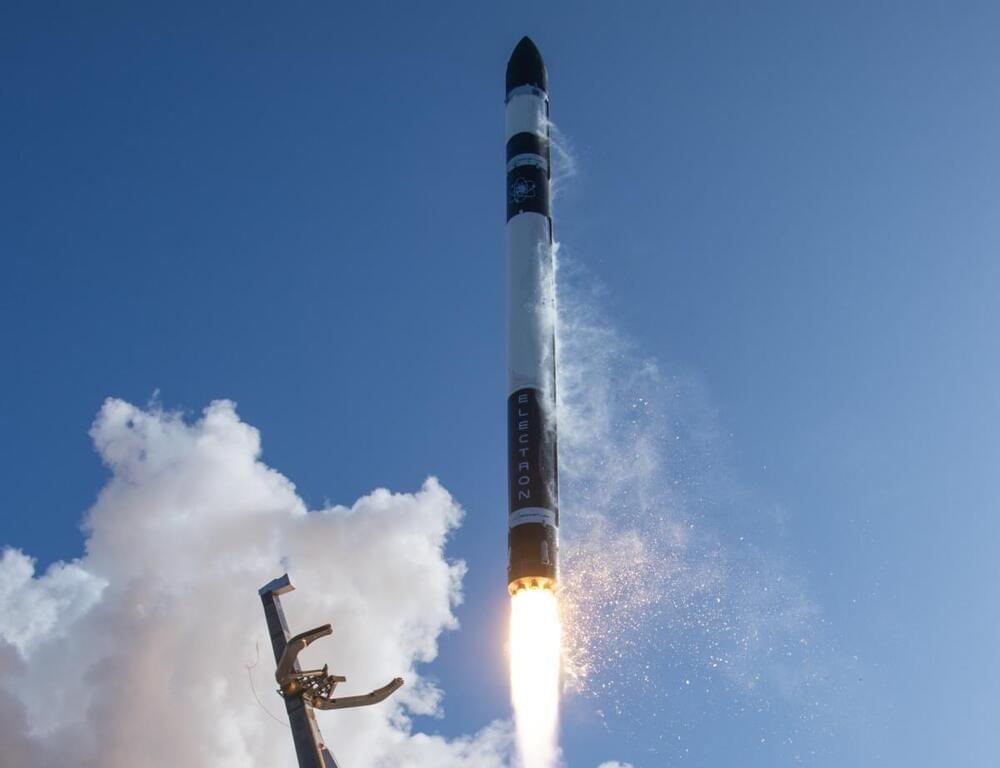
Today’s launch by Rocket Lab, “The Owl Spreads Its Wings,” was as unremarkable as a rocket going to orbit can be, but it also marked a few milestones for the growing space company: 30 launches and 150 satellites taken to space.
The company’s first trip to orbit was in January of 2018, technically Electron’s second test flight but the first successful delivery of a payload to space. That was after more than 10 years of design, engineering and manufacturing since the company was founded in 2006.
It then had an unbroken streak of 18 launches, but on its 20th there was an anomaly and it lost the payload and vehicle. But as founder and CEO Peter Beck told me shortly afterwards, “no more than seconds after we realized that we had an anomaly on our hands, the team was already working it.” And they were clear to fly a month later.