Greater scale and symbolic models are necessary before AI and machine learning can meet big challenges like breaking the best encryption algorithms.


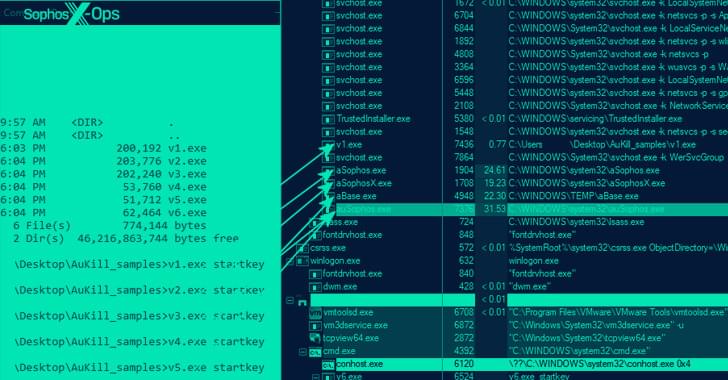
Play ransomware is notable for not only utilizing intermittent encryption to speed up the process, but also for the fact that it’s not operated on a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model. Evidence gathered so far points to Balloonfly carrying out the ransomware attacks as well as developing the malware themselves.
Grixba and VSS Copying Tool are the latest in a long list of proprietary tools such as Exmatter, Exbyte, and PowerShell-based scripts that are used by ransomware actors to establish more control over their operations, while also adding extra layers of complexity to persist in compromised environments and evade detection.
Another technique increasingly adopted by financially-motivated groups is the use of the Go programming language to develop cross-platform malware and resist analysis and reverse engineering efforts.
Quantum computers have the potential to break common cryptography techniques, search huge datasets and simulate quantum systems in a fraction of the time it would take today’s computers. But before this can happen, engineers need to be able to harness the properties of quantum bits or qubits.
Currently, one of the leading methods for creating qubits in materials involves exploiting the structural atomic defects in diamond. But several researchers at the University of Chicago and Argonne National Laboratory believe that if an analogue defect could be engineered into a less expensive material, the cost of manufacturing quantum technologies could be significantly reduced. Using supercomputers at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), which is located at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), these researchers have identified a possible candidate in aluminum nitride. Their findings were published in Nature Scientific Reports.
“Silicon semiconductors are reaching their physical limits—it’ll probably happen within the next five to 10 years—but if we can implement qubits into semiconductors, we will be able to move beyond silicon,” says Hosung Seo, University of Chicago Postdoctoral Researcher and a first author of the paper.
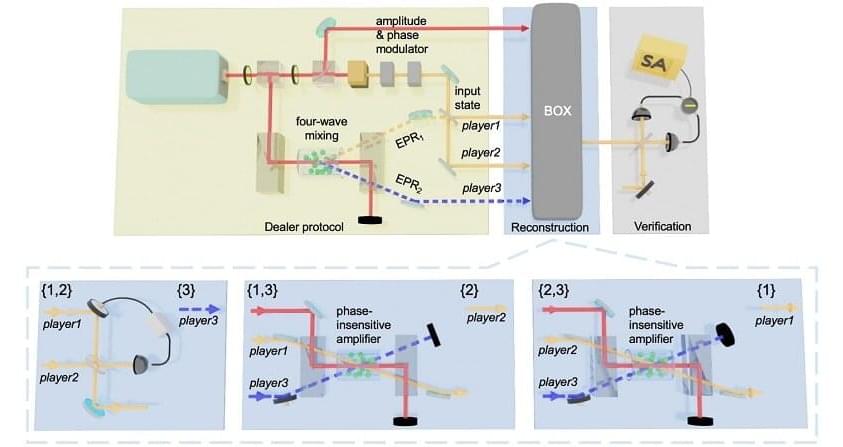
Quantum information is a powerful technology for increasing the amount of information that can be processed and communicated securely. Using quantum entanglement to securely distribute a secret quantum state among multiple parties is known as “quantum state sharing.”
