New gene therapy breakthrough from the University of Hawai’i offers safer, efficient treatments for genetic disorders like Hemophilia.



Summary: A new gene therapy has restored vision in patients with Leber congenital amaurosis type I (LCA1), a rare genetic condition causing blindness. In a small trial, those receiving the highest dose saw up to a 10,000-fold improvement in light sensitivity and significant gains in reading and navigation abilities.
The therapy, developed by researchers, uses a virus-based system to deliver a functioning gene into the retina’s light-sensitive cells. The results show promise for expanding this treatment, with further trials planned to confirm safety and efficacy.

The vision of people with a rare inherited condition that causes them to lose much of their sight early in childhood was 100 times better after they received gene therapy to address the genetic mutation causing it. Some patients even experienced a 10,000-fold improvement in their vision after receiving the highest dose of the therapy, according to researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania who co-led the clinical trial published in The Lancet.
“That 10,000-fold improvement is the same as a patient being able to see their surroundings on a moonlit night outdoors as opposed to requiring bright indoor lighting before treatment,” said the study’s lead author, Artur Cideciyan, Ph.D., a research professor of Ophthalmology and co-director of the Center for Hereditary Retinal Degenerations.
“One patient reported for the first time being able to navigate at midnight outdoors only with the light of a bonfire.”
Their…
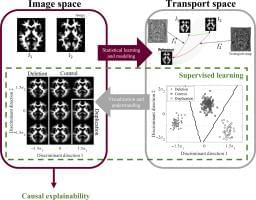
A multi-university research team co-led by University of Virginia engineering professor Gustavo K. Rohde has developed a system that can spot genetic markers of autism in brain images with 89 to 95% accuracy.
Their findings suggest doctors may one day see, classify and treat autism and related neurological conditions with this method, without having to rely on, or wait for, behavioral cues. And that means this truly personalized medicine could result in earlier interventions.
“Autism is traditionally diagnosed behaviorally but has a strong genetic basis. A genetics-first approach could transform understanding and treatment of autism,” the researchers wrote in a paper published June 12 in the journal Science Advances.

