Introducing JCED’s Latin America Special Issue. It comprises more than 30 articles from authors located in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico, and Puerto Rico, and recognizes the vibrant and growing community of high quality thermodynamics researchers in the region. Read this Special Issue Today!
Category: engineering – Page 226
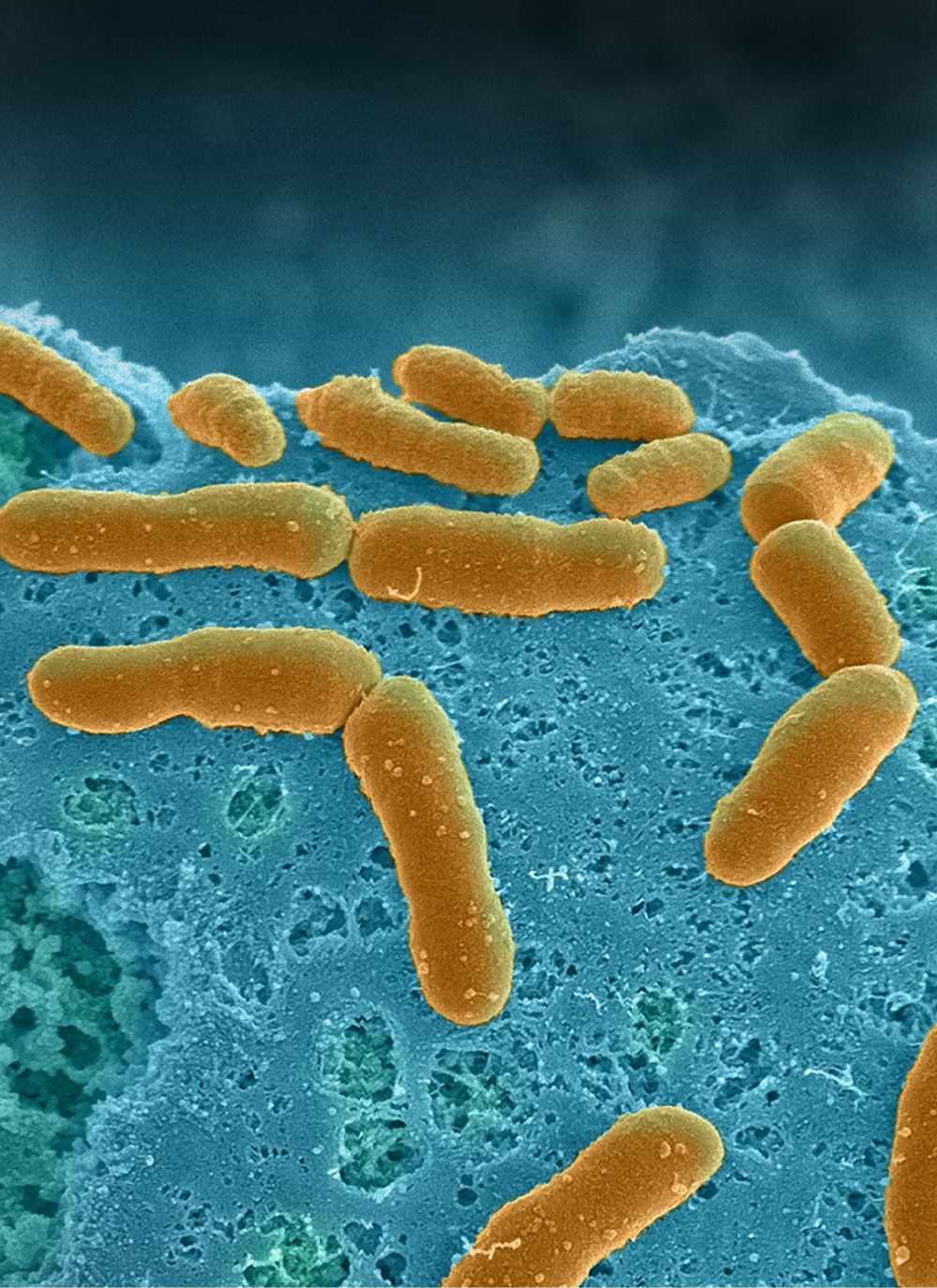
Human gut microbiome physiology can now be studied in vitro using Organ Chip technology
The human microbiome, the huge collection of microbes that live inside and on our body, profoundly affects human health and disease. The human gut flora in particular, which harbor the densest number of microbes, not only break down nutrients and release molecules important for our survival but are also key players in the development of many diseases including infections, inflammatory bowel diseases, cancer, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Most of what we know about human–microbiome interactions is based on correlational studies between disease state and bacterial DNA contained in stool samples using genomic or metagenomic analysis. This is because studying direct interactions between the microbiome and intestinal tissue outside the human body represents a formidable challenge, in large part because even commensal bacteria tend to overgrow and kill human cells within a day when grown on culture dishes. Many of the commensal microbes in the intestine are also anaerobic, and so they require very low oxygen conditions to grow which can injure human cells.
