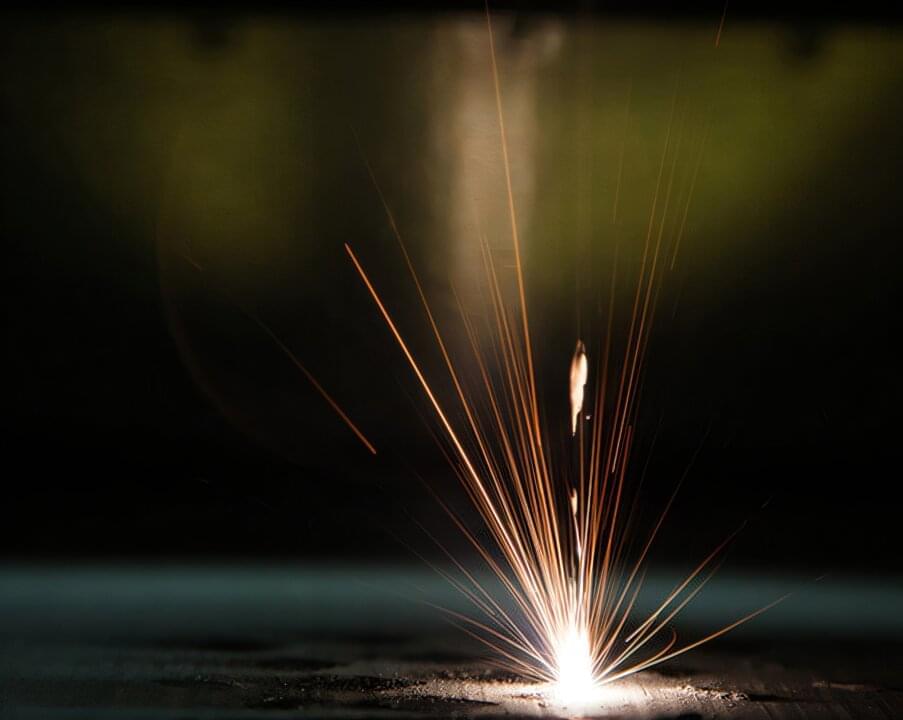
With the ability to print metal structures with complex shapes and unique mechanical properties, metal additive manufacturing (AM) could be revolutionary. However, without a better understanding of how metal AM structures behave as they are 3D printed, the technology remains too unreliable for widespread adoption in manufacturing and part quality remains a challenge.
Researchers in Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL)’s nondestructive evaluation (NDE) group are tackling this challenge by developing first-of-their-kind approaches to look at how materials and structures evolve inside a metal AM structure during printing. These NDE techniques can become enabling technologies for metal AM, giving manufacturers the data they need to develop better simulations, processing parameters and predictive controls to ensure part quality and consistency.
“If you want people to use metal AM components out in the world, you need NDE,” said David Stobbe, group leader for NDE ultrasonics and sensors in the Materials Engineering Division (MED). “If we can prove that AM-produced parts behave as designed, it will allow them to proliferate, be used in safety-critical components in aerospace, energy and other sectors and hopefully open a new paradigm in manufacturing.”