The remains of 182 people in unmarked Indigenous graves were found on the eve of Canada Day.
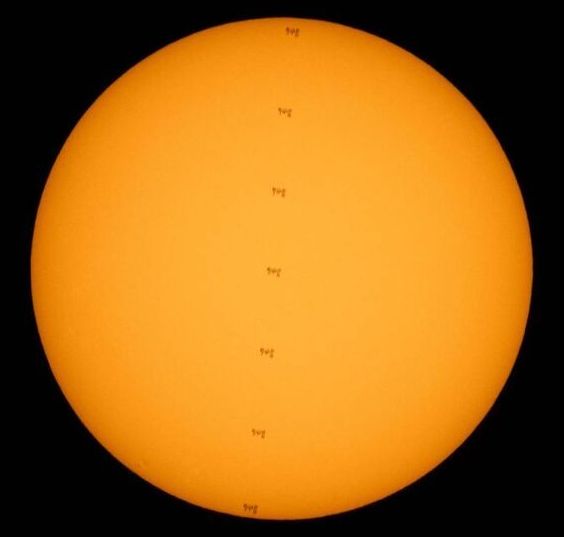




The mosaic image is a composition of seven subsequent frames taken from Nellysford, Virginia, as the space station traversed the face of the sun at the speed of roughly 5 miles per second, which is about 18000 mph (29000 kph), according to a NASA photo description.
The six-hour and 45-minute spacewalk was the third for Pesquet and Kimbrough in less than two weeks as they completed work on augmenting the space station’s power systems. The iROSA panel deployed on Friday was the second of six new panels to be installed at the station.
Friday’s extravehicular activity (EVA) positioned the second iROSA opposite the first on the far left, or port side of the space station’s backbone truss. Now both the 2B and 4B power channels on the port 6 (P6) truss have the new arrays deployed.
The US power grid needs all of support it can get. Sad that some would stand in the way of progress.
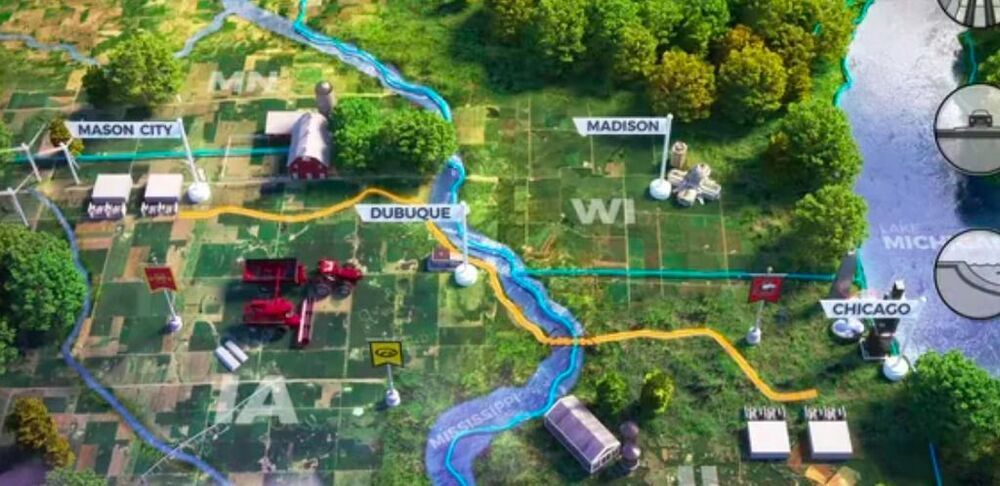
There is no love lost between the notorious Koch brothers and the nation’s railroad industry, and the relationship is about to get a lot unlovelier. A massive new, first-of-its-kind renewable energy transmission line is taking shape in the Midwest, which will cut into the Koch family’s fossil energy business. It has a good chance of succeeding where others have stalled, because it will bury the cables under existing rights-of-way using railroad rights-of-way and avoid stirring up the kind of opposition faced by conventional above-ground lines.
The Koch brothers and their family-owned company, Koch Industries, have earned a reputation for attempting to throttle the nation’s renewable energy sector. That makes sense, considering that the diversified, multinational firm owns thousands of miles of oil, gas, and chemical pipelines criss-crossing the US (and sometimes breaking down) in addition to other major operations that depend on rail and highway infrastructure.
Koch Industries owns fleets of rail cars, but one thing it doesn’t have is its own railroad right-of-way. That’s a bit ironic, considering that railroads provided the initial kickstart for the family business back in the 1920s, but that is where trouble has been brewing today.