An important protocol in quantum networks and cryptography, quantum state sharing works like this (in simple terms): a secret quantum state is divided into n shares and given to n players. The secret state can only be reconstructed if k (where kn/2) players cooperate, while the remaining n-k players cannot access the information. This protocol can also be used for quantum error correction, allowing the reconstruction of the secret state even if some of the information is lost.
In quantum information, there are two types of systems: discrete variable and continuous variable systems. Discrete variable systems are good because they don’t lose information easily, while continuous variable systems are good because the generation and processing of quantum states are deterministic rather than probabilistic, which enables a high degree of precision.
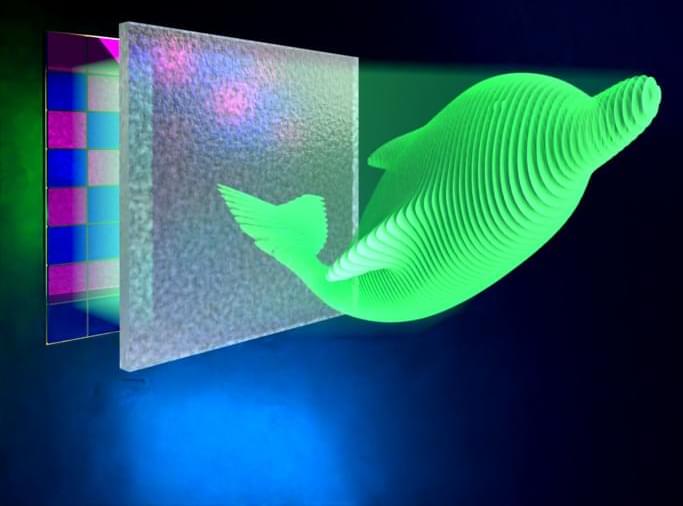
Researchers have developed a new method for creating realistic 3D holographic projections that are three orders of magnitude better than the current state-of-the-art technology. Previous attempts to improve the resolution of holograms have run into three basic roadblocks. However, this new ultrahigh-density method shows that two of those have now been solved, dramatically improving the overall quality, resolution, and appearance of holographic projections.
“Our new method overcomes two long-existing bottlenecks in current digital holographic techniques — low axial resolution and high interplane crosstalk — that prevent fine depth control of the hologram and thus limit the quality of the 3D display,” said Lei Gong, who led a research team from the University of Science and Technology of China. “Our approach could also improve holography-based optical encryption by allowing more data to be encrypted in the hologram.”
Limitations of Current Methods for Generating Holograms.
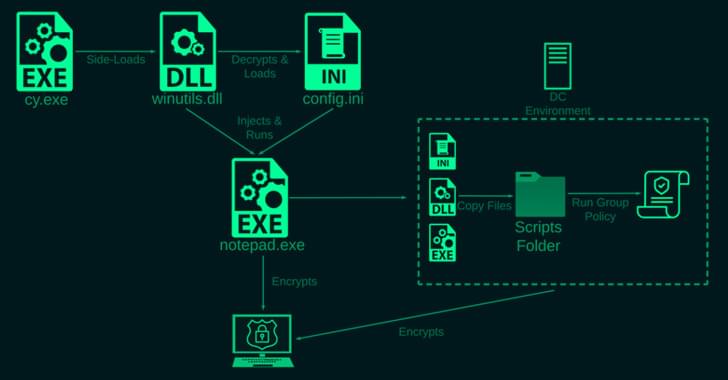
Cybersecurity researchers have taken the wraps off a previously undocumented ransomware strain called Rorschach that’s both sophisticated and fast.
“What makes Rorschach stand out from other ransomware strains is its high level of customization and its technically unique features that have not been seen before in ransomware,” Check Point Research said in a new report. “In fact, Rorschach is one of the fastest ransomware strains ever observed, in terms of the speed of its encryption.”
