a Bayesian approach to quantify metal strength uncertainty with tantalum and two common explosive materials and integrated it into a coupled metal/HE model. Their findings could lead to more accurate models for equation-of-state-studies, which assess the state of matter a material exists in under different conditions. Their paper —featured as an editor’s pick in the Journal of Applied Physics —also suggested that metal strength uncertainty may have an insignificant effect on result.
“There has been a long-standing field lore that HE model calibrations are sensitive to the metal strength,” said Matt Nelms, the paper’s first author and a group leader in LLNL’s Computational Engineering Division (CED). “By using a rigorous Bayesian approach, we found that this is not the case, at least when using tantalum.”

However, despite these advances, human progress is never without risks. Therefore, we must address urgent challenges, including the lack of transparency in algorithms, potential intrinsic biases and the possibility of AI usage for destructive purposes.
Philosophical And Ethical Implications
The singularity and transcendence of AI could imply a radical redefinition of the relationship between humans and technology in our society. A typical key question that may arise in this context is, “If AI surpasses human intelligence, who—or what—should make critical decisions about the planet’s future?” Looking even further, the concretization of transcendent AI could challenge the very concept of the soul, prompting theologians, philosophers and scientists to reconsider the basic foundations of beliefs established for centuries over human history.