Ocean thermal energy conversion makes use of the difference in temperatures between the warm surface of the oceans and the deeper cold waters.
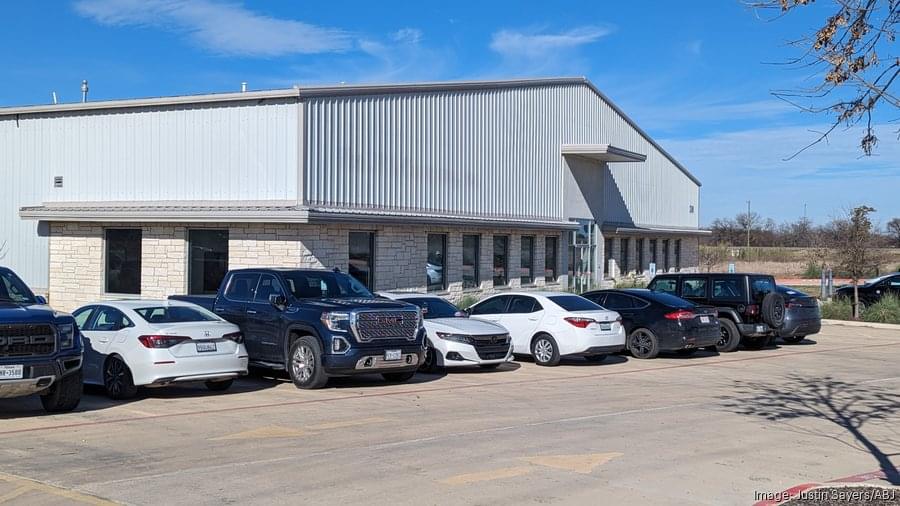



AUSTIN (Austin Business Journal) — Tesla Inc.’s growing footprint in the Austin area now includes a sizable facility in Hutto. But what it’s for remains unclear.
The Austin Business Journal visited the 36,000-square-foot site at 200 County Road 199 in the fast-growing industrial hub northeast of Austin in late December. The parking lot was full and a nondescript warehouse-style building was bustling with employees in construction vests and helmets, but there were no signs listing any companies and no clear indications of who was occupying it. The only traces it could be Tesla were a handful of the company’s electric vehicle charging stations out front.
But Elon Musk’s EV manufacturing and clean energy company is linked to the site in state filings, and it has been confirmed by Hutto officials. Tesla’s expansion to Hutto underscores the company’s wide-reaching plans for the region — as far south as San Antonio and, now, as far north as Hutto — as it continues buildout of its multibillion-dollar operation in eastern Travis County. The Hutto site is about 30 miles directly north of its gigafactory, which serves as the company’s headquarters, along State Highway 130.
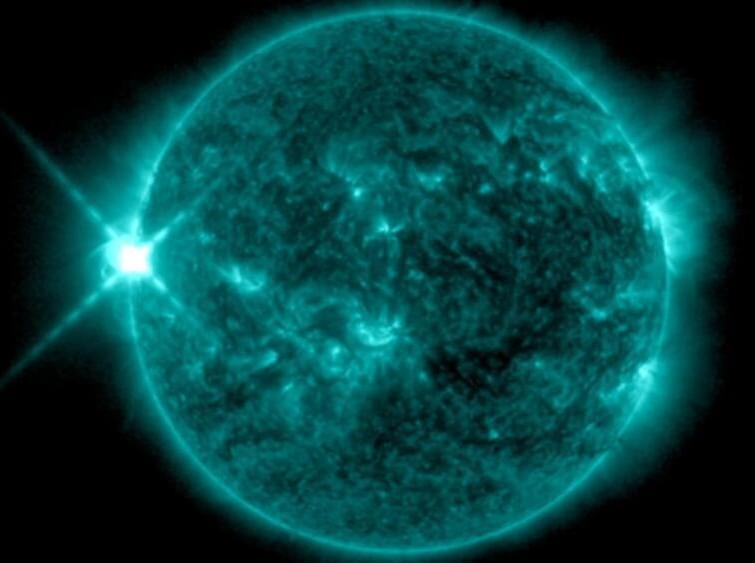