The cybersecurity firm said it observed the ransomware deployed against an unnamed U.S.-based company, adding it found no branding or overlaps that connect it to any previously known ransomware actors.
As more private data is stored and shared digitally, researchers are exploring new ways to protect data against attacks from bad actors. Current silicon technology exploits microscopic differences between computing components to create secure keys, but artificial intelligence (AI) techniques can be used to predict these keys and gain access to data. Now, Penn State researchers have designed a way to make the encrypted keys harder to crack.
Led by Saptarshi Das, assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics, the researchers used graphene — a layer of carbon one atom thick — to develop a novel low-power, scalable, reconfigurable hardware security device with significant resilience to AI attacks. They published their findings in Nature Electronics today (May 10).
“There has been more and more breaching of private data recently,” Das said. “We developed a new hardware security device that could eventually be implemented to protect these data across industries and sectors.”
Threat actors used a well-liked piece of corporate communication software from 3CX, according to security experts. In particular, reports state that a desktop client for the 3CX VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) service was used to specifically target 3CX’s clients.
It is believed that the attack is a multi-part process, with the first stage using a hacked version of the 3CX desktop application. Although the.exe file and the MSI package have the same name, preliminary research indicates that the MSI package is the one that may include DLLs that have been maliciously modified.
The beginning of the infection process occurs when 3CXDesktopApp.exe loads the ffmpeg.dll file. After that, ffmpeg.dll will read the encrypted code from d3dcompiler_47.dll and then decode it. It seems that the decrypted code is the backdoor payload that attempts to visit the IconStorage GiHub page in order to access an ICO file that contains the encrypted C&C server that the backdoor connects to in order to acquire the probable ultimate payload.
A quantum computer in the next decade could crack the encryption our society relies on using Shor’s Algorithm. Head to https://brilliant.org/veritasium to start your free 30-day trial, and the first 200 people get 20% off an annual premium subscription.
▀▀▀
A huge thank you to those who helped us understand this complex field and ensure we told this story accurately — Dr. Lorenz Panny, Prof. Serge Fehr, Dr. Dustin Moody, Prof. Benne de Weger, Prof. Tanja Lange, PhD candidate Jelle Vos, Gorjan Alagic, and Jack Hidary.
A huge thanks to those who helped us with the math behind Shor’s algorithm — Prof. David Elkouss, Javier Pagan Lacambra, Marc Serra Peralta, and Daniel Bedialauneta Rodriguez.
▀▀▀
References:
Joseph, D., et al. (2022). Transitioning organizations to post-quantum cryptography. Nature, 605(7909), 237–243. — https://ve42.co/Joseph2022
Bernstein, D. J., & Lange, T. (2017). Post-quantum cryptography. Nature, 549(7671), 188–194. — https://ve42.co/Bernstein2017
An Insight, An Idea with Sundar Pichai — Quantum Computing, Wold Economic Forum via YouTube — https://ve42.co/QCWEFyt.
Computer scientist Amit Sahai, PhD, is asked to explain the concept of zero-knowledge proofs to 5 different people; a child, a teen, a college student, a grad student, and an expert. Using a variety of techniques, Amit breaks down what zero-knowledge proofs are and why it’s so exciting in the world of cryptography.
Amit Sahai, PhD, is a professor of computer science at UCLA Samueli School of Engineering.
Still haven’t subscribed to WIRED on YouTube? ►► http://wrd.cm/15fP7B7
Listen to the Get WIRED podcast ►► https://link.chtbl.com/wired-ytc-desc.
Want more WIRED? Get the magazine ►► https://subscribe.wired.com/subscribe/splits/wired/WIR_YouTu…ription_ZZ
Follow WIRED:
Instagram ►►https://instagram.com/wired.
Twitter ►►http://www.twitter.com/wired.
Facebook ►►https://www.facebook.com/wired.
Get more incredible stories on science and tech with our daily newsletter: https://wrd.cm/DailyYT