A research team at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering led by the Institute’s Founding Director Donald Ingber has developed a solution to this problem using ‘organ-on-a-chip’ (Organ Chip) microfluidic culture technology. His team is now able to culture a stable complex human microbiome in direct contact with a vascularized human intestinal epithelium for at least 5 days in a human Intestine Chip in which an oxygen gradient is established that provides high levels to the endothelium and epithelium while maintaining hypoxic conditions in the intestinal lumen inhabited by the commensal bacteria. Their “anaerobic Intestine Chip” stably maintained a microbial diversity similar to that in human feces over days and a protective physiological barrier that was formed by human intestinal tissue. The study is published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The Challenge of Building a Self-Driving Car
Be one of the first 500 people to sign up with this link and get 20% off your subscription with Brilliant.org! https://brilliant.org/realengineering/
New vlog channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCMet4qY3027v8KjpaDtDx-g
Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/user?u=2825050&ty=h
Facebook:
http://facebook.com/realengineering1
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/brianjamesmcmanus
Twitter:
Tweets by TheBrianMcManus
Discord:
https://discord.gg/s8BhkmN
Get your Real Engineering shirts at: https://standard.tv/collections/real-engineering
Credits:
Writer/Narrator: Brian McManus
Editor: Stephanie Sammann (https://www.stephanie-sammann.com/)
Animator: Mike Ridolfi (https://www.moboxgraphics.com/)
Sound: Graham Haerther (https://haerther.net/)
Thumbnail: Simon Buckmaster https://twitter.com/forgottentowel
References:
The Biggest Problems We’re Facing Today & The Future of Engineering: Crash Course Engineering #46
In our final episode of Crash Course Engineering we are going to take all the tools and ideas we’ve discussed throughout this series and try to imagine where we’re headed. We’re going to explore some of the biggest problems that today’s engineers are trying to solve and make some guesses about what the future of the field might look like.
Crash Course Engineering is produced in association with PBS Digital Studios: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL1mtdjDVOoOqJzeaJAV15Tq0tZ1vKj7ZV
RESOURCES:
http://www.engineeringchallenges.org/
https://www.wired.com/2016/03/inside-cunning-unprecedented-h…ower-grid/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3866520/
***
Brain mapping: New technique reveals how information is processed
Scientists have discovered a new method for quickly and efficiently mapping the vast network of connections among neurons in the brain.
Researchers combined infrared laser stimulation techniques with functional magnetic resonance imaging in animals to generate mapping of connections throughout the brain. The technique was described in a study published in the journal Science Advances.
“This is a revolution in detecting connections in the brain,” said senior author Anna Wang Roe, Ph.D., a professor in the Division of Neuroscience at OHSU’s Oregon National Primate Research Center. “The ability to easily map connections in the living brain with high precision opens doors for other applications in medicine and engineering.”
Asteroid Mining: Getting the first mission off the ground
A fully-contained near-Earth asteroid retrieved to cislunar space can be used as a Research and Development destination for resource extraction and engineering tests as space-native material, unaltered by a radical change in environment, in industrial quantity, and in an accessible orbit.
As a geologist and data manager working in petroleum exploration, I’m not qualified to analyze an all-encompassing view of asteroid mining…but maybe I’m qualified to share what I see from my perspective. Rather than looking at all the reasons why asteroid mining is not currently happening, I’d like to dive deep into how changing decision-making perspectives may make a mission possible.
As human activity and accessibility to do business in space broadens, potential demand for resources delivered to space will also increase. Now is the time to start looking at alternative sources of materials to fuel this expansion. Rather than launching everything from Earth, some materials could be sourced from near-Earth asteroids that are energetically easier to reach than our Moon. While mining asteroids for bulk materials like water might be theoretically profitable compared to launch from Earth, the upfront costs so far have been prohibitive. We’ve already seen the first wave of asteroid mining startups come and go. The high cost of technology development and long timescales for return-on-investment have kept commercial asteroid mining missions grounded.
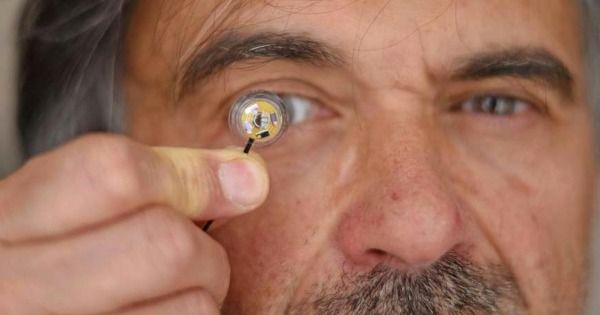
DARPA: This Smart Contact Lens Could Give Soldiers Superpowers
“Smart” contact lenses sound like something from a sci fi movie — but they’re real, and they could help troops in the field.
French engineering school IMT Atlantique revealed what it calls “the first stand-alone contact lens with a flexible micro battery” earlier this month.
And, notably, it caught the attention of the U.S. military’s attention: the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is reportedly interested in the contact lens to augment troops’ visual capabilities in the field, according to Task and Purpose — meaning the gadget could represent the augmented contact lens that DARPA has spent a decade searching for.