Earth will be struck today by a coronal mass ejection from a huge solar flare that erupted from the sun on New Year’s Eve.
The New Year’s Eve flare created a CME, a huge bubble of plasma from a region of the sun called the corona, which is equivalent to the sun’s outer atmosphere, and this has an Earth-directed component. Though this massive ejection of plasma will only graze the magnetic bubble surrounding our planet Tuesday (Jan. 2), the magnetosphere, it could trigger a geomagnetic storm that could affect communications and power infrastructure.
The coronal mass ejection CME was hurled into space by an X-class solar flare that burst from the surface of the sun at 4:55 p.m. EST (2155 GMT) on Sunday (Dec. 31). It is the most powerful flare that has happened on the sun during the current solar cycle, solar cycle 25, which began in Dec. 2019. In fact, the flare that ended 2023 with a bang is the largest that has been observed since Sept. 10, 2017, according to the Space Weather Prediction Center of the National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).



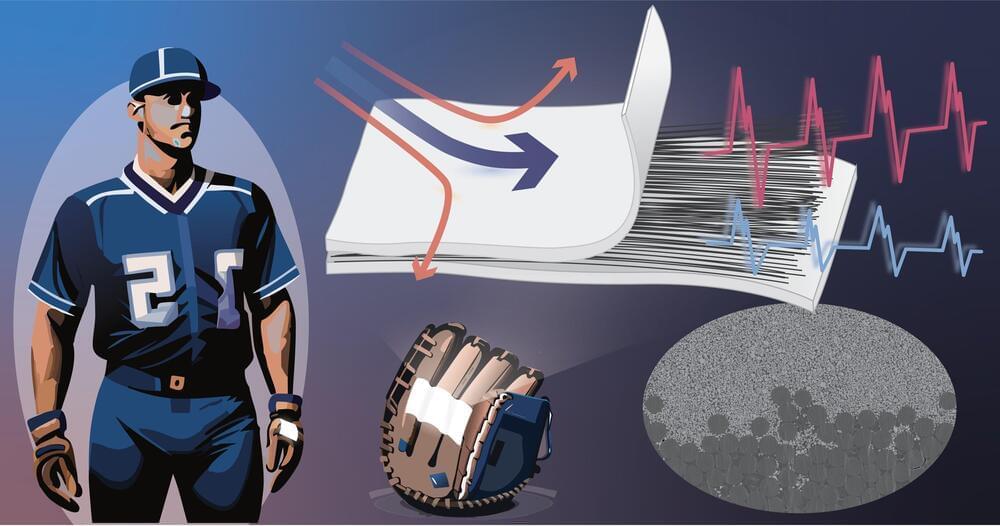
An international research group has engineered a novel, high-strength flexible device by combining piezoelectric composites with unidirectional carbon fiber (UDCF), an anisotropic material that provides strength only in the direction of the fibers. The new device transforms kinetic energy from human motion into electricity, providing an efficient and reliable means for high-strength and self-powered sensors.
Details of the group’s research were published in the journal Small on Dec.14, 2023.
Motion diction involves converting energy from human motion into measurable electrical signals and is something that may be crucial for ensuring a sustainable future.

On every count, nanoelectrofuel flow batteries appear to beat lithium-ion batteries for use in EVs and larger systems. Influit expects that its current generation of nanoelectrofuel, together with the entire ecosystem needed to produce, distribute, and recycle the fuel that the company is building around it, should cost $130/kWh when used in an EV. In comparison, lithium-ion batteries cost around $138/kWh. True, lithium-ion’s costs should drop below $100/kWh in a few years, but Influit expects its next-generation nanoelectrofuel to fall even further, to around $50 to $80/kWh. That next-gen system should have 5 times the energy density of present Li-ion systems.
Here’s what that means for an EV.
A typical EV battery today occupies about the same volume as would a flow battery with 400 liters of nanelectrofuel. If nanoparticles made up 30 percent of the weight of that fuel, the EV would have a range of only 105 km. Raise that to 40 percent, and the range would climb to 274 km. At 50 percent, it hits 362 km. And at 80 percent, it’s 724 km (450 miles). And that’s all assuming the flow battery’s tank remains the same size.
Tesla recorded $500M+ in gross profit from its Energy and Services (Supercharging) segments in Q3 2023. Elon Musk noted how strong energy gross margins were on the call, and insinuated strength in these businesses will continue. I think this is a super exciting development for Tesla investors as the company can smooth out cyclicality in it’s automotive business with consistent profits from its Energy and Services.