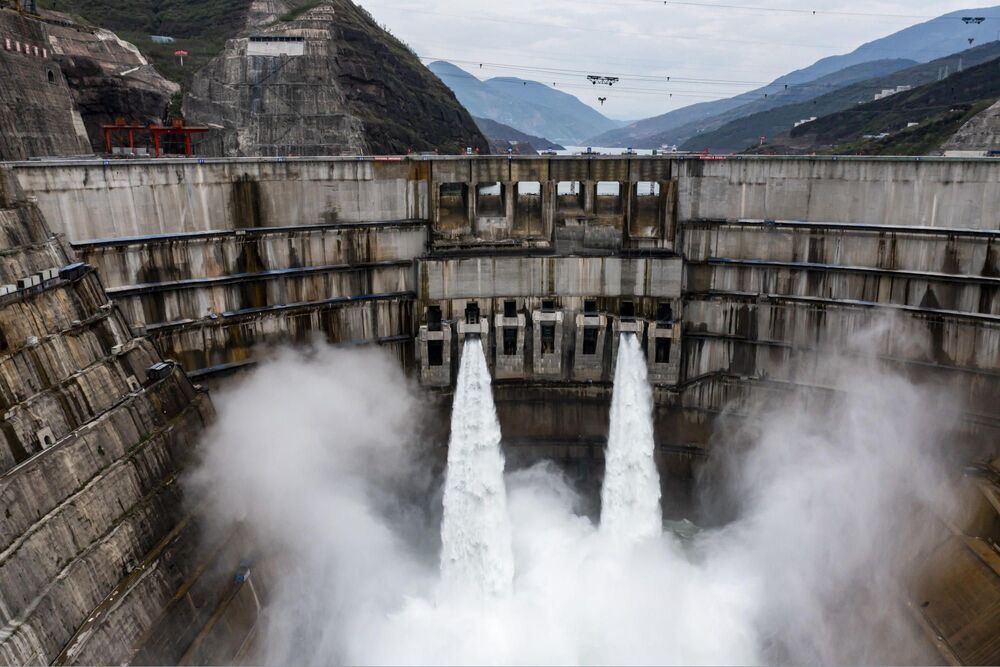

Plans call for the 289-meter-tall (954-foot-tall) Baihetan Dam to have 16 generating units with a capacity of 1 million kilowatts each. That will make it second in size after the Three Gorges Dam, opened in 2003 on the Yangtze, with 22.5 million kilowatts of generating capacity.
BEIJING (AP) — The first two generating units of the world’s second-biggest hydroelectric dam were officially turned on Monday in southwestern China, the government announced.
The Baihetan Dam on the Jinsha River, a tributary of the Yangtze, is part of Chinese efforts to curb surging fossil fuel demand by building more hydropower capacity at a time when dams have fallen out of favor in other countries due to environmental complaints.
The announcement comes ahead of the ruling Communist Party’s celebration this week of the official 100th anniversary of its 1921 founding.
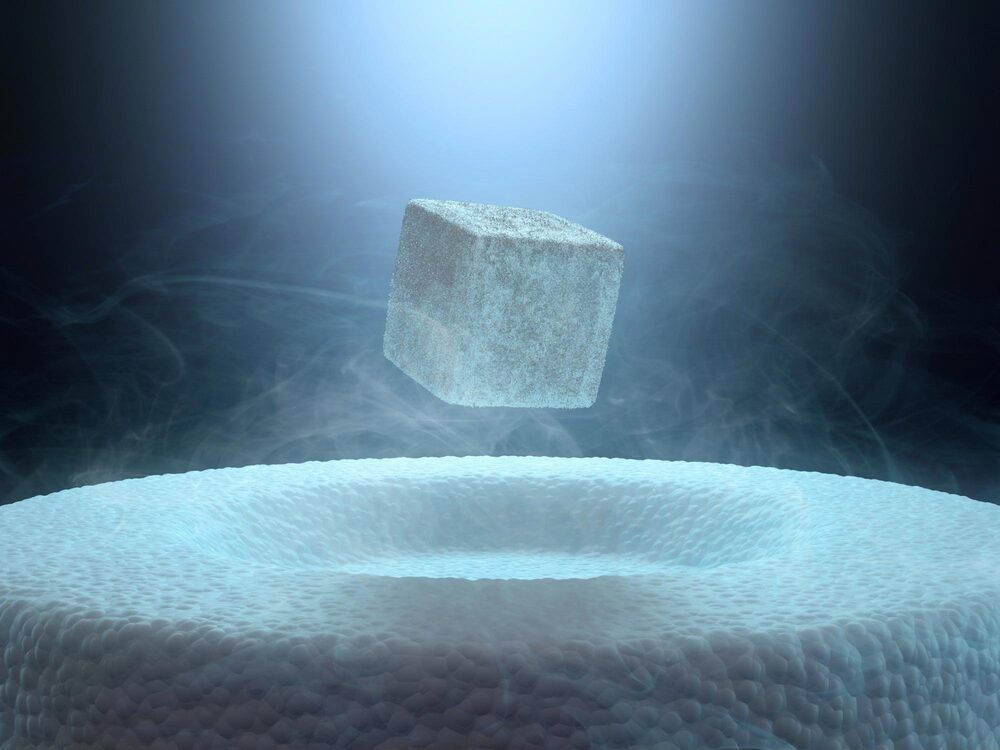

Research led by Kent and the STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory has resulted in the discovery of a new rare topological superconductor, LaPt3P. This discovery may be of huge importance to the future operations of quantum computers.