Weird Flex
The biggest challenge that IMT Atlantique engineers encountered was to scale down the battery. But thanks to a newly developed flexible micro battery, they found a way to continuously light an LED light source for “several hours,” according to a press release.
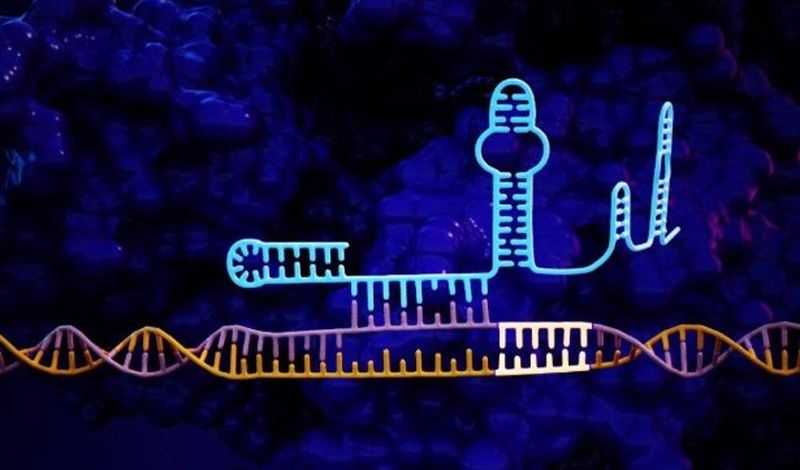
CRISPR accuracy increased 50-fold
Biomedical engineers at Duke University, North Carolina, have developed a method for improving the accuracy of CRISPR genome editing by an average of 50-fold. They believe it can be easily translated to any of the technology’s continually expanding formats.
The approach adds a short tail to the guide RNA which is used to identify a sequence of DNA for editing. This added tail folds back and binds onto itself, creating a “lock” that can only be undone by the targeted DNA sequence.
“CRISPR is generally incredibly accurate, but there are examples that have shown off-target activity, so there’s been broad interest across the field in increasing specificity,” said Charles Gersbach, Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Duke. “But the solutions proposed thus far cannot be easily translated between different CRISPR systems.”
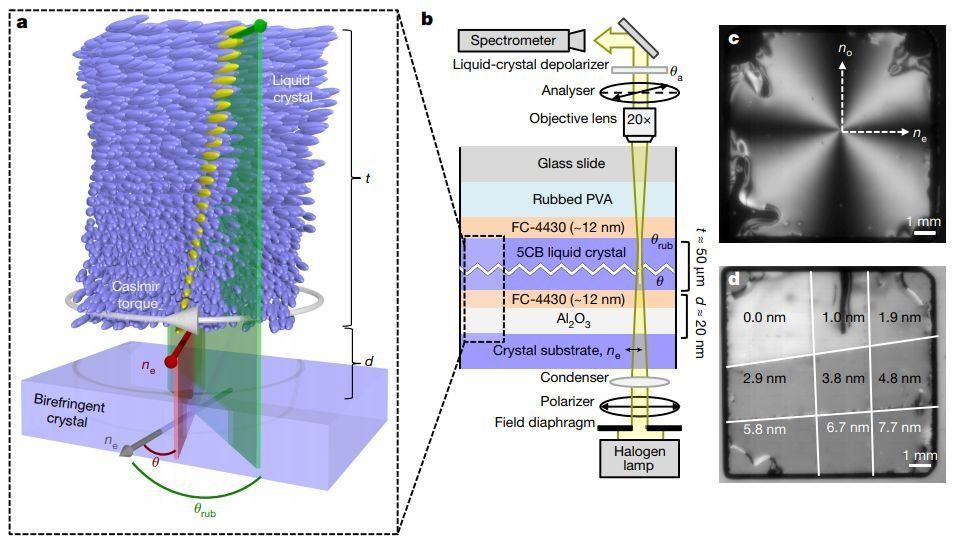
The Casimir torque: Scientists measure previously unexamined tiny force
Researchers from the University of Maryland have for the first time measured an effect that was predicted more than 40 years ago, called the Casimir torque.
When placed together in a vacuum less than the diameter of a bacterium (one micron) apart, two pieces of metal attract each other. This is called the Casimir effect. The Casimir torque—a related phenomenon that is caused by the same quantum electromagnetic effects that attract the materials—pushes the materials into a spin. Because it is such a tiny effect, the Casimir torque has been difficult to study. The research team, which includes members from UMD’s departments of electrical and computer engineering and physics and Institute for Research in Electronics and Applied Physics, has built an apparatus to measure the decades-old prediction of this phenomenon and published their results in the December 20th issue of the journal Nature.
“This is an interesting situation where industry is using something because it works, but the mechanism is not well-understood,” said Jeremy Munday, the leader of the research. “For LCD displays, for example, we know how to create twisted liquid crystals, but we don’t really know why they twist. Our study proves that the Casimir torque is a crucial component of liquid crystal alignment. It is the first to quantify the contribution of the Casimir effect, but is not the first to prove that it contributes.”