Generating electricity from geothermal energy requires devices that can somehow make use of the heat within the Earth’s crust.


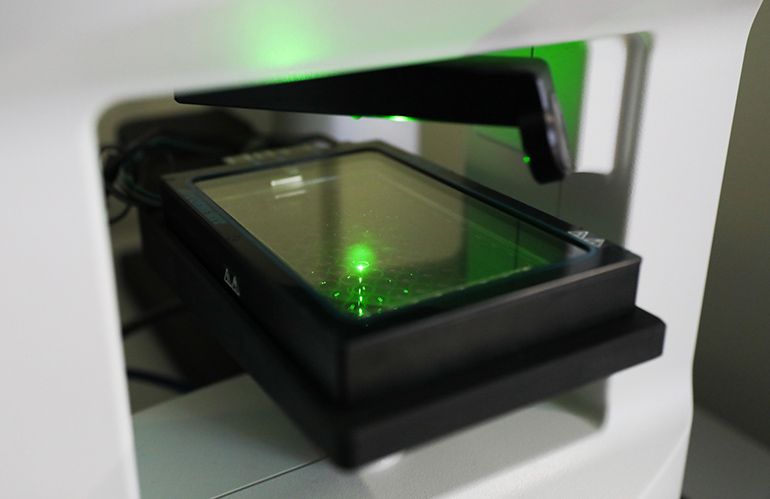
Nanolive, a spinoff company of École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) in Switzerland, has just introduced a holographic microscope that can image live cells at high resolution over extended time periods.
Nanolive’s CX-A device relies on a low energy light beam to penetrate the sample, which does not interfere with internal cell activity. At every exposure, the system creates a 3D dataset of the sample, down to resolutions below 200 nanometers, which it can do repeatedly for hours at a time. Since entire 96-well plates can be imaged by the microscope, 96 individual experiments can be performed at once.
The system requires no cell preparation such as staining and doesn’t cause any phototoxicity or photo-bleaching in the samples.

ABERDEEN PROVING GROUND, Md. — Army officials announced the exclusive licensing of a new technology designed to harvest hydrogen from an aluminum alloy powder and any fluid that contains water.
“This is on-demand hydrogen production,” said Dr. Anit Giri, a materials scientist at the U.S. Army CCDC Army Research Laboratory at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland. “Utilizing hydrogen, you can generate power on-demand, which is very important for the Soldier.”
Army researchers discovered a structurally-stable, aluminum-based nanogalvanic alloy powder in 2017, which reacts with water or any water-based liquid to produce on-demand hydrogen for power generation without a catalyst.
A group of islands halfway between Australia and Hawaii have been found to contain deadly levels of radiation, 1000 times higher than toxic sites of stricken nuclear power stations at Chernobyl and Fukushima.
The Marshall Islands in the central Pacific Ocean were once an idyllic tropical paradise before they were hit with more than 60 nuclear bombs during testing carried out by the United States between 1946 and 1958.
Locals were forced to flee their homes after they were hit with bombs and decades later nuclear waste is now flowing into the water.

(Natural News) A series of incidents that have occurred in close proximity to each other over the past several days are leading many to believe that technology is failing society and that U.S. infrastructure is collapsing faster than previously believed.
On Saturday, a wide swath of Manhattan’s West Side was plunged into darkness for several hours, and the electric company officials responsible for providing the power — Con Edison — are not sure why the failure occurred.
As reported by the New York Post, the company said in a statement late Sunday morning that it “will be conducting a diligent and vigorous investigation to determine the root cause of the incident.”

American scientist and best-selling #scifi author David Brin predicts what our world would like in the year 2050. Read it on our #Earth2050 platform:
By 2040, the international community has concluded that using nonrenewable resources is irrational. The first kind of asteroid to be mined was of the carbonaceous variety, to get water that can keep astronauts alive, or be used to create rocket fuel. Later, explorers prospected dozens of other varieties of asteroids with suitable iron, nickel, cobalt, platinoid, and rare-earth element deposits. Odyssey is the first ever space base focused on mining these minerals.
The station was launched in 2049. Because of magnetic storms and drastic changes in temperature, the main part of the base had to be built several meters below the asteroid’s surface. Almost all work on the base was automated. Small teams of engineers and technicians needed for station management stay for 6-month shifts. Using solar mirrors, they melt and refine precious metal ores and blow them into gleaming bubbles that can safely descend through Earth’s atmosphere to float in the ocean, for collection. The iron is used for construction in space.
This space project — the Odyssey — is so profitable that on April 22, 2055, Earth Day, the UN’s General Assembly adopts a resolution: to decrease mineral mining on our planet and to transfer some profits made from space to restore and preserve the Earth’s ecology.
The success of the project is based not only on the commercial value of mining but also on scientific advancements. The Odyssey houses laboratories with different specializations. New space discoveries make it possible to create new stations and even cities farther away from Earth.
Are made up of many thin layers of semiconductor. An injected electron makes a small energy transition as it moves from one layer to the next, emitting light on each cascade. Because the energy steps are small, quantum cascade lasers can produce long-wavelength mid-infrared or terahertz radiation.