Superconductors are vital materials able to conduct electricity without any resistance when cooled below a certain temperature, making them highly desirable in a society needing to reduce its energy consumption.
They manifest quantum properties on the scale of everyday objects, making them highly attractive candidates for building computers that use quantum physics to store data and perform computing operations, and can vastly outperform even the best supercomputers in certain tasks. As a result, there is an increasing demand from leading tech companies like Google, IBM and Microsoft to make quantum computers on an industrial scale using superconductors.
😃
Is Fungus the Plastic of the Future? Use the code “Undecided” to get CuriosityStream for less than $15 a year! https://curiositystream.com/Undecided. Plastic changed the course of manufacturing forever, but came at a cost. Mycelium technology might be the solution and the next big boom… a plastic-like replacement with so many uses and new opportunities for products, companies, and profits. Let’s explore mycelium technology and how it can help us achieve a more renewable and cleaner future.
Watch The Future of Solid State Wind Energy — No More Blades: https://youtu.be/nNp21zTeCDc?list=PLnTSM-ORSgi4dFnLD9622FK77atWtQVv7
Video script and citations:
https://undecidedmf.com/episodes/is-fungus-the-plastic-of-the-future.
Follow-up podcast:
😃
As COVID-19 continues to ravage global populations, the world is singularly focused on finding ways to battle the novel coronavirus. That includes the UC Santa Barbara’s Solid State Lighting & Energy Electronics Center (SSLEEC) and member companies. Researchers there are developing ultraviolet LEDs that have the ability to decontaminate surfaces — and potentially air and water — that have come in contact with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
“One major application is in medical situations — the disinfection of personal protective equipment, surfaces, floors, within the HVAC systems, et cetera,” said materials doctoral researcher Christian Zollner, whose work centers on advancing deep ultraviolet light LED technology for sanitation and purification purposes. He added that a small market already exists for UV-C disinfection products in medical contexts.
Indeed, much attention of late has turned to the power of ultraviolet light to inactivate the novel coronavirus. As a technology, ultraviolet light disinfection has been around for a while. And while practical, large-scale efficacy against the spread of SARS-CoV-2 has yet to be shown. UV light shows a lot of promise: SSLEEC member company Seoul Semiconductor in early April reported a “99.9% sterilization of coronavirus (COVID-19) in 30 seconds” with their UV LED products. Their technology currently is being adopted for automotive use, in UV LED lamps that sterilize the interior of unoccupied vehicles.
Bismuth has been around for thousands of years, yet it’s only been used in a handful of applications — and mostly to treat stomach ailments. But as the world looks for cleaner and safer energy, bismuth might soon become the star of the heavy metals family.
Subscribe: http://bit.ly/2FqJZMl.
Like Verge Science on Facebook: http://bit.ly/2hoSukO
Follow on Twitter: http://bit.ly/2Kr29B9
Follow on Instagram: https://goo.gl/7ZeLvX
Community guidelines: http://bit.ly/2D0hlAv.

A few days ago, millions of tons of super-heated gas shot off from the surface of the sun and hurtled 90 million miles toward Earth.
The eruption, called a coronal mass ejection, wasn’t particularly powerful on the space-weather scale, but when it hit the Earth’s magnetic field it triggered the strongest geomagnetic storm seen for years. There wasn’t much disruption this time—few people probably even knew it happened—but it served as a reminder the sun has woken from a yearslong slumber.
While invisible and harmless to anyone on the Earth’s surface, the geomagnetic waves unleashed by solar storms can cripple power grids, jam radio communications, bathe airline crews in dangerous levels of radiation and knock critical satellites off kilter. The sun began a new 11-year cycle last year and as it reaches its peak in 2025 the specter of powerful space weather creating havoc for humans grows, threatening chaos in a world that has become ever more reliant on technology since the last big storms hit 17 years ago. A recent study suggested hardening the grid could lead to $27 billion worth of benefits to the U.S. power industry.