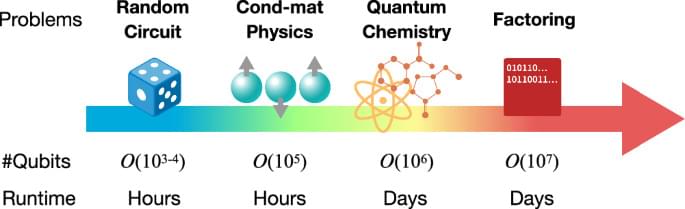
The intensive pursuit for quantum advantage in terms of computational complexity has further led to a modernized crucial question of when and how will quantum computers outperform classical computers. The next milestone is undoubtedly the realization of quantum acceleration in practical problems. Here we provide a clear evidence and arguments that the primary target is likely to be condensed matter physics. Our primary contributions are summarized as follows: 1) Proposal of systematic error/runtime analysis on state-of-the-art classical algorithm based on tensor networks; 2) Dedicated and high-resolution analysis on quantum resource performed at the level of executable logical instructions; 3) Clarification of quantum-classical crosspoint for ground-state simulation to be within runtime of hours using only a few hundreds of thousand physical qubits for 2d Heisenberg and 2d Fermi-Hubbard models, assuming that logical qubits are encoded via the surface code with the physical error rate of p = 10–3. To our knowledge, we argue that condensed matter problems offer the earliest platform for demonstration of practical quantum advantage that is order-of-magnitude more feasible than ever known candidates, in terms of both qubit counts and total runtime.
Yoshioka, N., Okubo, T., Suzuki, Y. et al. Hunting for quantum-classical crossover in condensed matter problems. npj Quantum Inf 10, 45 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-024-00839-4