Chinese scientists have developed a method using genetic engineering to potentially enhance brain-computer interface (BCI) technology by enlarging neurons for better signal transmission.
The researchers, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ National Centre for Nanoscience…
Gene sequence could be implanted with electrodes to make neurons larger and easier to ‘read’ in quest for better mind control of devices.
Synthetic Plants For A Sustainable Future — Dr. Angie Burnett, Ph.D. — Program Director, Advanced Research + Invention Agency (ARIA)
Dr. Angie Burnett, Ph.D. is Program Director at the Advanced Research and Invention Agency (ARIA — https://www.aria.org.uk/), a UK organization created by an Act of Parliament, and sponsored by the Department for Science, Innovation, and Technology, to fund projects across a full spectrum of R\&D disciplines, approaches, and institutions, per the ARIA mission statement to “Look beyond what exists today to the breakthroughs we’ll need tomorrow”
Prior to this role, Dr. Burnett was a Research Associate in the Department of Plant Sciences, and a former David MacKay Research Associate at Darwin College and Cambridge Zero where her work focused on understanding the response of maize plants to high light and cold temperature stresses, and the genetic basis for stress tolerance, so that breeders can produce plants which are better able to withstand environmental stress.
Dr. Burnett’s background is in plant physiology. She holds a BA from the University of Cambridge and a PhD from the University of Sheffield, where she was awarded the inaugural PhD studentship from the Society for Experimental Biology. Before commencing her role at the University of Cambridge, she worked as a postdoctoral research associate at Brookhaven National Laboratory in the USA and as a Consultant at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in Italy.
Important Episode Links.
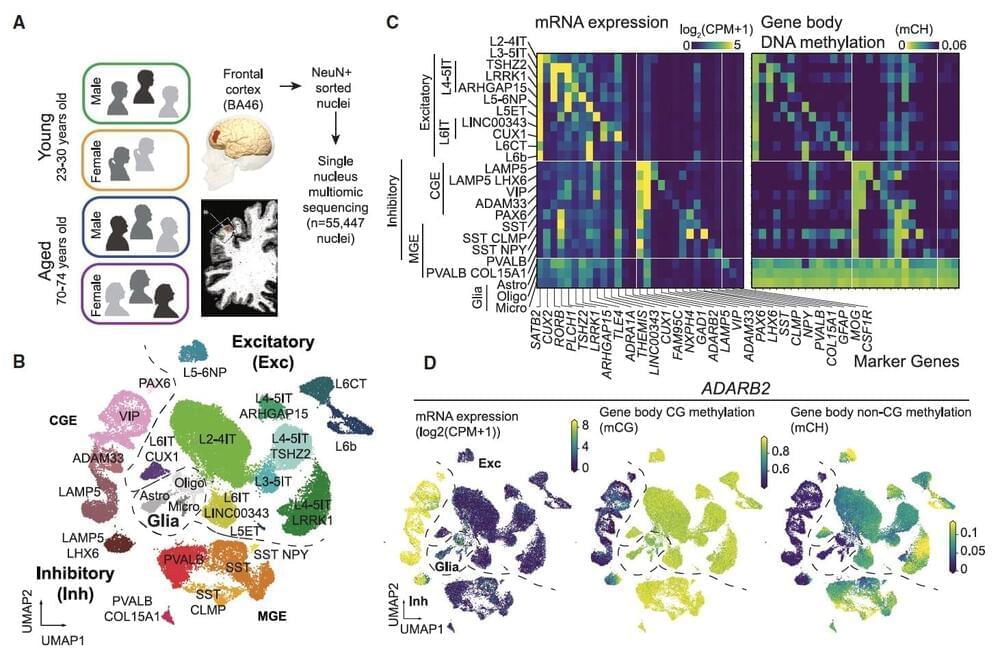
Aging is known to have profound effects on the human brain, prompting changes in the composition of cells and the expression of genes, while also altering aspects of the interaction between genes and environmental factors. While past neuroscience studies have pinpointed many of the molecular changes associated with aging, the age-related genetic factors influencing specific neuron populations remains poorly understood.
Recent studies on flies, mice, primates and human brain tissue utilizing single-cell or single-nucleus RNA-sequencing and genetic experimental techniques shed new light on these cell-type-specific changes. For instance, they unveiled the effects of aging on glial cells in the mouse and human brain, associations between cell-specific changes and modified chromatin proteins, and the influence of DNA methylation in the aging of various tissues.
Researchers at University of California (UC) San Diego and Salk Institute recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how both age and sex impact human cortical neurons at a single-cell level. Their findings, published in Neuron, offer new insights into how aging affects cell composition, gene expression and DNA methylation across human brain cell types, while also uncovering differences between gene expression and DNA methylation in females and males.

Alternative splicing is a genetic process where different segments of genes are removed, and the remaining pieces are joined together during transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA). This mechanism increases the diversity of proteins that can be generated from genes, by assembling sections of genetic code into different combinations. This is believed to enhance biological complexity by allowing genes to produce different versions of proteins, or protein isoforms, for many different uses.
Summary: Researchers identified how gene variations lead to brain changes associated with essential tremor, a common movement disorder affecting over 60 million people worldwide. The study used brain MRI scans and genetic data from over 33,000 adults to uncover genetic links to structural changes in the brain’s cortex and cerebellum.
These findings could lead to new drug targets by revealing how faulty protein disposal systems disrupt neural pathways, resulting in uncontrollable hand tremors. The research marks a significant step toward understanding and treating essential tremor more effectively.
The brain’s white matter comprises areas of the central nervous system made up of myelinated axons. Its name is derived from the pale appearance of the lipids that comprise myelin. Myelin is a segmented sheath that insulates axons, ensuring the conduction of neural signals. The loss of myelin is documented in a number of neurodegenerative pathologies, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and perhaps most notably, multiple sclerosis. As people age, demyelination becomes more likely.
Researchers have long suspected a relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness and the integrity of the brain’s white matter as people age. However, a lack of specific evidence has led researchers at the National Institutes of Health to conduct a study examining the strength of this correlation, now published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
To establish a correlation between cardiovascular fitness and cerebral myelination, the researchers recruited a cohort of 125 participants from age 22 to 94 years old. The cardiovascular fitness of the participants was quantified as the maximum rate of oxygen consumption, popularly and succinctly known as VO2max. Myelin content was defined as the myelin water fraction, which the researchers estimated through an advanced multicomponent relaxometry MRI method.