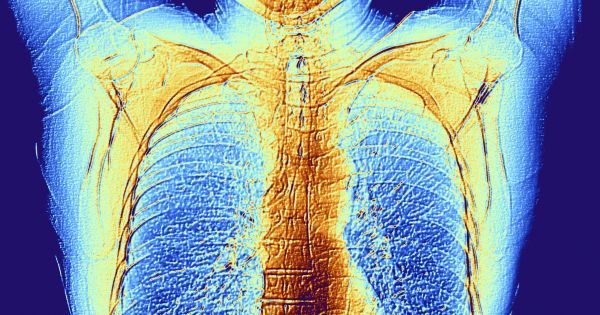
For many years doctors have been able to get a look inside a person’s body using X-ray scans, or placing a tiny camera inside the body. But those tools provide a limited view and can only reveal so much. A recently developed camera, however, may give doctors the ability to see everything happening in the human body, no matter where it is.
The camera was developed by researchers from the University of Edinburgh, and it’s meant to work while paired with an endoscope — a long, slender piece of equipment that usually has a camera, sensors, and lights at its tip.
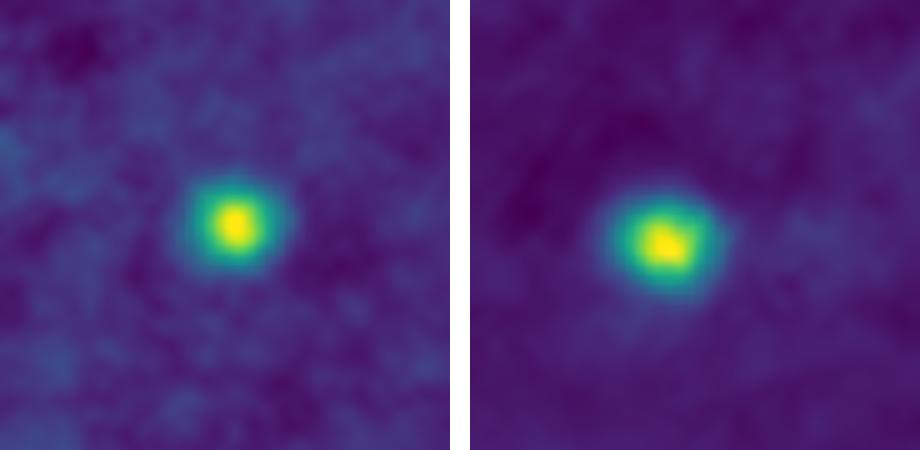
Light emitted by the endoscope typically scatters when it comes into contact with structures within the body, such as body tissue, but the new camera is able to pick up on it thanks to the photon detectors inside of it. The camera is able to detect light sources behind as much as 20 centimeters (7.9 inches) of bodily tissue.