China has big plans for the future, including lunar sample return, a robotic research base, and potentially human missions.



Soviet physicist Lev Landau is being honoured with a Google Doodle on what would have been his 111th birthday.
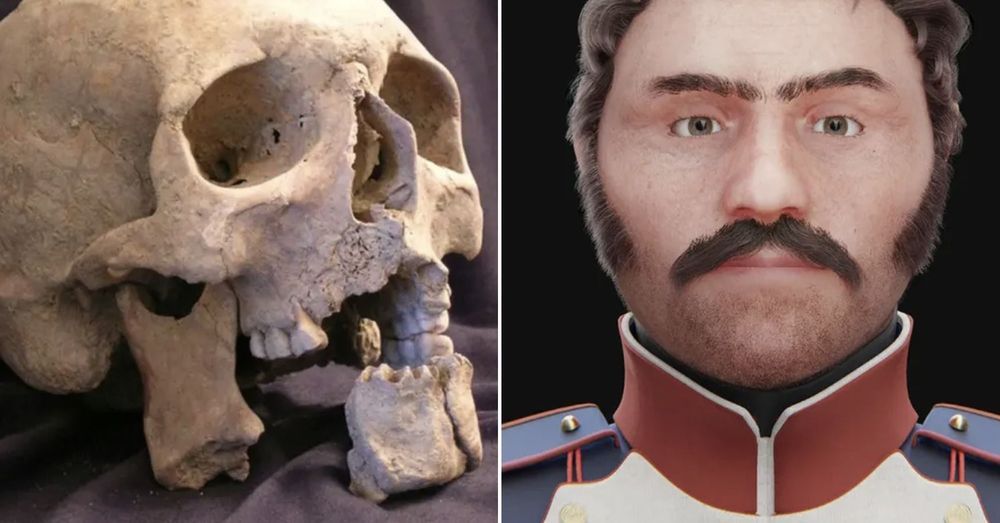

“It is a sad story, but unfortunately it is also the story of hundreds of thousands of young soldiers,” said one archaeologist.
By Dan Vergano
BuzzFeed News Reporter

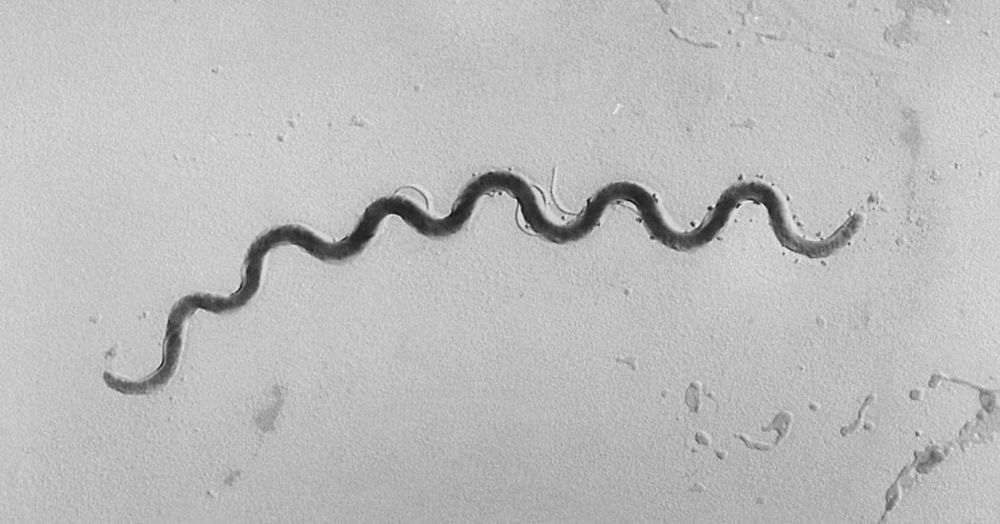
Scientists at Oregon State University have determined why foreshocks are such common indicators of large and deadly earthquakes.
Scientists involved in groundbreaking new research at Oregon State University have determined that major earthquakes are often preceded by “silent slips” and have finally discovered why foreshocks are common indicators of large and deadly earthquakes.
According to Oregon Live, major earthquakes normally follow “shallow mantle creep” and “seismic swarms,” and researchers are much clearer in their understanding now of the “silent slip,” which is what happens when different sections of the Earth’s crust can be observed shifting along the fault line. However, when this occurs, no seismic activity is ever detected, which has been confusing to researchers in the past.
A team of researchers based at the Universities of Oxford and Edinburgh have recreated for the first time the famous Draupner freak wave measured in the North Sea in 1995.

Facebook has been in the news frequently of late for privacy issues that make people wary of the social networking giant. Facebook is doing something very cool with a pair of new observatories that are being built on Mount Wilson in California. These won’t be used to house giant telescopes that scan the skies for science.